In the contemporary digital landscape, the proliferation of communication technologies has revolutionized the way we connect, share, and express ourselves. However, with this evolution comes an alarming vulnerability—our private communications are increasingly subject to surveillance, eavesdropping, and malicious exploitation. This predicament brings us to the pivotal concept of encrypted messages: communications that have been encoded to prevent unauthorized access and ensure confidentiality. What are encrypted messages, and why do they matter? This exploration delves into their mechanics, significance, and the burgeoning realm of cryptography.
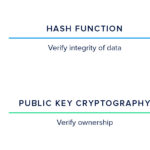
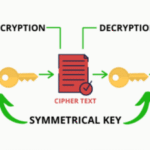
At its core, encrypted messaging involves transforming readable information—known as plaintext—into a scrambled format termed ciphertext. This transformation is accomplished through the use of cryptographic algorithms, which are complex mathematical functions designed to secure data. The essence of encryption lies in its ability to render messages incomprehensible to anyone who does not possess the requisite decryption key. Thus, even if a clandestine actor intercepts the transmission, they would be incapable of interpreting its contents. The cipher serves as a protective wall, safeguarding sensitive information against prying eyes.
The origins of cryptography can be traced back to antiquity when soldiers employed rudimentary ciphers to communicate strategies without the risk of interception by enemies. Today, cryptographic techniques have experienced remarkable advancement, evolving from simple substitution ciphers to intricate asymmetric and symmetric encryption schemes. The latter employs a singular shared key for both encryption and decryption, while the former utilizes a pair of keys: a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption. This divergence ensures that communication can be secured even in the absence of a pre-established agreement between parties.
The importance of encrypted messages resonated profoundly during the onset of the internet age. As individuals rapidly embraced digital communication, personal data became increasingly vulnerable to unauthorized access and data breaches. The ramifications were profound: identity theft, corporate espionage, and governmental surveillance proliferated unchecked. In response to these threats, individuals and organizations sought methods to enhance data security. The realization that encryption serves as a formidable defense mechanism led to its widespread implementation across various domains, from online banking to email communication.
Furthermore, encrypted messaging applications—ranging from popular services like WhatsApp to niche tools designed for heightened privacy—have gained momentum among users desiring discretion. What motivates this quest for privacy? At its foundation lies the intrinsic human desire for autonomy and control over personal information. In an era defined by digital footprints, users increasingly recognize the heightened vulnerability of their communications.
The significance of encrypted messages extends beyond individual privacy; it has implications for broader societal constructs. The dialectic between security and transparency is at the forefront of contemporary discourse. Governments, in their pursuit of national security, often advocate for surveillance measures that can infringe upon civil liberties. However, this stance raises the question: does public safety justify the compromise of privacy? Encrypted messages serve as a formidable counterbalance, affording individuals the protection to express dissenting opinions, engage in political activism, and voice concerns without the fear of retribution.
Moreover, encrypted messaging assumes a pivotal role in business interactions. Organizations have a vested interest in safeguarding proprietary information, trade secrets, and confidential client communications. A breach of such sensitive data can destabilize a company’s reputation, undermine stakeholder trust, and lead to financial ramifications. Encrypted messages mitigate these risks, enabling organizations to cultivate secure environments for collaboration and innovation. The sanctity of internal discussions—from brainstorming sessions to strategic planning—rests on the foundation of robust encryption.
However, the implementation of encrypted messaging is not without its challenges. The duality of its existence presents an inherent tension between privacy advocates and law enforcement agencies. While encryption fortifies personal security, it complicates investigative efforts. Encrypted communications can hinder criminal investigations, as authorities may struggle to access incriminating evidence without contravening privacy rights. This dichotomy engenders heated debates regarding the most prudent avenues for balancing security needs with individual rights. As society grapples with these issues, the conversation surrounding encryption will undoubtedly shape the regulatory landscape of the future.
As we contemplate the future trajectory of encrypted messages, emerging technologies such as quantum computing pose both opportunities and threats. The advent of quantum computing holds the potential to revolutionize encryption methodologies; however, it also threatens to render current encryption techniques obsolete. This impending evolution underscores the necessity for adaptive and forward-thinking approaches within the field of cryptography, as researchers and professionals strive to forge new algorithms capable of withstanding quantum attacks.
In conclusion, encrypted messages represent a critical intersection of technology, privacy, and security in an increasingly interconnected world. Their capacity to safeguard personal communications, uphold democratic values, and bolster institutional integrity underscores their significance in our daily lives. As we continue to navigate the complexities of the digital age, the fascination with encryption remains palpable; it embodies the perennial struggle for knowledge, freedom, and security. Encrypted messages are not merely abstract mathematical constructs but rather indispensable components of the modern communication landscape, shaping how we interact in an era characterized by constant scrutiny and digital omnipresence.







Leave a Comment