In the intricate world of network architecture, SSL offloading stands out as a crucial mechanism designed to enhance server efficiency and security. This multifaceted process involves the delegation of SSL encryption and decryption tasks from the application server to a dedicated device—typically a load balancer or a specialized SSL offloading appliance. This strategy not only alleviates the processing burden on application servers but also accelerates the handling of HTTPS traffic, fostering a more responsive user experience.
As the prevalence of secure connections burgeons due to heightened concerns regarding data privacy and security, SSL offloading has emerged as a pragmatic solution. The underlying principle operates on a fundamental premise: the computational overhead associated with SSL/TLS encryption is substantial. By offloading this taxing process, organizations can significantly optimize their server performance, thereby enhancing the scalability of their applications.
To comprehend the advantages of SSL offloading, it is imperative to consider the SSL/TLS handshake—a series of intricate exchanges that establish a secure session between a client and a server. This handshake incorporates the negotiation of cryptographic parameters, server authentication, and the exchange of keys. Each of these steps demands considerable computational power, potentially slowing down server response times during peak usage. It’s within this context that the promise of SSL offloading becomes apparent.
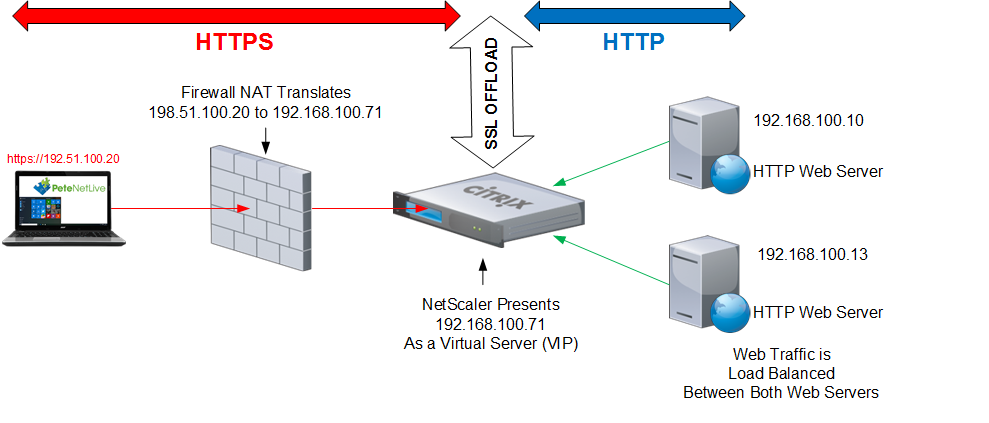
When SSL offloading is implemented, the dedicated offloading device manages the heavy cryptographic operations involved in the SSL/TLS handshake. Once the secure connection is established, only the decrypted data is forwarded to the application server. This streamlined approach allows application servers to focus on their core functionality—processing requests and delivering content—while the offloading device secures the data transmission.
Moreover, SSL offloading plays a pivotal role in load balancing scenarios. By distributing SSL decryption tasks across multiple offloading devices, organizations can effectively manage high volumes of traffic. This distribution not only prevents bottlenecks but also ensures that users experience seamless access to services without the frustrating slowdowns often associated with SSL connections.
Another salient aspect of SSL offloading is its impact on resource utilization. Application servers are frequently equipped with vast computing resources that can be better employed for application logic rather than handling cryptographic processes. This bifurcation of duties leads to enhanced performance. For instance, an e-commerce platform experiencing surges in user traffic during seasonal sales can rely on SSL offloading to maintain a quick response time, ultimately contributing to improved conversion rates and customer satisfaction.
In addition to performance benefits, SSL offloading also presents a strategic advantage with respect to security management. Centralizing the SSL termination point simplifies the management of SSL certificates. Instead of updating certificates on multiple servers throughout a network, IT teams can administer them from a single device, thereby reducing the risk of errors and ensuring consistent security policies across applications.
However, the deployment of SSL offloading is not without considerations. Organizations must ensure that the offloading device is robust enough to handle the encrypted traffic without introducing its own latency. The choice of vendor becomes critical as variations in architectural designs and processing capabilities can lead to significant disparities in performance. Security implications must also be scrutinized; while centralizing SSL termination adds efficiency, it could create a single point of failure if not adequately protected.
As the digital landscape continually evolves, the ramifications of SSL offloading extend beyond mere performance improvements. The increasing complexity of cyber threats necessitates a proactive approach to security. SSL offloading not only addresses the computational demands of encryption but also allows for the integration of advanced threat detection systems at the edge of the network. This proactive stance equips organizations with the tools needed to respond to potential security incidents swiftly and efficiently.
From an architectural perspective, the incorporation of SSL offloading reflects a significant shift in how organizations approach security and performance. An interwoven fabric of different technologies—including firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and content delivery networks—can be constructed, creating a more resilient infrastructure. This unified approach enables organizations to not only manage their performance metrics better but also fortifies their defenses against a constantly evolving threat landscape.
In summation, SSL offloading is reshaping the paradigm of server management in an age where security and performance are paramount. By redistributing the taxing processes of encryption away from application servers, organizations can optimize resource allocation, enhance response times, and fortify their security posture. The trajectory toward a more efficient and secure network architecture is evident in the adoption of SSL offloading, making it an essential consideration for any organization striving to thrive in today’s digital universe.
Through understanding the operational mechanics and advantages of SSL offloading, businesses can position themselves at the forefront of technological advancement, thereby paving the way for a future where security and performance coexist harmoniously. The exploration of SSL offloading is not merely a technical endeavor; it is an invitation to reevaluate how businesses can leverage technology to provide superior services while ensuring the safety and integrity of their data.






Leave a Comment