In an era where the digitization of information reigns supreme, the concept of digital signatures has emerged as a key component within the blockchain technology framework. The allure of digital signatures lies not merely in their functional capacity to validate electronic documents, but in their inherent ability to ensure security, authentication, and integrity in an increasingly interconnected digital landscape.
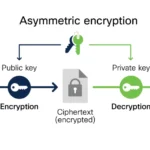
The mechanism of a digital signature is grounded in cryptographic principles, primarily employing asymmetric cryptography. This technique involves the utilization of a pair of keys: a private key, which is kept secret by the signer, and a public key, which is disseminated for validation purposes. The digital signature operates similarly to a handwritten signature, but with a degree of security and authenticity that the latter cannot guarantee.
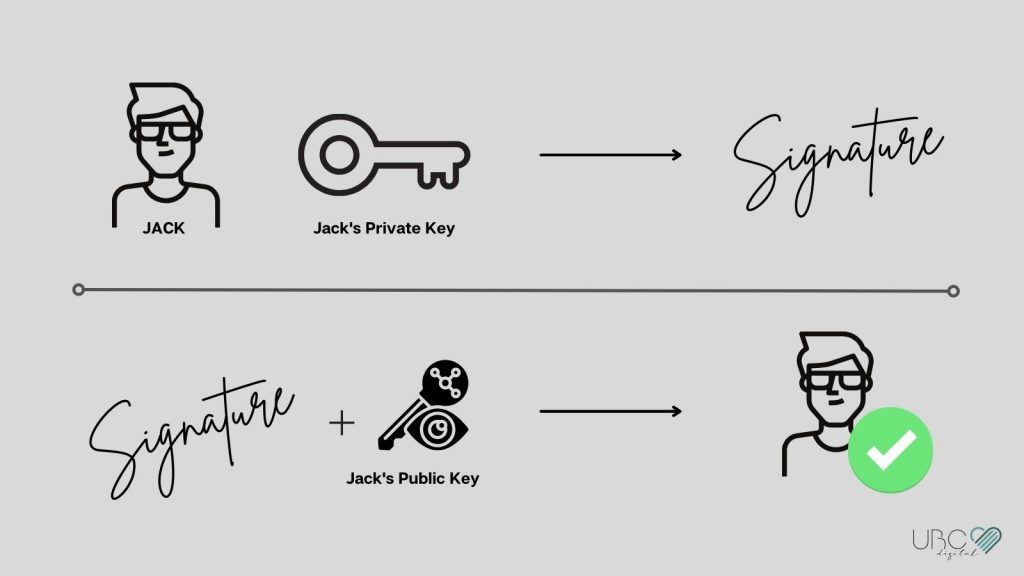
To understand how digital signatures function, it is imperative to examine the steps involved in their creation. When a sender wishes to sign a digital document, they first generate a hash of the document using a cryptographic hash function. This hash serves as a unique representation of the document’s content. Subsequently, the sender encrypts this hash with their private key, resulting in a digital signature that is unique to both the document and the signer.
Upon receiving the signed document, the recipient can verify its authenticity by employing the sender’s public key to decrypt the signature, yielding the original hash. Simultaneously, the recipient computes the hash of the received document. If the computed hash matches the decrypted hash from the signature, it is established that the document has not been altered and that the sender’s identity is authentic. This verification process fortifies the integrity of transactions and communications across blockchain networks.
In the context of blockchain, digital signatures assume a pivotal role. Every transaction on a blockchain is associated with a digital signature, which not only provides evidence of consent by the transaction initiator but also contributes to the overall immutability of the blockchain. Once a transaction is confirmed and added to a block, it becomes part of a distributed ledger that is virtually impervious to tampering. The interconnectedness of blocks ensures that altering any information requires an insurmountable amount of computational power, making fraud effectively impractical.
The importance of digital signatures extends beyond mere transactional integrity; they also facilitate trust within decentralized systems. In traditional systems, a trusted third-party intermediary is often required to verify the authenticity of documents or transactions. However, blockchain technology disintermediates this process by enabling peer-to-peer transactions that rely solely on digital signatures. This transition represents a paradigm shift in how trust is established in digital ecosystems.
The fascination surrounding blockchain and digital signatures further stems from their potential to disrupt various sectors, from finance to supply chain management. For instance, in the finance domain, digital signatures allow for secure and efficient transactions without the need for banks or other financial institutions. This democratization of finance paves the way for broader access to financial services, particularly in underbanked regions.
Similarly, in supply chain management, verifying the authenticity of goods and their origins can enhance transparency and reduce fraud. By employing blockchain technology combined with digital signatures, businesses can trace products from their inception to delivery, assuring consumers of authenticity and compliance with legal standards. This amalgamation of technology fosters consumer trust and loyalty, which is paramount in today’s marketplace.
Despite the evident advantages of digital signatures and blockchain technology, there remains a layer of complexity that can perplex stakeholders. One common observation is the skepticism surrounding the perceived lack of regulation within decentralized systems. While the absence of a central authority can facilitate innovation, it also raises concerns about accountability, especially in cases of disputes. The inherent challenge lies in addressing these concerns without undermining the decentralized ethos that makes blockchain appealing.
Moreover, the security of digital signatures, although robust, is not infallible. Advances in quantum computing could potentially jeopardize the cryptographic algorithms underpinning digital signatures, necessitating the development of quantum-resistant cryptographic standards. This evolving landscape underscores the importance of continuous research and adaptation within the field of cryptography to safeguard digital signatures against future vulnerabilities.
Ultimately, the fascination with digital signatures and blockchain technology can be attributed to their profound implications for the future of secure and trusted digital interactions. As digital signatures continue to power blockchain, they not only enhance transactional security but also challenge conventional notions of trust and authority in various industries. The evolution of this technology embodies a paradigm shift—a movement towards a more decentralized, secure, and transparent digital milieu.
In conclusion, digital signatures play a vital role in the blockchain ecosystem by ensuring authenticity, integrity, and non-repudiation. Their integration with blockchain technology heralds a new era of digital transactions, fostering a decentralized landscape where individuals can engage with one another with increased trust and reduced reliance on third-party authorities. As this technology advances, its implications for various sectors will continue to unfold, marking significant strides toward achieving a more secure and transparent world.




Leave a Comment