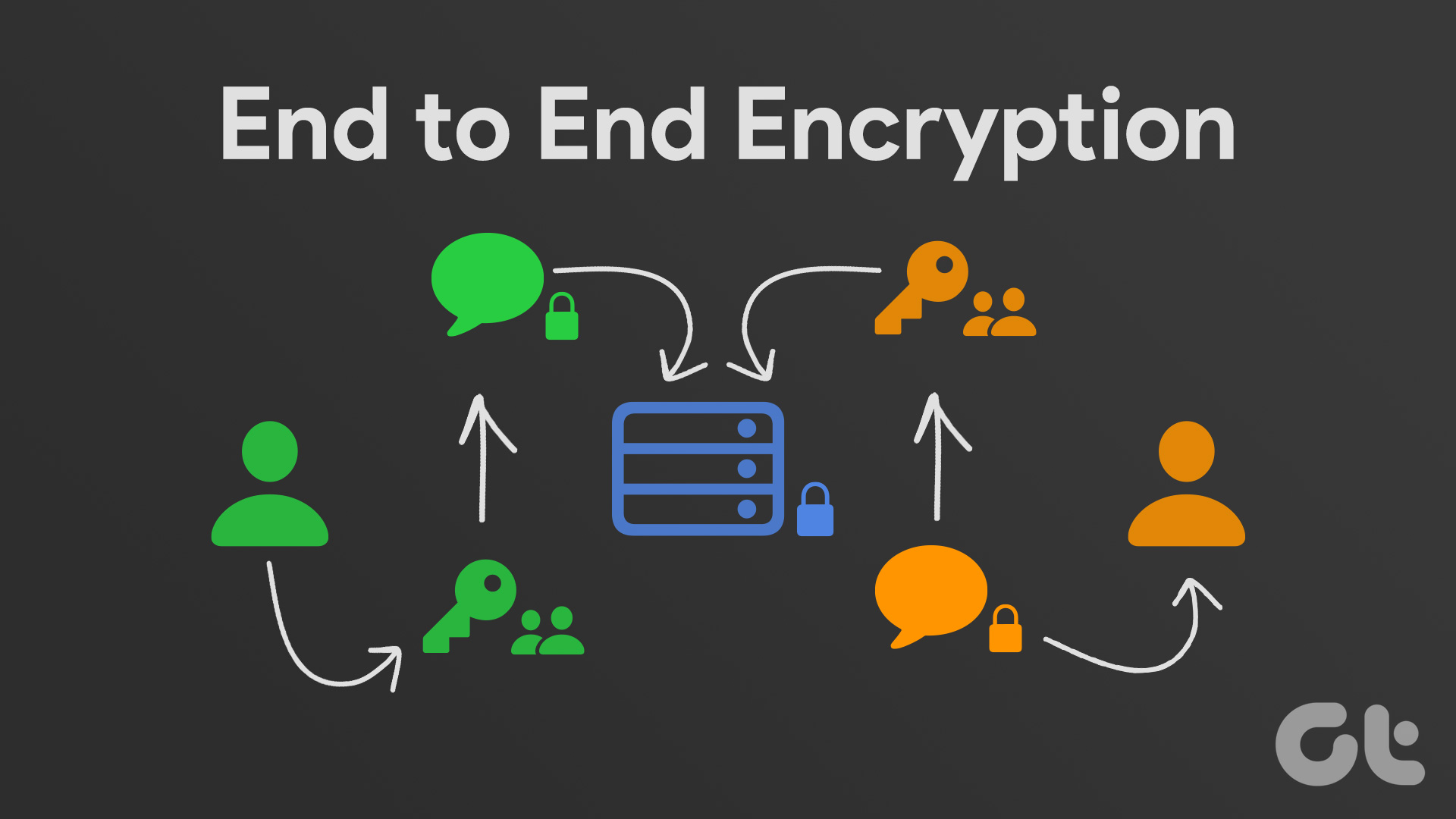
In a digital world teeming with data, the concept of End-to-End Encryption (E2EE) emerges as a fortress, safeguarding the citadel of our personal communications from prying eyes. It is akin to sending a meticulously crafted message contained within a bottle, where only the intended recipient possesses the key to unlock its secrets. This method of data protection garners fervent support and criticism alike, evoking vivid debates that intertwine privacy, security, and the implications for society. This article explores the multifaceted arguments for and against End-to-End Encryption, delving into the complexities that define this cryptographic safeguard.
The Bastion of Privacy
Advocates argue that E2EE fortifies individual privacy in an age where data breaches and mass surveillance loom large. Personal privacy stands as a fundamental right, and for many, E2EE embodies an essential bulwark against unauthorized access. Just as a locked diary contains intimate thoughts that remain concealed from prying eyes, E2EE ensures that messages and files shared between individuals are shielded from potential eavesdroppers.
The allure of E2EE lies in its capacity to offer unparalleled confidentiality. When data is encrypted at the source, only the sender and receiver possess the decryption keys, preventing intermediaries—be it corporations or government entities—from intercepting or deciphering the information. This architecture fosters a sense of autonomy, allowing individuals to communicate without fear of scrutiny. Furthermore, this confidential environment encourages free expression, enabling users to engage in discussions that may be sensitive or controversial without the apprehension of surveillance.
Protection Against Cyber Threats
In an era rife with cybersecurity threats, E2EE presents a formidable defense against malicious actors. Cybercriminals continually refine their strategies, deploying sophisticated tools to corrupt, steal, or manipulate sensitive information. E2EE serves as a deterrent to such nefarious endeavors, ensuring that even if data is intercepted, it remains unintelligible to the aggressor. The metaphor of a digital drawbridge effectively encapsulates this point: while intruders may approach the gates, the encrypted information remains secure behind an impenetrable barrier.
This is particularly salient in the context of business communications and sensitive transactions. Organizations often exchange proprietary information, client data, or financial details that, if compromised, could lead to substantial losses. By implementing E2EE, businesses can protect their intellectual capital, securing a competitive advantage while also maintaining stakeholder trust.
The Dilemma of Regulation and Law Enforcement
However, the advocacy for E2EE is not without its complications. Critics argue that as society grapples with crimes ranging from cyberbullying to terrorism, E2EE poses significant challenges for law enforcement. The very attribute that protects individual privacy can also obstruct justice. Imagine a scenario where encrypted communications conceal the plans of nefarious actors; the cloak of protection shields the guilty from accountability. This presents a conundrum: can the right to privacy coexist with the imperative for public safety?
Opponents advocate for a balanced approach, suggesting modified encryption models that allow for lawful access under regulated circumstances. The notion of “backdoors” has been proposed as a solution, granting authorities the ability to decrypt messages during investigations. Yet, the implementation of such measures raises a panoply of concerns. By creating vulnerabilities for law enforcement, one inadvertently invites exploitation by cybercriminals, effectively undermining the integrity of E2EE.
The False Sense of Security
Another argument against E2EE revolves around the psychological implications of perceived security. Individuals may develop a false sense of invulnerability, believing that their communications are impervious to breaches solely because they rely on E2EE technologies. This complacency can lead to negligence in employing other security measures, such as strong passwords or two-factor authentication. Furthermore, users may unwittingly expose themselves to phishing attacks or malware, believing incorrectly that encryption alone provides comprehensive protection. Thus, while E2EE is a stalwart component of digital security, it is not a panacea.
Implications for Technological Innovation
Moreover, the debate surrounding E2EE raises fundamental questions about technological innovation and accountability. As companies innovate and develop new platforms employing E2EE, they often face scrutiny over their responsibility to ensure user compliance and security. The evolving landscape poses dilemmas that compel organizations to strike a balance between fostering innovation while adhering to ethical standards. Encouragingly, many tech firms are increasingly prioritizing privacy by design, embedding E2EE as a core feature in their offerings.
However, as public trust in digital communications wanes, the need for transparent practices grows more pressing. The ultimate challenge resides in creating frameworks that enable data security without severing the threads of accountability. Balancing privacy with regulatory oversight may lead to innovative solutions that secure freedoms without compromising safety.
Conclusion: Navigating the Future of Privacy
End-to-End Encryption stands at the nexus of privacy, security, and societal responsibility. The arguments both for and against E2EE unveil a complex tapestry, woven with threads of individual rights, public safety, and accountability. As we traverse the digital landscape, the commitment to safeguarding our communications must not come at the expense of advancing justice or innovation. The discourse surrounding E2EE is not merely academic; it shapes the framework of modern communication and how society navigates the intricacies of its digital existence. Balancing these concerns may lead to a collaborative practice that honors the sanctity of privacy while responding effectively to the necessities of law enforcement. The journey towards a secure digital future demands thoughtful consideration—an endeavor requiring the collective wisdom of all stakeholders involved.







Leave a Comment