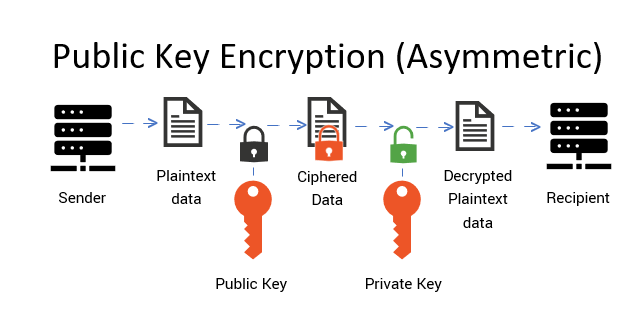
Public key encryption, a hallmark of modern cryptography, operates on the principles of asymmetric key cryptography. This ingenious method harks back to the early days of computer science, creating a paradigm shift in how data is secured. Unlike traditional symmetric key algorithms, where the same key is shared between parties, public key systems utilize a pair of keys – a public key, which is openly disseminated, and a private key, which is kept secret. This fascinating duality not only enhances security but also plays a pivotal role in various everyday applications that have become so integral to our digital lives. Here, we explore five everyday uses of public key encryption that exemplify its significance and practicality in today’s interconnected world.
1. Secure Online Banking
In an age where financial transactions are predominantly conducted online, public key encryption is a linchpin of secure online banking. Banks employ sophisticated encryption algorithms to protect sensitive customer information, including account details and transaction data. When a customer logs into their bank account, their device utilizes the bank’s public key to encrypt data before transmission. This ensures that even if data packets are intercepted by malicious actors, the information remains indecipherable without the corresponding private key. By leveraging this technology, banks can instill confidence in their clients, assuring them that their financial information is safeguarded against the ever-increasing threats of cybercrime.
2. Secure Email Communication
Another ubiquitous application of public key encryption is found in secure email communication. Privacy concerns have become paramount in the digital age, as sensitive information can easily be intercepted by nefarious entities. Email services that embrace public key infrastructure (PKI) allow users to encrypt messages using the recipient’s public key. This methodology not only protects the content of the email from prying eyes but also verifies the sender’s identity through digital signatures. When recipients receive an email, they can be confident that the message has not been tampered with in transit. As concerns about data breaches and unauthorized access grow, utilizing public key encryption for email becomes increasingly imperative.
3. Virtual Private Networks (VPNs)
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) have surged in popularity, especially among individuals seeking to anonymize their online activities. Public key encryption is a cornerstone of secure communication within these networks. When a user connects to a VPN, their device and the VPN server engage in a handshake process that involves exchanging public keys. This process establishes a secure tunnel, encrypting all data transmitted between the user and the server. As a result, even if an internet service provider or hacker monitors the connection, the data remains encoded and private. With the rise of remote work and the increasing desire for internet privacy, public key encryption has become indispensable in maintaining secure, private browsing experiences.
4. Digital Signatures for Document Integrity
In both personal and business contexts, the integrity of documents is of paramount importance. Public key encryption facilitates the use of digital signatures, offering a solution to verify authenticity and integrity. When a document is signed digitally, the signer encrypts a hash of the document using their private key. The recipient can then decrypt this hash with the signer’s public key to validate its authenticity. This process guarantees that the document has not been altered post-signing, thereby ensuring trust in digital transactions. Digital signatures are particularly crucial in legal contexts, where the authenticity of contracts and agreements can significantly impact parties involved. This robust mechanism underscores the practicality of public key encryption beyond just securing data transmission.
5. Secure Software Updates
As software applications evolve, so too do the potential vulnerabilities associated with them. Public key encryption plays an essential role in verifying the authenticity of software updates, an aspect often overlooked in cybersecurity discussions. Developers digitally sign their software packages using private keys, and users’ systems utilize the developers’ public keys to verify these signatures prior to installation. This meticulous verification process ensures that the software has not been tampered with or compromised during distribution. As cyber threats increasingly target software supply chains, ensuring the integrity of updates through public key encryption is a crucial step in protecting users from malicious software and ensuring a reliable computing experience.
In conclusion, public key encryption pervades various aspects of modern life. Its applications in secure online banking, email communication, VPNs, digital signatures, and software updates elucidate an essential layer of security that underpins daily interactions in a digitized world. The ability to protect sensitive information while authenticating identities signifies a monumental leap forward in ensuring privacy and trust in the digital era. As technologies evolve and new threats emerge, the significance of public key encryption will undoubtedly continue to expand, reinforcing its intricate role in safeguarding our digital existence.







Leave a Comment