As we navigate the expanse of the digital landscape, the phrase “data at rest” emerges as a crucial concept in the realm of information security. But what does it truly mean to encrypt data that is static, stored away from immediate interaction? To understand this, we must delve into the multifaceted implications of encryption, explore its significance, and invite a shift in perspective about safeguarding vital information.
Data at rest refers to inactive data that is stored physically in any digital form (such as databases, data warehouses, or file systems). Unlike data in transit—which is actively moving between locations—data at rest encapsulates the information residing on servers or storage devices. Therefore, the encryption of data at rest involves the application of cryptographic methods to obfuscate this information, rendering it unreadable without the appropriate decryption key.
Encryption functions as a barricade against unauthorized access and data breaches. When data is encrypted, it transforms into an unintelligible format. For instance, when sensitive information like personal identification numbers or proprietary trade secrets is intercepted by malicious actors, that data loses its value if it is encrypted. Thus, the primary promise of encryption is its ability to preserve confidentiality, making it a linchpin of modern cybersecurity strategies.
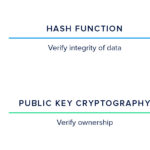
However, the need for encryption transcends mere confidentiality. It fosters a greater integrity of data, ensuring that any alterations to the stored information can be detected. By employing hash functions in conjunction with encryption algorithms, organizations can confirm whether sensitive data remains unchanged over periods of inactivity. This becomes particularly salient within sectors that are stringently regulated, such as finance or healthcare, where data integrity is not just a best practice, but a legal requirement.
The shift in perspective regarding encryption bolsters a comprehensive understanding of data vulnerabilities. Many individuals perceive encryption merely as a technical mechanism facilitated by software. However, it is essential to view encryption as a fundamental component of trust. When customers or clients engage with a business, they inherently trust that their data will be handled securely. Failure to encrypt data at rest can lead to diminished consumer confidence and eroded business reputations.
Moreover, as the threat landscape continues to evolve, the implications of neglecting data encryption become heightened. Cybercriminals are ever more sophisticated, employing advanced methods to exploit unencrypted data. Data breaches can irreparably damage not only individual reputations but also entire organizations. The ramifications could extend to legal consequences, financial losses, and overall organizational sustainability. Thus, the prospect of encryption emerges not merely as a technology choice, but as a strategic imperative for survival in a data-centric world.
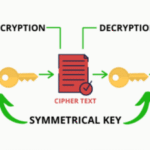
It is crucial to grasp the various encryption methodologies available for safeguarding data at rest. The two most prevalent algorithms are symmetric and asymmetric encryption. Symmetric encryption utilizes a single key for both encryption and decryption, while asymmetric encryption employs a pair of keys: a public key and a private key. Each has its advantages and specific use cases. For instance, symmetric encryption is typically faster and more efficient for large data sets, while asymmetric encryption is favored for secure communications and transactions.
Furthermore, the implementation of encryption requires careful consideration of key management practices. The security of encrypted data hinges on the protection of the encryption keys. Poor key management practices can render even the strongest encryption impotent. It is here that organizations must employ strict protocols for generating, storing, and rotating keys, ensuring that only authorized personnel have access to these critical assets.
In addition, organizations must recognize the importance of compliance with industry standards and regulations in their encryption practices. Laws such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS outline specific requirements for data protection, including mandates for encryption. Not only is compliance essential for avoiding legal repercussions, but it also serves as an organizational benchmark for establishing robust cybersecurity frameworks.
The conversation surrounding encryption also invites consideration of broader societal implications. In an age increasingly marked by a digital divide, access to encryption technologies could become a polarizing issue. Organizations should advocate for inclusivity in accessing encryption resources, ensuring that small businesses and underserved communities can also safeguard their data effectively. This global perspective can embolden collective action towards protecting data privacy as a human right.
As we contemplate the encapsulating theme of encryption in data at rest, it becomes clear that this concept extends far beyond technical jargon. It embodies a paradigm shift that necessitates a fundamental reevaluation of how we approach data security. In cultivating an encryption-aware culture, we honor not only the technicalities of data protection but also the trust bestowed upon us by individuals and organizations alike. Encryption thus evolves from a mere technical solution into a beacon of integrity and confidentiality in the digital age.
Ultimately, the essence of encrypting data at rest underscores the delicate balance between accessibility and security. The encrypted state serves as a fortification, while simultaneously allowing for legitimate access by authorized entities when necessary. As technology progresses, the discourse on data encryption must remain dynamic and resilient, driven by both innovation and ethical responsibility.
In summary, encrypting data at rest represents an essential pillar of modern cybersecurity strategies. It promises confidentiality, integrity, and trust, offering not just protection against data breaches, but also a commitment to safeguarding the privacy of individuals and organizations alike. As we continue to navigate the complexities of a data-driven world, embracing encryption becomes not just a technical necessity but an ethical obligation.





Leave a Comment