The nexus of blockchain technology and public key cryptography constitutes a compelling intersection of innovation and security. In a digital landscape fraught with threats, the ability to verify and secure transactions without the need for a central authority is a revolutionary aspect of blockchain. This article delves into the mechanics of how blockchain employs public key cryptography, unraveling the intricacies that contribute to its allure and utility.
At its essence, blockchain operates as a decentralized ledger, where each transaction is immortalized in a chronologically ordered chain of blocks. This decentralized approach enhances transparency and minimizes the likelihood of data tampering, yet it raises an inevitable question: how does the technology ensure that only the rightful owner can access or transfer assets? Here, the principles of public key cryptography come into play.
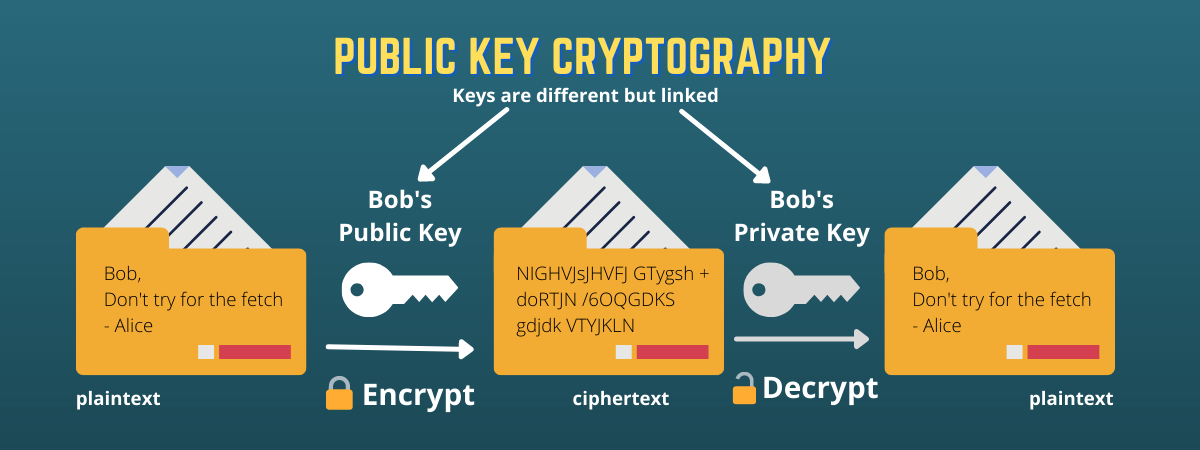
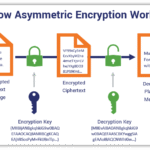
Public key cryptography, also known as asymmetric cryptography, utilizes a pair of keys: a public key and a private key. The public key is disseminated widely, while the private key remains confidential, known only to its owner. This bifurcation of keys is pivotal, enabling secure transaction verification. When a user wishes to initiate a transaction on the blockchain, they sign it digitally using their private key. This signature acts as a unique identifier that validates the authenticity of the transaction and confirms the user’s consent.
Upon receiving the transaction, nodes on the network can use the corresponding public key to verify the digital signature. If the signature matches the information encapsulated in the transaction, it demonstrates that it was indeed the holder of the private key who initiated the transaction. This verification process is both swift and efficient, ensuring that transactions can be processed in real-time while maintaining a high level of security.
One of the notable advantages of this system is that it eliminates the need for a central authority or intermediary. Traditional financial systems typically rely on a third party—such as a bank—to authenticate transactions. This reliance can foster inefficiencies and introduce vulnerabilities. In contrast, the decentralized architecture of blockchain, fortified by public key cryptography, empowers individuals to transact directly, enhancing the system’s resilience against fraud and unilateral control.
However, the elegance of this cryptographic framework does not come without its nuances and challenges. While public key cryptography enables secure transactions, the security of an individual’s assets is inherently tied to the protection of their private key. Should this key be compromised or lost, the user risks relinquishing control over their funds. Consequently, the responsibility of safeguarding private keys cannot be understated, as the ramifications of their loss are irrevocable in a blockchain context.
In the backdrop of these practical considerations lies a deeper exploration into the nature of trust in digital transactions. Blockchain, through the employment of public key cryptography, shifts the paradigm of trust away from centralized institutions towards cryptographic verification. This evolution is significant, as it potentially redefines our understanding of accountability in the digital age. One could argue that this paradigm shift fosters a greater reliance on technology itself rather than on human institutions, a fascinating commentary on the evolving relationship between society and technology.
Moreover, the allure of blockchain and its cryptographic underpinnings extends beyond mere transactional efficiency. It opens doors to myriad applications across various sectors, be it finance, supply chain management, or even social activism. By leveraging public key cryptography, innovators are crafting decentralized applications that promote trustless interactions, ultimately spawning a new ecosystem that challenges traditional norms.
However, it is crucial to address the technological dichotomy present in the world of blockchain. While the principles underpinning public key cryptography offer robust security, they also present unique vulnerabilities. For instance, advancements in quantum computing threaten to upend the foundations of current cryptographic protocols. Theoretically, a sufficiently advanced quantum computer could break traditional cryptographic schemes in relatively short timeframes, thereby posing significant risks to blockchain systems reliant on current public key frameworks. Such considerations evoke a pressing call for the evolution of cryptography itself to safeguard the future of blockchain technology.
Furthermore, the philosophical implications of public key cryptography integrated within blockchain merit examination. The democratization of secure transactions signifies a shift towards greater autonomy for individuals, challenging conventional power dynamics. In a world rife with surveillance and control, the idea that individuals can secure their assets and identities through cryptographic means is inherently empowering. This burgeoning autonomy invites further discourse on the ethical ramifications of such technologies and their potential to disrupt societal structures.
In summary, the intertwining of blockchain and public key cryptography is not just a tale of technological innovation. It embodies a profound exploration of trust, autonomy, and potential disruption. As transaction verification and security become paramount in today’s digital economy, the role of public key cryptography will undoubtedly continue to evolve. With its capacity to forge trustless interactions, catalyze decentralized applications, and define our understanding of identity in the digital realm, the fascination surrounding this technology is as multifaceted as the challenges it presents.
Consequently, ongoing discourse and research into the realms of encryption and blockchain technology are essential. Indeed, as we continue to traverse this digital frontier, understanding the profound implications of public key cryptography remains critical for harnessing its transformative potential and navigating the intricate landscapes it creates.






Leave a Comment