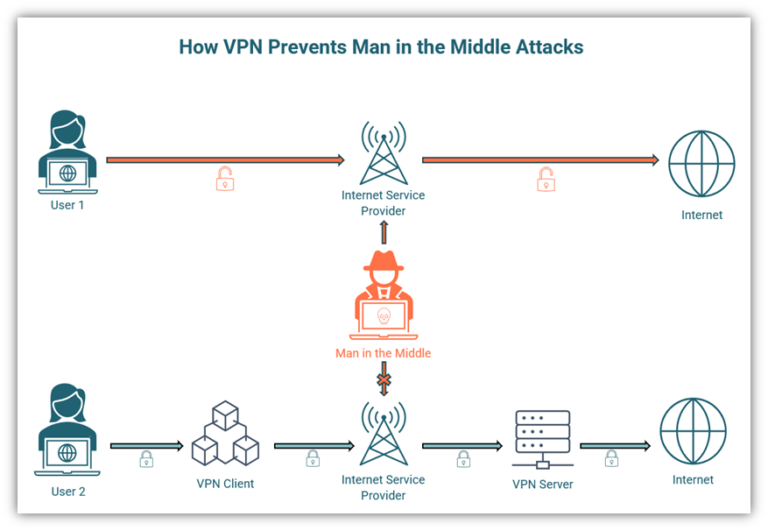
In the digital age, the prevalence of public Wi-Fi networks has revolutionized the way we connect to the internet. But, how secure are these connections really? Connecting to a public Wi-Fi network can feel like jumping into a pool without checking for water first. We often assume it’s safe, yet lurking beneath the surface are potential threats. One of the most pernicious threats is the man-in-the-middle (MitM) attack, where malicious actors intercept communications between two parties. This article delves into how Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) effectively mitigates such attacks, particularly in environments like public Wi-Fi, and addresses the challenges associated with its implementation.
The Mechanics of SSL
To grasp how SSL functions in thwarting MitM attacks, it’s crucial to understand the fundamental mechanics of this technology. SSL is a protocol that establishes an encrypted link between a web server and a browser, ensuring that all data passed between them remains private and integral. When a user accesses an SSL-secured website, their browser initiates a handshake process. This process involves the exchange of cryptographic keys that create a secure channel. The encryption ensures that even if data packets are intercepted by any unauthorized entities, they are rendered unreadable.
But how does this directly counter MitM threats? An imposter attempting to intercept the session cannot decrypt the information transferred between the server and the legitimate client without access to the encryption keys. Thus, the integrity of the communication is maintained. However, the success of this mechanism largely depends on users’ awareness and the proper implementation of SSL across websites.
Public Wi-Fi: A Breeding Ground for Man-in-the-Middle Attacks
Public Wi-Fi networks often lack the robust security measures found in private networks, making them ideal environments for MitM attacks. As users connect to these networks, they unwittingly expose themselves to potential spoofing, whereby attackers create rogue hotspots that mimic legitimate networks. Unsuspecting users connect, believing they are communicating securely, only to have their sensitive information harvested by malicious actors.
This situation raises a playful question: Would you trust a stranger’s claim to be an old friend in an unauthorized chat? In the digital realm, this analogy translates to trusting unverified Wi-Fi networks, where threats abound. Fortunately, SSL acts as a safeguard against such scenarios.
Implementing SSL: A Double-Edged Sword
Despite its effectiveness, implementing SSL is not without its challenges. Firstly, website owners must procure SSL certificates from trusted Certificate Authorities (CAs), which can involve a financial cost. Many businesses may perceive this as an unnecessary expense, particularly smaller enterprises or those operating on tight budgets. Additionally, maintaining an SSL certificate requires ongoing management to ensure it remains valid and effective.
Moreover, while SSL significantly bolsters security, it is not a panacea. Users still need to exercise due diligence by ensuring that they are interacting with SSL-enabled websites. The presence of HTTPS in the URL is a primary indicator of a secure connection. However, even savvy users can fall prey to sophisticated phishing attacks where attackers disguise malicious URLs as genuine. Consequently, user education around recognizing secure sites is paramount.
Advantages Beyond Security
The implementation of SSL extends beyond merely enhancing security against MitM attacks. Websites employing SSL often experience improved search engine rankings, as search engines like Google prioritize sites with HTTPS over those without. This preferential treatment can lead to increased traffic and enhanced user trust. In a world where consumers are becoming increasingly conscientious about their privacy, demonstrating a commitment to safeguarding user data can set businesses apart.
Moreover, SSL is often correlated with comprehensive cybersecurity measures. Websites that prioritize SSL typically engage in better security practices overall, beyond just encryption. These include regular vulnerability assessments, timely software updates, and fostering a culture of cyber hygiene. As such, the commitment to SSL can catalyze broader security improvements within an organization, enhancing overall resilience against various cyber threats.
Navigating Challenges: The Role of User Education
Combating MitM attacks effectively demands a collective effort between technology implementation and user awareness. It is insufficient for businesses to simply install SSL certificates; they must also cultivate a security-conscious environment. Engaging users through educational resources about the importance of recognizing secure connections and avoiding untrusted networks is vital. Conducting training and awareness campaigns can empower users, making them less vulnerable to the subtleties of social engineering tactics often employed in hacking attempts.
The Future of SSL in a Changing Digital Landscape
As technology evolves, so too will the tactics of cybercriminals. The longevity of SSL as an effective defense against MitM attacks will depend on its continued adaptation to emerging threats. Innovations such as Transport Layer Security (TLS) continue to evolve from SSL, offering enhanced encryption protocols to keep up with more sophisticated attack vectors.
Conclusion
The threat posed by MitM attacks, particularly in places like public Wi-Fi networks, underscores the necessity of SSL in today’s interconnected environment. Secure connections not only protect sensitive information but also foster trust between consumers and providers. While the implementation of SSL presents challenges, its benefits far outweigh the drawbacks. The combination of robust technology and user vigilance offers a viable route to mitigating the risks associated with insecure communication. As we navigate an increasingly digital world, ensuring safety through SSL remains indispensable.






Leave a Comment