In the modern digital landscape, where personal information often feels precariously vulnerable, the ability to encrypt and decrypt text stands as a guardian of privacy. This process is not just an exercise in technical prowess; it is a veritable art form that encapsulates the craft of cybersecurity. Engaging in encryption and decryption is akin to a performance by a cyber ninja, requiring agility, precision, and an understanding of the underlying mechanisms that protect information. This article delves into the intricacies of these processes, revealing the techniques that empower users to navigate the realms of confidentiality and data protection.
Understanding Encryption and Decryption
At its core, encryption is the process of transforming plain text into an unreadable format, known as ciphertext, utilizing algorithms and keys. This practice ensures that sensitive data is accessible only to individuals possessing the decryption key. Conversely, decryption is the reversal of this process, converting ciphertext back into its original form. The fundamental appeal of encryption lies in its ability to safeguard sensitive information against unauthorized access, thereby preserving individual privacy and enhancing security.
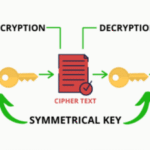
Two primary categories of encryption exist: symmetric and asymmetric. Symmetric encryption employs a single key for both encryption and decryption, which means that the same key must be meticulously shared between the communicating parties. In contrast, asymmetric encryption utilizes a pair of keys: a public key, which can be disseminated freely, and a private key, which must remain confidential. This differentiation serves as a foundation for understanding how to effectively maneuver through the world of cryptographic practices.
Tools of the Trade
To embark on the journey of encrypting and decrypting text, one must first assemble a robust arsenal of tools. A plethora of software solutions exist, ranging from user-friendly applications to command-line interfaces that cater to seasoned technologists. Programs such as GnuPG (GNU Privacy Guard) exemplify the capabilities of public key cryptography, enabling users to generate key pairs and encrypt files seamlessly. Moreover, OpenSSL is a powerful library that serves as both a versatile cryptographic toolkit and an essential resource for developers seeking to implement encryption in their applications. Understanding the strengths and limitations of each tool is critical for achieving one’s security objectives.
Implementing Encryption Techniques
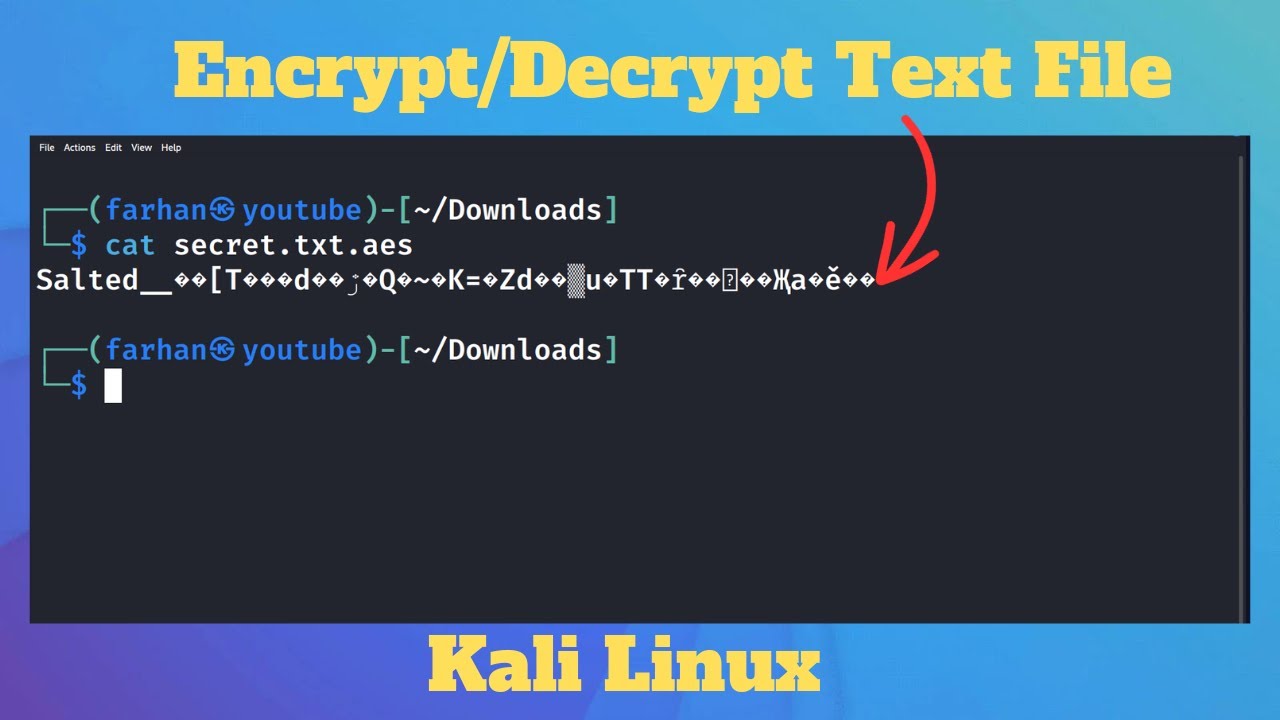
Once the tools are established, the next step involves employing practical techniques to secure text. A common method involves using the GnuPG command-line interface to encrypt a text file. For instance, executing the command ‘gpg -c filename.txt’ prompts the user to enter a passphrase, which is subsequently utilized to encrypt the file using symmetric key encryption. The result is a securely encrypted file, accessible only to those possessing the passphrase.
On the other hand, the decryption process is equally straightforward. The user can restore access to the plaintext by executing ‘gpg filename.txt.gpg’ and entering the correct passphrase. The simplicity of these commands belies the underlying complexity of cryptographic principles involved, illustrating how advanced techniques can be executed with both efficiency and elegance.
Code Examples
For practical application, consider the following examples that illustrate encryption using GnuPG. To encrypt a file named ‘secret.txt’, the command would appear as:
gpg -c secret.txtUpon execution, the program will prompt for a passphrase. This passphrase must be memorable yet complex enough to deter unauthorized decryption attempts.
Once encrypted, the file can be decrypted with the following command:
gpg secret.txt.gpgThis command once again calls upon the passphrase, further emphasizing the importance of crafting a strong, secure phrase that balances memorability with complexity.
Advanced Techniques: The Art of Key Management
The realm of encryption not only encompasses the methods of securing information but also the strategies for managing cryptographic keys. Efficient key management is a pivotal element that mitigates the risks of data compromise. It involves the generation, distribution, storage, and eventual revocation of keys, aligning with the principles of least privilege and segregation of duties. Implementing a system of public key infrastructure (PKI) can significantly enhance key management, providing a robust framework for validating identities and facilitating secure communications.
The Psychological Dimension of Cryptography
Beyond the technical aspects, the fascination with encryption and decryption is also psychological. There is an inherent allure in the idea of secrecy, the mystique surrounding the ability to cloak information from prying eyes. This emotional connection has likely propelled the growth of cryptographic practices. The challenges presented by deciphering encrypted data resonate with humanity’s long-standing relationship with codes and ciphers, harkening back to historical epochs where secrecy was paramount.
Real-World Applications
The implications of encryption and decryption extend far beyond individual privacy. They serve as bedrocks in various contexts, from secure communication in governmental transactions to safeguarding personal data in online banking. Furthermore, cryptography plays a crucial role in bolstering cybersecurity against the incessant threat of data breaches and cyberattacks. As digital landscapes evolve, the necessity for encryption becomes not merely advantageous but indispensable.
Conclusion: The Imperative of Enlightenment in Encryption
As we navigate the intricacies of the digital age, the importance of encryption and decryption cannot be overstated. Their role as guardians of privacy and security underscores the profound knowledge that can empower individuals and organizations alike. Engaging in these practices cultivates a deeper understanding of the digital world, ensuring that information remains safeguarded amidst an ever-increasing barrage of threats. Mastery of encryption techniques transforms one into a cyber ninja—fully equipped to tackle the challenges of information security with precision and agility.






Leave a Comment