In the realm of cybersecurity, brute force attacks frequently emerge as a subject of intrigue and concern. But how can you ethically explore the boundaries of these techniques while simulating them in a controlled environment? For those inclined towards ethical hacking, setting up a PC cluster for brute force testing presents an opportunity to rigorously evaluate defenses without infringing upon any rights. This guide elucidates the processes, considerations, and potential challenges to pave the way for an ethical exploration of brute force methodologies.
To commence your venture into creating a brute force testing environment, a deliberate plan is paramount. One must first ponder a critical question: How would you fortify a digital fortress against relentless waves of automated attackers? This playful inquiry not only stimulates thought but also underscores the necessity of understanding the adversary’s tactics.
**1. Define Objectives and Ethical Boundaries**
The initiation of any project warrants a clear articulation of objectives. Are you testing password strength, assessing system resilience, or perhaps evaluating a specific application’s defenses? Clarity in purpose guides the entire setup and ensures compliance with ethical standards. Establish boundaries; ensure testing occurs on systems or environments you own or have obtained explicit permission to test. This prevents infringement upon privacy rights and the violation of laws.
**2. Hardware Requirements**
To establish a robust PC cluster, prerequisites in hardware are essential. A minimum of three interconnected systems can create a rudimentary cluster, allowing distributed processing throughout the testing phase. Ideal specifications include multi-core processors, an ample supply of RAM (preferably 16 GB or higher), and solid-state drives (SSDs) for accelerated data processing. The selection of hardware plays a pivotal role, as efficiency directly influences the outcomes.
**3. Software Selection**
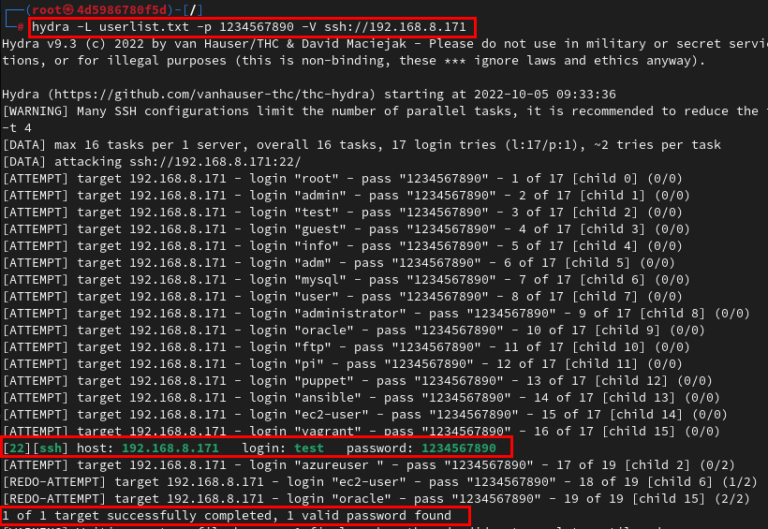
Next, choosing the appropriate software tools becomes imperative. Several software solutions cater to brute force testing; tools such as Hashcat and John the Ripper are notable mentions. These applications allow the orchestrating of password combinations systematically. Additionally, consider utilizing a framework for managing distributed tasks, like Apache Mesos or Kubernetes. These systems facilitate the parallel processing power of your cluster, thereby expediting the testing process.
**4. Configuration of the Cluster**
Creating a functional PC cluster entails configuring the nodes to ensure communication and synchronization. Within your operating system—Linux is often favored—establish cluster management by implementing SSH (Secure Shell) for secure access across your machines. Configure the software chosen earlier to run collectively across nodes, effectively allowing each machine to contribute to the computational load. This configuration often proves intricate, requiring a profound understanding of networking and command-line interfaces.
**5. Implementing Testing Scenarios**
Once the technical setup is in place, it is time to design testing scenarios. Formulate realistic attack simulations that reflect potential threats faced by your target systems. Employ different attack vectors, such as dictionary and hybrid attacks, alongside pure brute force strategies. The variation in methods underlines the importance of passwords as your own testing environment can reveal vulnerabilities that may have been overlooked previously.
**6. Monitoring and Data Collection**
As with any scientific endeavor, the importance of monitoring cannot be overstated. Utilize logging tools to capture detailed information about your testing processes and outcomes. Consider incorporating network analysis tools to observe traffic patterns during attacks. This data not only enhances transparency but serves as a foundation for post-test analysis; thus, understanding your systems’ responses enhances engagement with security measures.
**7. Ethical Considerations and Compliance**
Throughout the entire process, adhering to ethical standards stands as a non-negotiable pillar. This is where a potential challenge may arise: striking a balance between thorough testing and ethical responsibility. Constantly remember to revisit your ethical framework, ensuring that all actions remain within legal confines. Engage with a community of ethical hackers for insights and to continuously refine your methods while staying informed about the evolving landscape of cybersecurity law.
**8. Analyzing Results and Refining Security**
Upon completion of testing, the analysis of results involves examining data landscapes and identifying weaknesses. Did certain methodologies yield efficacious results? Was there a noticeable weakness in password strength? Use this critical analysis as leverage to enhance your security protocols and systems. By refining defenses based on empirical evidence, the insights attained from brute force testing translate into practical enhancements.
**9. Concluding Thoughts**
As your ethical exploration through brute force testing converges, the prospective challenges along the way serve as invaluable learning experiences. Each step taken in setting up a PC cluster illustrates a commitment to understanding and reinforcing digital security. Moreover, healthy inquiry into the adversarial landscape solidifies the ethical stance against malicious practices. The deployment of these strategies not only fortifies your systems but also amplifies the call for ethical consideration in cybersecurity as a whole.
Ultimately, your foray into the world of ethical brute force testing begs the introspective question: Are we truly prepared for the inevitable wave of cyber threats that challenges our security foundations? Embrace the questions, arm yourself with knowledge, and address security concerns head-on.






Leave a Comment