In an age where data breaches and information theft are ubiquitous, the question of whether database encryption is a prudent measure has garnered significant attention. Encryption serves as a formidable barrier, converting plaintext into an unreadable format, thereby safeguarding sensitive information. However, it comes with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. This article delves into the pros and cons of database encryption, providing a comprehensive overview for organizations contemplating its implementation.
Understanding Database Encryption
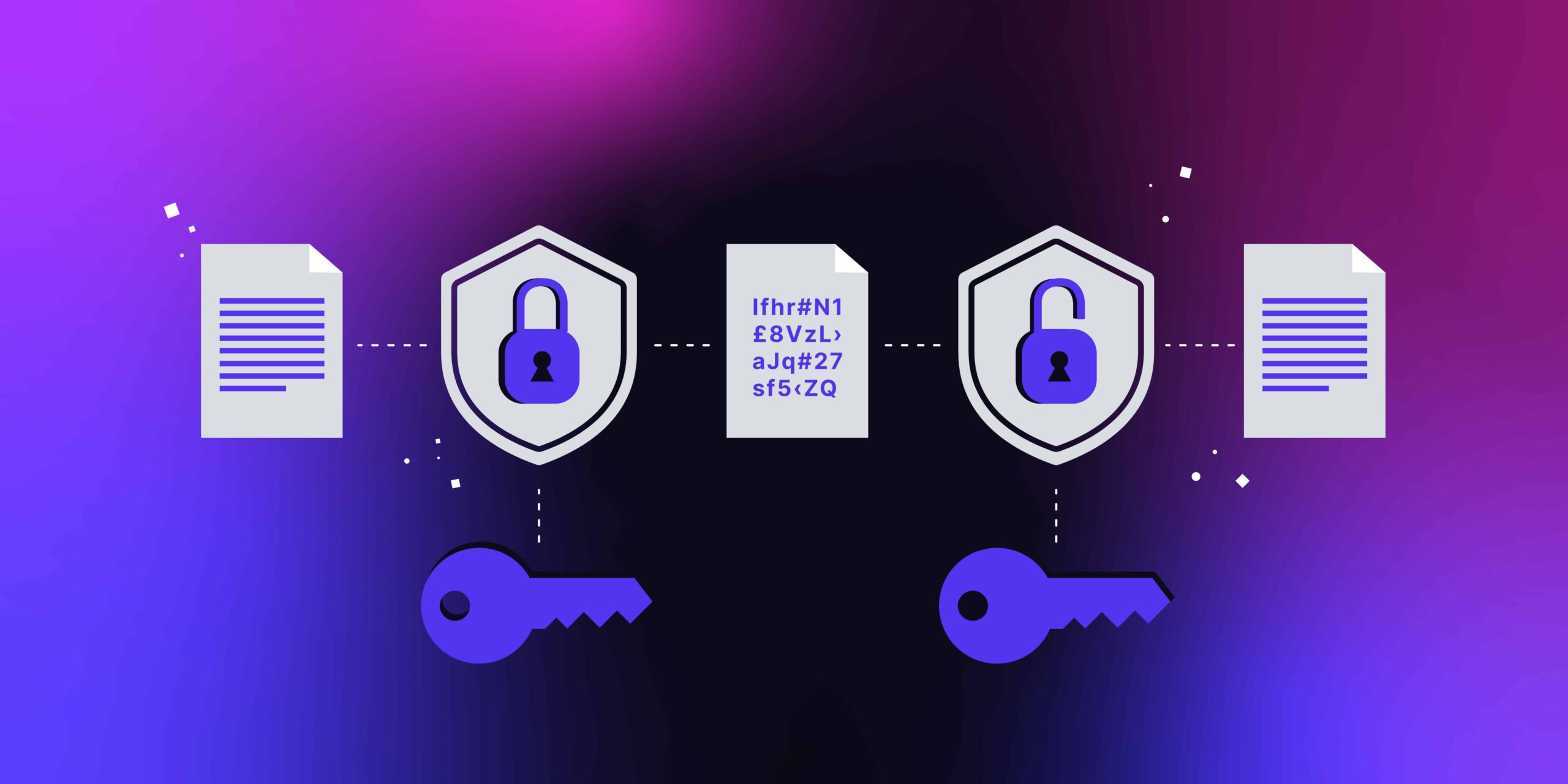
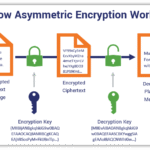
Database encryption primarily involves the application of cryptographic algorithms to encode data stored within databases. It ensures that only authorized users with the proper decryption keys can access the plaintext data. This capability is crucial for organizations dealing with sensitive information, such as financial data, personally identifiable information (PII), and proprietary business secrets.
Pros of Database Encryption
1. Enhanced Security Measures
The most compelling argument in favor of database encryption is its ability to significantly bolster security. In the event of unauthorized access or data breaches, encrypted data remains indecipherable to hackers. Without access to the decryption keys, stolen data holds little value. This security measure is particularly vital in industries that handle highly sensitive information, including banking, healthcare, and e-commerce.
2. Compliance with Regulatory Standards
Organizations are often subjected to rigorous regulatory frameworks, such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). Database encryption can assist organizations in achieving compliance with these laws, which mandate the protection of sensitive data. Failure to comply can result in severe fines and reputational damage.
3. Mitigating Insider Threats
While external threats are a significant concern, insider threats—whether malicious or inadvertent—are equally daunting. Database encryption acts as a safeguard against unauthorized access by internal personnel. By restricting access to sensitive information based solely on roles and responsibilities, organizations can minimize the risk of data exposure from within.
4. Data Integrity Assurance
Encryption not only secures data but can also help ensure its integrity. Employing encryption techniques such as hashing alongside encryption provides assurance that data has not been tampered with. This capability is essential for maintaining trust and reliability in business transactions.
5. Peace of Mind
Implementing database encryption fosters a culture of security within an organization. Employees and stakeholders can have confidence that sensitive data is protected. This psychological reassurance can translate to better business practices and an overall heightened sense of responsibility regarding data handling.
Cons of Database Encryption
1. Performance Overhead
One of the notable drawbacks of database encryption is the performance overhead it introduces. Encryption and decryption processes require computational resources, which can slow down database operations. This lag can adversely affect user experience especially in high-performance environments where speed is crucial.
2. Complexity of Management
Implementing and managing encryption protocols can be a complex endeavor. Organizations must not only choose the appropriate encryption algorithms but also manage key distribution and storage. Improper key management can lead to data inaccessibility if keys are lost or compromised. This complexity often necessitates additional layers of training and support.
3. Cost Implications
The financial implications of database encryption cannot be overlooked. Alongside the costs associated with implementing encryption technologies, organizations may need to invest in training personnel, purchasing additional hardware, or upgrading systems to ensure compatibility with encryption practices. For smaller organizations, these expenses can be significant.
4. Potential for False Security
Database encryption may evoke a false sense of security among users. Many organizations may believe that simply encrypting their data absolves them of further security measures. This misconception can lead to complacency and a lack of comprehensive security strategies that incorporate multiple protective layers.
5. Regulatory Challenges
While encryption can aid in compliance, it can also introduce regulatory challenges. Different jurisdictions may have varying regulations regarding encryption, including stipulations on key management and data access. Organizations operating internationally may find themselves grappling with a patchwork of legal requirements, complicating their approach to data protection.
Conclusion
Considering the myriad pros and cons of database encryption, organizations must weigh the benefits against the challenges unique to their operational context. Enhanced security and compliance are compelling motivators for encryption. Yet, operational impacts, costs, and potential over-reliance on encryption as a panacea must also be critically evaluated. Ultimately, effective data protection arises not solely from implementing encryption but from developing a holistic approach to data security that encompasses various techniques and strategies tailored to organizational needs.






Leave a Comment