As we traverse this brave new world of technological advancement, have you ever pondered how secure your personal information truly is? In an age where information is both a commodity and a target, the necessity of robust means to protect data has never been more pronounced. Encryption emerges as a formidable guardian in this landscape, allowing individuals and organizations to protect sensitive information from prying eyes. This article elucidates the multifaceted role of encryption in safeguarding personal and professional data in the digital age while also addressing the intricacies that accompany its use.
To understand the pivotal role encryption plays, one must first grasp the foundational concept of data security. In essence, data security encapsulates measures taken to safeguard digital information from unauthorized access, corruption, or theft. Among the arsenal of tools available to achieve security, encryption stands out due to its dual purpose: it not only renders data unreadable to unauthorized entities but also ensures that the intended recipients can access this information seamlessly.
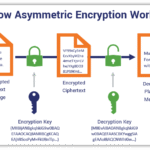
Encryption operates on the principle of transforming readable data, also known as plaintext, into an unreadable format dubbed ciphertext. This transformation employs an algorithm and a key. The only way to convert ciphertext back into plaintext is through the application of the corresponding decryption key. This essential component raises an intriguing challenge: what happens when you lose that key? The intricacies of key management are a vital aspect of encryption, warranting careful consideration and strategic planning.
One of the most salient benefits of encryption lies in its ability to protect data in transit. With the soaring prevalence of cloud computing, personal and sensitive information often traverses vast digital networks. When you send an email or submit personal information on a website, encryption acts as a sentry, ensuring that even if the data is intercepted, it remains inscrutable to any entities without authorization. For instance, protocols such as TLS (Transport Layer Security) encrypt data during transmission, bolstering the integrity of communication channels considerably. However, this also leads us to another question—how often do individuals verify whether the websites they use employ these protocols effectively?
Moreover, encryption serves as a bulwark for data at rest. Data stored on devices, whether personal laptops, smartphones, or enterprise servers, can be targeted by hackers or malicious software. Full-disk encryption (FDE) technologies enable users to protect the entirety of their hard drives or specific files. This level of encryption ensures that even if a device is stolen or compromised, the data contained within remains inaccessible without the appropriate key. Nevertheless, the implementation of such encryption mechanisms invites scrutiny: how can companies and individuals balance the need for security with the potential for data accessibility issues?
Yet, while encryption is a powerful ally in the fight against digital threats, it is not without its limitations and challenges. One substantial concern is the potential for misuse by nefarious actors. Criminals can exploit encryption to conceal their activities, which has led to heated debate among policymakers regarding “backdoors.” These backdoors would allow law enforcement agencies to bypass encryption in certain scenarios, yet they also threaten the privacy and security of law-abiding citizens. This dichotomy begs the question: how can authorities strike the right balance between security and privacy without compromising the integrity of encryption?
Moreover, encryption is not impervious. Advances in computational technology, particularly with the advent of quantum computing, pose significant threats to traditional encryption algorithms. As quantum computers evolve, they may possess the capability to decipher current encryption methodologies, rendering them obsolete. In light of this, organizations and individuals must remain vigilant and proactive in adopting post-quantum encryption techniques to future-proof their data security. This brings forth an additional challenge—how can stakeholders stay abreast of cryptographic advancements while implementing resilient security practices?
Education and awareness also play crucial roles in ensuring that encryption serves its purpose effectively. Users need to familiarize themselves with encryption technologies and best practices. A common misconception is that merely using encryption tools suffices for complete protection. However, the effectiveness of encryption is contingent upon proper implementation, regular updates, and understanding the nuances of key management. This requires a comprehensive strategy that embraces continual learning and adaptation to emerging threats.
In conclusion, encryption serves as a cornerstone in the realm of data security, illuminating pathways to protect sensitive information in an increasingly digital landscape. Its ability to secure data in transit and at rest offers a robust framework for protecting personal and organizational data. However, challenges surrounding key management, the potential for misuse, and emerging technological threats underscore the complexities inherent in encryption. A proactive approach that encompasses education, awareness, and compliance with developments in the cryptographic landscape is imperative for safeguarding our sensitive information. As we continue to navigate the complexities of the digital age, the role of encryption remains paramount—an enduring shield against the relentless tide of cyber threats.







Leave a Comment