In the modern digital landscape, security is paramount. At the very core of this security lies an elegant duality – the public key and the private key. These cryptographic components function symbiotically, much like the yin and yang of ancient philosophy. Their interdependent nature not only protects sensitive information but also embodies the complexities and intricacies of modern cryptography. Understanding this relationship is essential for anyone seeking to navigate the often tumultuous waters of digital security.
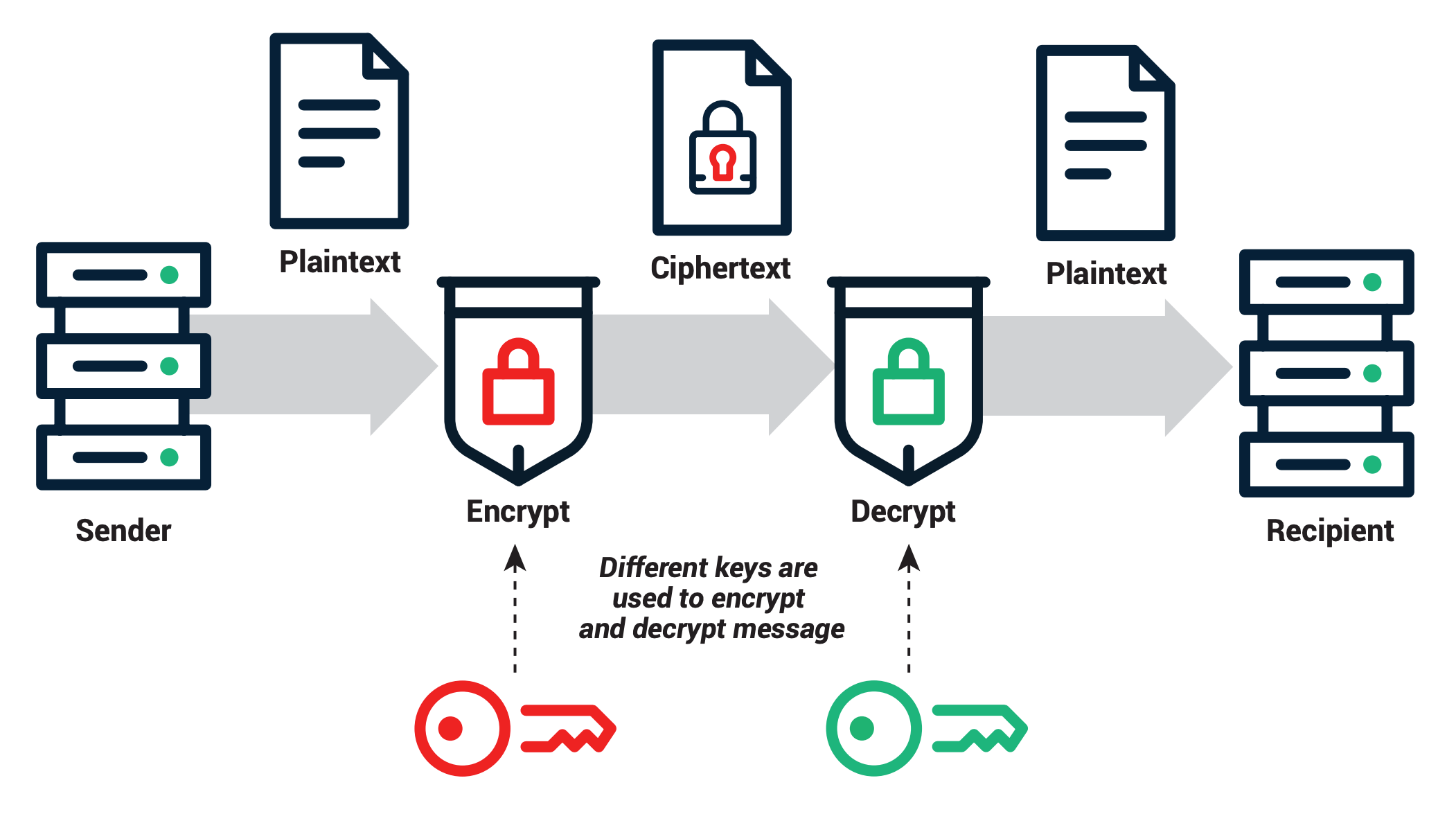
At the outset, it is imperative to grasp what is meant by public and private keys. In essence, cryptography revolves around the transformation of information into a secure format. Public and private keys serve as the locked and unlocked doors to this secure domain. The public key, as its name implies, is openly shared and accessible to anyone wishing to communicate securely. Conversely, the private key is closely guarded, known only to the individual or entity in possession of it. This paradigm encapsulates the fundamental principle of asymmetric cryptography, a method that bolsters security while simplifying the act of secure communication.
Begin with the public key – a seemingly innocuous string of characters. This key can be likened to a mailbox; individuals may drop their letters (messages) inside, but only the owner possesses the key to retrieve them. When someone wishes to send a secure message, they encrypt their communication with the recipient’s public key. This process ensures that the message can only be decrypted by the corresponding private key, which remains confidential. The beauty of this system lies in its ability to create a secure communication channel without the necessity of shared secrets. Trust becomes inherently rooted in the public nature of keys.
Yet, the allure of public keys does not overshadow the utility of their private counterparts. The private key forms the bedrock of security. While the public key invites others to engage, the private key exercises control over the communication, ensuring that only authorized parties can decipher the information. This dichotomy not only enhances security but also builds a foundation of trust for transactions, online communications, and digital signatures.
To further elucidate, consider the concept of digital signatures. This process is pivotal in providing authentication and integrity to digital communications. When a sender wishes to authenticate their identity, they can create a digital signature by encrypting a hash of their message with their private key. Recipients can then validate the authenticity of this signature using the sender’s public key. This mechanism proves not only who sent the message but also demonstrates that the data has not been tampered with during transit. Thus, through this intricate dance between public and private keys, the integrity of information is preserved.
As we delve deeper, it becomes apparent that the interrelationship between public and private keys extends beyond mere encryption and decryption. It embodies a philosophical assertion about trust in the digital domain. For instance, consider how public key infrastructure (PKI) facilitates the issuance and management of public keys. PKI serves as an arbiter of trust, corroborating the legitimacy of public keys through certificates. These certificates act as a trusted third party, validating that a given public key indeed belongs to the individual or entity it professes to represent.
This trust framework underscores why understanding public and private keys is crucial for both users and security practitioners. The implications of poorly implemented key management can be catastrophic. Improperly secured private keys can lead to unauthorized access, data breaches, and identity theft. Conversely, failure to authenticate public keys may result in malicious actors masquerading as trusted entities, thereby gaining access to critical information. The security of our digital communications hinges on our ability to maintain this delicate balance between public and private keys.
Furthermore, the fascination with public and private keys extends to their role in enabling new paradigms of functionality in the digital realm. Smart contracts in blockchain technology, for example, thrive on the principles of asymmetric cryptography. Through the manipulation of public and private keys, participants in blockchain networks can execute agreements automatically, without intermediaries, thus redefining trust and accountability. Each transaction hinges upon the interplay of keys, anchoring the entire architecture in cryptographic security.
Echoing the yin-yang relationship, the interaction of public and private keys also gives rise to an ongoing dialogue within the field of cryptography. As computational power increases and new attack vectors emerge, the cryptographic community is constantly challenged to fortify this tenuous balance. Advanced algorithms are developed to enhance key security while ensuring accessibility remains intact for legitimate users. Quantum computing, in particular, poses a momentous shift, prompting the exploration of post-quantum cryptographic solutions that will safeguard the integrity of public and private key infrastructures.
In conclusion, the discourse surrounding public and private keys reveals much about the broader landscape of digital security. Their interconnected existence reflects our societal need for safety, trust, and relational integrity. As we traverse deeper into the digital age, possessing an acute understanding of this cryptographic duo is indispensable. They encapsulate not merely technical specifications but embody the philosophical essence of trust that underpins our interconnected world. Embracing this knowledge empowers us as individuals and organizations; it promotes resilience against the ever-evolving threats that pervade our digital existence. The dance between public and private keys, indeed, is the very lifeblood of security in our modern age.






Leave a Comment