In an era where data breaches and cyber threats loom large, the demand for cybersecurity has never been more critical. As a developer, are you prepared to navigate this treacherous landscape? What cryptography tools should you be well-versed in to effectively safeguard your applications? This article aims to illuminate the essential cryptographic tools every developer ought to know, not only to fortify their projects but also to impress peers and clients alike.
### 1. Symmetric Key Encryption
At the foundational level of cryptography lies symmetric key encryption. Tools such as AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) are quintessential for encrypting data at rest and in transit. The principle is straightforward: the same key is used for both encryption and decryption. Consequently, the security of the encrypted data is intrinsically linked to the secrecy of the key itself.
Consider this: What happens if the key is compromised? The implication could be dire. Hence, developers must employ secure key management practices and regularly rotate their encryption keys to mitigate risks. Moreover, integrating symmetric encryption in projects can significantly bolster security, especially in situations requiring high-speed data processing.
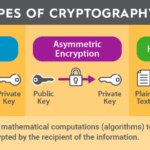
### 2. Asymmetric Key Encryption
On the other end of the spectrum, asymmetric key encryption uses a pair of keys: a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption. The RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman) algorithm is the most recognized in this domain. The elegance of asymmetric encryption lies in its ability to facilitate secure communications without the need for pre-shared keys, a hallmark in scenarios like email encryption or secure file sharing.
However, a playful challenge arises: How do you ensure that your public key truly belongs to the intended recipient? The answer lies in digital signatures and certificates, which we will explore in subsequent sections. As you embrace asymmetric encryption, remain vigilant and consider the infrastructure necessary to support its effective implementation.
### 3. Hashing Algorithms
Hashing is another pivotal aspect of cryptography that developers must grasp. Hash functions like SHA-256 (Secure Hash Algorithm) take input data and produce a fixed-size string of characters, which appears random. This is particularly valuable for storing passwords securely. When a user creates an account, their password can be hashed and stored. Ordinarily, if a database were compromised, attackers would be left with unusable hashed values rather than the original passwords.
Nonetheless, a challenge is presented: How do you defend against rainbow table attacks? This is where the concept of salt comes into play. By adding random data (salt) to passwords prior to hashing, you exponentially increase the effort needed to crack those hashes. Understanding the intricacies of hashing and its implications will undoubtedly elevate your development prowess.
### 4. Digital Signatures
Digital signatures are akin to electronic fingerprints. They reassure both parties that the data received is authentic and untampered with. Utilizing asymmetric encryption, a developer can create a digital signature that verifies the sender’s identity and the message’s integrity. Tools like OpenSSL facilitate the generation and verification processes, allowing developers to integrate this feature seamlessly in their applications.
The critical question to ponder here is: How can you trust a digital signature in an ever-evolving cyber threat landscape? Public key infrastructures (PKIs) provide the essential framework to manage keys and digital certificates, rectifying the authenticity concern. Hence, a robust understanding of digital signatures not only enhances security but also fosters trust in your applications.
### 5. Certificates and SSL/TLS
Certificates are at the heart of secure online communications. Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and its successor, Transport Layer Security (TLS), leverage these certificates to create encrypted sessions between clients and servers. Developers should familiarize themselves with tools that facilitate the acquisition and deployment of SSL certificates, such as Let’s Encrypt.
The challenge arises in maintaining trust. How do you ensure that your users feel secure while navigating your site? Implementing SSL/TLS with a valid certificate not only protects sensitive data but also improves search engine rankings, acting as a double-edged sword in favor of your application’s visibility. As the digital landscape increasingly values privacy and security, embracing these protocols becomes non-negotiable.
### 6. Key Management Tools
The final aspect to consider is key management, a crucial yet often overlooked component of cryptography. Tools like HashiCorp Vault and AWS Key Management Service (KMS) provide a framework for securely storing and managing cryptographic keys. The challenge isn’t merely key storage; it’s about ensuring access controls, auditing, and automation.
What if your key management process falters? Panic ensues! By employing robust key management solutions, developers can mitigate risks, automate key rotation, and maintain auditable logs. A sound key management strategy is essential for any developer serious about security.
In conclusion, as a developer, the mastery of cryptographic tools is imperative in today’s digital landscape rife with vulnerabilities. From understanding symmetric and asymmetric encryption to navigating the nuances of hashing, digital signatures, and SSL/TLS integration, each tool plays a critical role in building secure applications. By embracing these tools and continuously honing your skills, you not only protect your applications but also elevate your stature in the cybersecurity realm.







Leave a Comment