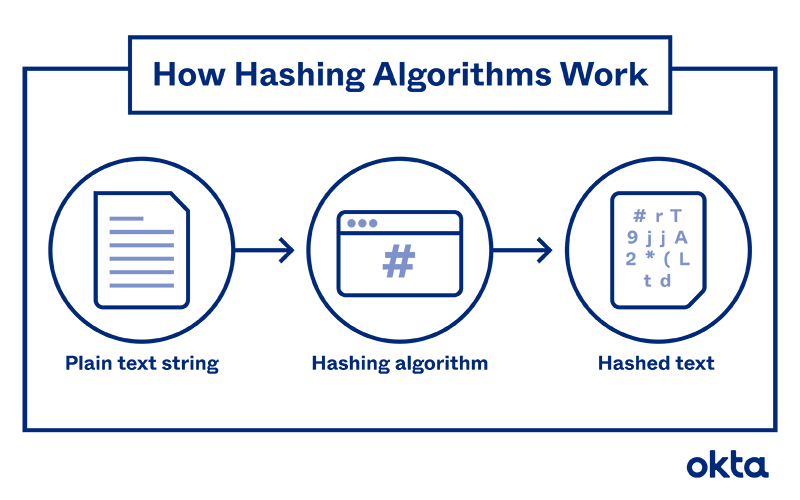
Hashing algorithms, though often relegated to the back alleys of cybersecurity discussions, play an instrumental role in modern technology, far beyond their typical associations with password protection and data integrity. These algorithms convert input data into fixed-length representations, known as hash values, through a deterministic process. Their obscured elegance lies not just in their utility for securing sensitive information but also in their applications across various domains. Here, we explore some fascinating real-world uses of hashing algorithms that tend to elude the everyday observer.
1. Data Deduplication in Cloud Storage
One of the more pragmatic applications of hashing algorithms is in data deduplication within cloud storage systems. As businesses continue to generate copious amounts of data, the redundancy that emerges from storing identical copies of files can lead to inefficiency and excessive costs. Hashing algorithms are employed to create unique hash values for files; when a file is uploaded, its hash is calculated. If a file with the same hash already exists in the database, the system recognizes it as a duplicate and only saves a reference to the original file rather than duplicating it. This method conserves both storage space and bandwidth, streamlining data management immensely.
2. Blockchain Technology
Blockchain, the backbone of cryptocurrencies and decentralized applications, relies heavily on hashing algorithms to maintain the integrity and immutability of its data. Every block in a blockchain contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, alongside its own data and timestamp. This forms a chain of blocks that is resistant to tampering, as altering any single block would require recalculating the hashes of all subsequent blocks, a computationally insurmountable task for any would-be attacker. Beyond cryptocurrencies, blockchains are increasingly utilized in supply chain management, voting systems, and digital identity verification, showcasing the versatility of hashing algorithms in ensuring data integrity across a myriad of sectors.
3. Digital Signatures for Authentication
Digital signatures employ hashing algorithms as a pivotal mechanism for authentication in electronic communications. When a user signs a document electronically, a hash of the document is generated. This hash, combined with the signer’s private key, is then used to create the digital signature. Recipients can validate the signature by hashing the original document again and comparing it to the decrypted signature. This process not only guarantees the authenticity of the document but also ensures that it has not been altered during transmission. Such applications are essential in legal agreements and secure communications, thereby enhancing trust in digital interactions.
4. Password Management and Security
Password hashing is a ubiquitous yet often underestimated implementation of hashing algorithms. When users create accounts, their passwords are transformed into hashes before storage, rendering them unreadable to unauthorized parties. This process protects sensitive information even if a database breach occurs. Advances such as salting—adding random data to the password before hashing—further fortify security against precompiled attacks like rainbow tables. This practice extends beyond standard user accounts; it is vital for safeguarding access to sensitive data in enterprise systems, thereby preserving user privacy.
5. File Integrity Verification
Hashing algorithms serve a critical function in file integrity verification, ensuring that files have not been altered or corrupted. This application is particularly valuable in software distribution and updates. Developers often provide hash values of downloadable files, which users can compute to verify the files’ integrity. If the computed hash matches the provided hash, the file is deemed authentic and untampered. This method prevents the introduction of malware and assures users that the software they are installing is genuine and secure.
6. Digital Fingerprinting
The concept of digital fingerprinting employs hashing algorithms to create unique identifiers for various forms of content. In digital marketing and content management, hashing is used to track and analyze user engagement and preferences. For instance, unique hashes generated from user interactions with specific content can reveal valuable insights into consumer behavior without compromising individual privacy. This practice allows marketers to create targeted campaigns based on aggregated, anonymized data rather than relying on identifiable information.
7. Content Addressable Storage
Content addressable storage (CAS) employs hashing algorithms as a cornerstone for organizing and retrieving data. Rather than using traditional file names or directories, CAS systems utilize the hash of the content itself as the address for storage. This approach enables efficient data retrieval and management, as identical pieces of content always share the same address. In environments where large amounts of data must be accessed and stored—such as in digital archives or cloud storage—this method not only enhances performance but also simplifies data management workflows.
8. Remote Sensing and Geospatial Data
In the realm of remote sensing and geospatial data, hashing algorithms can be utilized to ensure the integrity of large datasets collected from satellite imagery or sensor networks. By generating hashes for every data package received, researchers can confirm that the data has not been altered during transmission or storage. This application is particularly crucial given the volume and sensitivity of the data involved in environmental monitoring, urban planning, and disaster response scenarios, where accuracy is paramount.
Conclusion
The multifaceted applications of hashing algorithms extend far beyond their association with data security and password management. From enhancing storage efficiency through deduplication to ensuring data integrity in emerging technologies like blockchain and remote sensing, hashing algorithms play an indispensable role in a multitude of industries. Each of these use cases highlights the deeper fascination with the elegance and versatility of hashing, illuminating a vital aspect of contemporary technological infrastructures that often goes unnoticed.






Leave a Comment