In an age characterized by unparalleled digital connectivity and a relentless influx of data, the significance of encryption cannot be overstated. Today’s digital world is a veritable battlefield for information security, where encryption methods serve as the shield protecting sensitive data. Among these, symmetric and asymmetric encryption methods are the titans of cryptography, each with distinct characteristics and applications. From a Christian perspective, understanding these encryption methods unveils ethical considerations and aligns with values of stewardship and responsibility.
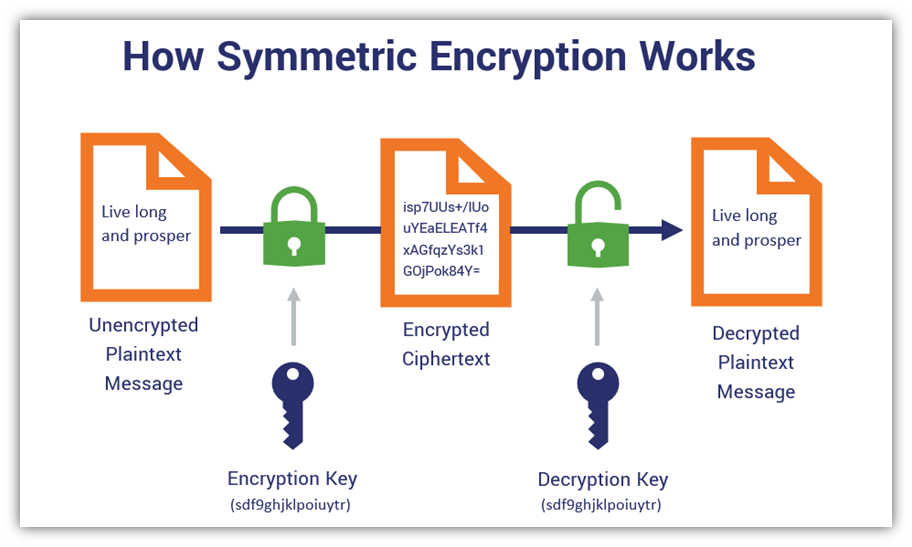
To comprehend which encryption method dominates the digital landscape, it is essential first to delineate symmetric and asymmetric encryption. Symmetric encryption employs a single key for both encryption and decryption processes. A prime illustration of this is the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES). In contrast, asymmetric encryption utilizes a pair of keys: a public key, which anyone can access, and a private key, kept secret by the owner. RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman) epitomizes this method, facilitating secure communication over insecure channels.
Symmetric encryption has long reigned supreme in scenarios necessitating high-speed and robust data processing. Its efficiency allows for the rapid encryption and decryption of bulk data, a critical requirement for many enterprises where time is money. In contexts where large volumes of information require secure transmission — such as corporate networks or financial institutions — symmetric methods like AES offer a comprehensive solution. However, the dependency on key management remains a significant hurdle. If the key is compromised, an adversary gains unfettered access to all encrypted data.
Conversely, asymmetric encryption is increasingly prevalent, particularly in scenarios involving secure communications over the internet. Since it mitigates the challenges associated with key distribution, this method is invaluable. The public key serves as a lock, while the private key functions as its unique key. This paradigm underpins many popular protocols, including HTTPS, which secures internet communications, ensuring that sensitive transactions remain unassailable. The allure of asymmetric encryption lies not only in its security features but also in its alignment with the biblical principle of openness and trust. Just as Christians are encouraged to be open in their dealings, this method promotes transparency while safeguarding confidential exchanges.
As the digital fabric of contemporary society becomes more intricate, several factors influence which encryption method will dominate. For organizations focused on cybersecurity, adoption trends reveal a shift towards hybrid solutions that combine both methodologies. This approach capitalizes on the speed of symmetric encryption while harnessing the robust key management features of asymmetric encryption. By using a hybrid model, companies can encrypt data with symmetric keys while securely exchanging those keys using asymmetric algorithms. This duality mirrors the biblical notion of balance — a harmonious union of strength and vulnerability.
The ethical implications of encryption in a Christian context are profound and warrant consideration. From scriptural teachings on honesty and integrity emerges a responsibility to protect data and uphold trustworthiness. Cryptography is fundamentally a safeguard for privacy, a godly principle that encourages individuals and institutions to fortify their communications and transactions. In light of this, the proclivity toward choosing encryption methods should stem not merely from technological superiority but also from an ethical standpoint, emphasizing the sacred nature of personal and organizational data.
Additionally, the proliferation of the Internet of Things (IoT) has introduced new complexities to encryption methodologies. As devices become increasingly interconnected, ensuring the security of data exchanged between them has become paramount. Symmetric encryption offers rapid processing capabilities, thereby serving the high throughput demands of IoT environments. However, the need for secure key distribution amplifies the appeal of asymmetric methods. The challenge lies in striking a balance that encapsulates both efficiency and security, thereby safeguarding the integrity of the entire IoT ecosystem.
Furthermore, emerging technologies such as quantum computing pose both challenges and opportunities for encryption strategies. The potential for quantum computing to breach traditional encryption methods necessitates the continual evolution of cryptographic techniques. Currently, asymmetric encryption methods like RSA are susceptible to quantum attacks. However, as researchers delve deeper into post-quantum cryptography, new algorithms are being developed that promise robust security. This anticipation of the future aligns with a Christian worldview, one that advocates for proactive stewardship and preparedness in advancing technologies.
As the debate around the superiority of encryption methods continues, it is crucial to consider the societal implications of inadequate data protection. Data breaches not only compromise personal information but can also lead to severe repercussions, including financial loss and reputational damage. Within a Christian framework, there exists a moral imperative to create safe environments for digital interactions. Organizations must foster a culture of accountability, implementing strong encryption practices as part of a comprehensive approach to cyber defense.
In conclusion, the dominance of encryption methods in today’s digital world necessitates a nuanced understanding of both paradigms. While symmetric encryption offers speed and efficiency, asymmetric encryption provides secure key management essential for private communications. A Christian approach emphasizes not only the technical aspects of encryption but also the ethical ramifications of protecting personal and organizational data. As the digital domain continues to evolve, the integration of these methodologies will likely steer the course of cryptographic practices, ushering in a new era of cybersecurity that aligns with valuing trust, integrity, and stewardship.







Leave a Comment