In a contemporary landscape characterized by an incessant maelstrom of cyber threats and data breaches, the necessity of securing sensitive information has become paramount. As digital vulnerabilities multiply, individuals and organizations alike find themselves confronted with the daunting task of protecting data meant to remain confidential. This examination delves into the intricate methodologies employed to safeguard sensitive data in an environment rife with insecurity, offering insights into the complexities of modern cryptographic strategies.
One of the fundamental principles of information security is the distinction between data at rest and data in transit. Data at rest pertains to information stored on devices or servers, while data in transit encompasses information actively moving across networks. Each state presents unique vulnerabilities that require tailored security measures. For instance, data at rest, left unprotected, is susceptible to unauthorized access and theft, often exploited through physical or remote means. Conversely, data in transit can be intercepted, leading to potential breaches if adequate precautions are not implemented.
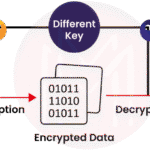
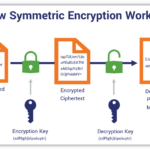
Encryption stands out as the cornerstone of contemporary data protection. It serves as a robust barrier, converting plaintext into ciphertext, rendering it incomprehensible to unauthorized individuals. Various encryption algorithms exist, each exhibiting distinct characteristics and suitability for specific contexts. Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) is widely recognized for its efficacy and is often employed to secure sensitive data at rest. Its symmetrical cryptographic design ensures rapid processing speeds while adhering to stringent security protocols.
The choice of encryption algorithm must be informed by an understanding of the potential threats and the necessary balance between performance and security. While AES is particularly effective in many scenarios, other forms, such as RSA or ECC (Elliptic Curve Cryptography), are preferable in different contexts, especially in encrypting data in transit due to their public-key infrastructure. However, this preference also requires proper key management, as compromised keys can render even the most sophisticated encryptions futile.
Key management itself warrants substantial investigation. It is of utmost importance in the realm of cryptography; the security of encrypted information is only as strong as the security of its keys. Vulnerable key storage, poor access controls, or lack of proper rotation policies can severely undermine even the most advanced encryption systems. Moreover, the advent of quantum computing poses an existential threat to current cryptographic standards, necessitating a profound re-evaluation of how sensitive data is encrypted and protected.
To compound these challenges, user behavior plays a critical role in data security. Human error remains one of the most significant vulnerabilities in any security framework. Phishing attacks, for example, exploit human psychology to gain access to secure systems and sensitive data. The proliferation of social engineering tactics further exacerbates the situation, leading to compromised data integrity and breaches. Consequently, comprehensive training and awareness programs are essential for individuals to recognize potential threats and practice prudent data management. This includes adopting rigorous password policies, utilizing multifactor authentication, and maintaining scepticism towards unsolicited communications.
Cloud computing has revolutionized data storage and accessibility, offering unprecedented flexibility and scalability. However, this transformation comes with inherent risks. When sensitive data is stored in the cloud, the responsibility for security becomes a shared mechanism between the service provider and the customer. It is imperative to rigorously vet service providers for their security protocols and compliance with regulatory standards. Data should be encrypted not only during transmission but also while housed on third-party servers. Deploying a comprehensive data protection strategy involves understanding the implications of a multi-cloud environment, where security measures must be uniformly applied across disparate systems.
Regulatory frameworks mandate further scrutiny and coherence in data management practices. An array of laws governs the collection, storage, and processing of sensitive information, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States. These regulations underscore the necessity of implementing robust security measures and facilitate a collective approach towards protecting individuals’ data rights. Organizations must therefore maintain compliance with these legal standards while continuing to evolve their strategies to mitigate emerging threats.
As organizations strive to secure sensitive data amidst growing uncertainties, the adoption of innovative technologies cannot be understated. Blockchain technology, initially synonymous with cryptocurrencies, offers promising avenues for data integrity and security. Its decentralized framework could revolutionize data sharing, rendering it more resistant to tampering and unauthorized access. Additionally, artificial intelligence can enhance data security by identifying patterns indicative of security breaches, thereby enabling predictive responses to evolving threats.
The dynamic interplay of technology, regulations, and human behavior ultimately shapes the landscape of data security. As digital antagonists develop increasingly sophisticated methods to infiltrate systems, the need for proactive and multifaceted security strategies becomes acutely evident. It is imperative for individuals and organizations alike to cultivate a culture of security awareness, utilizing advanced cryptographic techniques while remaining vigilant against the ever-evolving tapestry of threats that may arise.
In conclusion, securing sensitive data in an insecure world is not simply a technological challenge but a multifaceted endeavor that incorporates behavior, compliance, and innovation. Each layer, from encryption algorithms to user education, contributes to a holistic approach towards data security. Embracing this complexity, while remaining agile enough to adapt, is essential in navigating the volatile realm of information security and maintaining the sanctity of sensitive data.







Leave a Comment