In the vast expanse of the digital universe, where information flows unabated like an uncharted river, the need for security arises as a formidable lighthouse amidst the looming fog of threats. This beacon, known as Secure Sockets Layer (SSL), serves as both guard and guide, illuminating the pathways through which sensitive data traverses. Understanding the intricate mechanisms of how SSL empowers HTTPS can be likened to deciphering the arithmetic of a well-concealed treasure map, where each element must be understood to unveil the prize of secure communication.
At its core, HTTPS, which stands for Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure, is an extension of HTTP. Yet, it is fortified with SSL/TLS protocols that develop a robust framework for encrypting messages between users and websites. Envision a ziggurat, constructed brick by brick, where every layer represents a critical stage in securing information as it ascends toward its destination. SSL acts as the talented architect orchestrating a seamless blend of pivotal elements: authentication, encryption, and data integrity. Each plays a quintessential role in ensuring that the information remains unscathed and trustworthy against potential interlopers.
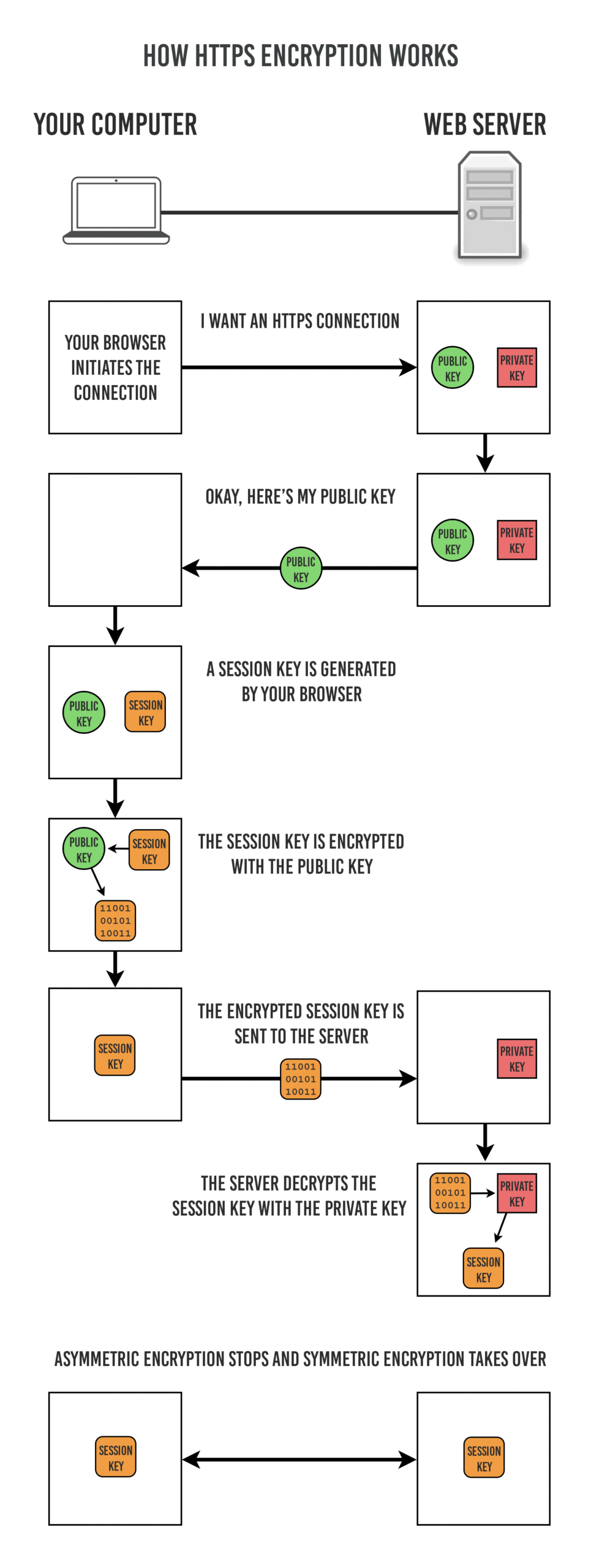
The funds of trustworthiness are established through a perceptible triad: the public key infrastructure (PKI). Picture it as an elaborate garden where certificates bloom—a digital flora representing the entities involved in communication. A fundamental aspect of PKI is the digital certificate, serving as a digital passport issued by a Certificate Authority (CA). This authority stands as a custodian, credentialing identities within the garden. When a browser initiates a secure session, it first requests the server’s certificate. Only when the browser verifies the validity of this certificate does it trust the navigating path ahead.
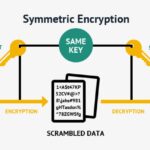
Once trust is established, SSL gallantly ushers in the encryption process, wrapping data in layers akin to the nesting of protective shells around fragile eggs. Applying cryptographic techniques, SSL establishes a secure session using symmetric encryption, a method where a common key shared between the server and the client illuminates the pathway. This key facilitates rapid encapsulation of data packets, rendering them unintelligible to any third party who dares intrude upon the channel’s sanctity.
The heart of SSL’s enchanting opera is rooted in the handshake process, where the server and client perform a series of orchestrated gestures to communicate intentions and capabilities. The handshake begins with the client sending a “Hello” message, expressing its desire to establish a secure connection. The server reciprocates with its own “Hello,” attached with the digital certificate previously discussed. As this interaction unfolds, the client engages in an evaluation of the server’s credentials, above and beyond mere visual verification; cryptographic algorithms validate the server’s integrity, an art of verification discreet yet indispensable.
Upon the successful verification of the certificate, the session keys negotiated between the client and server grant them entry into a privileged chamber where information is maintained in secrecy. The usage of ephemeral keys during this stage adds another layer of sophistication, ensuring that even if one key were compromised, the integrity of past communications remains intact—much like a vault where keys are changed with every heist, minimizing potential losses while maximizing security. This dynamic nature of key exchange enriches the landscape of online communication, offering ephemeral guarantees in a world saturated with persistent threats.
Furthermore, data integrity remains paramount in the domain of SSL. Each data packet is syntactically sealed with a message authentication code (MAC), a cryptographic checksum verifying that the transmitted information remains untouched. Picture it as a secure seal affixed to an envelope containing secrets. If a rogue element dares to tamper with the envelope, the seal shatters, alerting both the sender and receiver to the breach. This meticulous attention to detail underpins the efficacy of SSL, ensuring that the sanctity of the information is upheld throughout its voyage.
The advantages of employing SSL are manifold. Users are often bestowed with the visual assurance of a padlock icon in their browser’s address bar—a symbol of security that transcends mere aesthetics. This emblem generates trust, inviting users to engage in online transactions with confidence and ease. Moreover, search engines prioritize websites fortified with HTTPS, enhancing visibility amidst the cacophony of competitors vying for the attention of digital wanderers. Thus, SSL fulfills an essential societal need, fostering an ecosystem where secure communications blossom and flourish.
As we draw closer to understanding the profound implications of SSL and HTTPS, it is imperative to acknowledge the ongoing arms race between security experts and malicious actors. Cyber threats evolve analogous to shape-shifters, cunningly attempting to bypass the meticulous constructs of SSL. Consequently, internet security becomes a perpetual cycle of innovation and adaptation, challenging those who pursue safe passage through the nebulous realms of cyberspace to remain vigilant. Regular updates and upgrades to encryption standards, much like the continuous fortifications of a castle, are essential in this relentless struggle.
In conclusion, the enigma that is SSL and HTTPS unfolds not merely as a collection of technicalities but as a fundamental facet of the digital experience. As the cogs of this intricate mechanism turn, they ensure that every piece of information traversing the sprawling web is cloaked in a veil of protection. It resonates as a narrative of trust, innovation, and unwavering diligence, echoing through the frames of our connected existence. In this age of digital interconnectedness, SSL stands as a crucial sentinel, guarding the gates to the realms of secure communication.






Leave a Comment