In an era where data breaches and cyber threats loom ominously, one wonders: how do websites ensure their visitors’ information remains confidential and secure? The answer to this pivotal question often lies in the implementation of SSL (Secure Socket Layer) certificates. These digital certificates are crucial in establishing a secure connection between a user’s browser and the server hosting the website. This article delves into the intricate workings of SSL certificates, elucidating the ways in which they effectively lock down websites against various cyber threats.
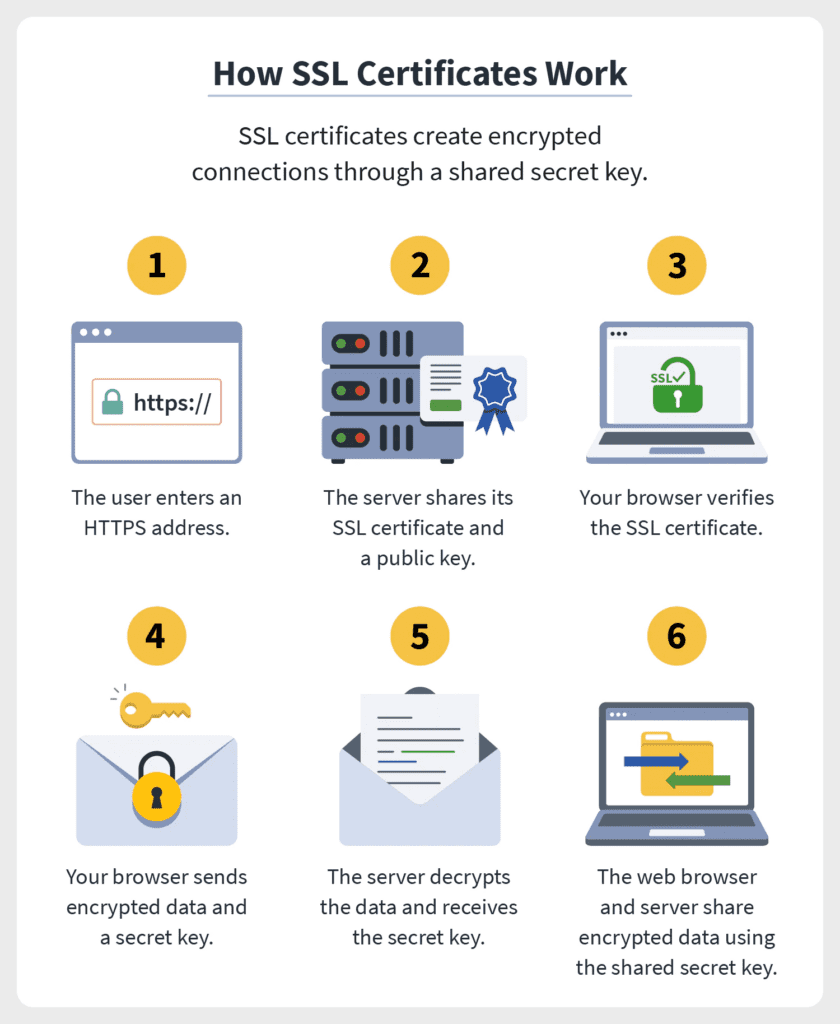
To understand the mechanism of SSL certificates, it’s essential to first explore the nature of web traffic. When a user sends information online—be it personal details, credit card information, or login credentials—this data traverses through multiple networks, all of which are potentially susceptible to interception. Without a protective mechanism, sensitive information is exposed to cybercriminals who could exploit it for nefarious purposes. Herein lies the fundamental purpose of SSL certificates: they encrypt the data being transmitted, creating a secure channel that is impervious to eavesdroppers.
The encryption process begins when a user attempts to connect to a website. This request prompts the server to respond with an SSL certificate, which contains crucial information, including the website’s public key and details about the entity that owns the website. This public key plays a vital role in the encryption process. Upon verifying the SSL certificate, the user’s browser generates a session key for encryption, ensuring that all subsequent data transmissions are securely encoded. Thus, even if an unauthorized party attempts to intercept the data, it would be rendered incomprehensible without the corresponding decryption key.
Another pivotal question arises: how can users ascertain that a website is utilizing SSL? The presence of “HTTPS” in the website’s URL, as opposed to “HTTP,” is a clear indicator of an active SSL certificate. Additionally, most modern web browsers provide visual cues, such as a padlock icon in the address bar, signaling that the connection is secure. These discernible indicators not only bolster user confidence but also foster trust between the website and its visitors. When users see these signs, they can better understand that their data is being handled with care and secured by stringent protocols.
However, the challenge of maintaining this security does not end with acquiring an SSL certificate. Cyber threats continue to evolve, necessitating vigilant practices. One significant issue is the potential for SSL certificates to become outdated. Typically, certificates must be renewed every one to two years, depending on the issuing authority. Neglecting to update an SSL certificate could result in error messages displayed to users, warning them of potential security threats and deterring them from proceeding further. Thus, website administrators must remain diligent in monitoring the status of their certificates and implementing timely renewals.
Moreover, while SSL encryption safeguards data during transmission, it does not automatically protect against all forms of cyber attacks. For instance, cross-site scripting (XSS) and SQL injection are common vulnerabilities that SSL cannot mitigate. XSS attacks exploit weaknesses in the website’s code, allowing attackers to inject malicious scripts that can capture sensitive data or manipulate user behavior. Similarly, SQL injection attacks target the database of an application, enabling unauthorized access to confidential information. To counteract these threats, website owners must adopt a comprehensive security strategy that encompasses secure coding practices, regular software updates, and vulnerability assessments.
The implications of not utilizing SSL certificates extend further, encompassing reputational damage alongside data breaches. In a digital landscape saturated with competition, maintaining a solid reputation is imperative for online businesses. Users are increasingly astute; they actively seek secure environments, which means that websites lacking SSL certificates may deter potential customers. Studies indicate that users feel more comfortable providing personal information to sites that are marked as secure. Therefore, not only do SSL certificates serve a protective function, but they also play a pivotal role in the credibility of a website.
Interestingly, the deployment of SSL has evolved beyond merely securing user information. It now acts as an essential component of search engine optimization (SEO) strategies. Major search engines, including Google, consider SSL security as a ranking factor. Websites equipped with SSL certificates are often afforded higher search rankings, thereby increasing visibility and attracting more visitors. This shift emphasizes how security and digital marketing intersect, shaping how businesses approach their online presence.
While SSL certificates are instrumental in locking down websites, one must not overlook the potential challenges associated with their implementation. From costs to management issues, these factors can complicate a business’s online security measures. However, the value of protecting sensitive data and ensuring user trust far outweighs the challenges presented. Investing in SSL certificates is not merely a technical requirement but a necessary commitment to ethical online behavior, embodying the principles of data protection.
In conclusion, SSL certificates serve as a critical foundation in the effort to secure online interactions. By encrypting data, authenticating the identity of website owners, and fostering user trust, they play a vital role in protecting sensitive information in an increasingly perilous digital environment. The continuous advancement of cyber threats underscores the importance of staying abreast of best practices in web security. As we navigate this complex landscape, understanding the pivotal functions of SSL certificates illuminates their necessity in ensuring a secure online experience for all.







Leave a Comment