As we navigate through the digital landscape, have you ever pondered the intricacies of how your online information remains secure? The realm of cybersecurity presents an ongoing challenge for individuals and organizations alike, where digital threats lurk at every corner. One of the fundamental mechanisms in this defense system is encryption. This article delves into the significance of encryption as a bulwark against cyber invasions, illustrating its necessity in contemporary network security frameworks.
Encryption serves as a method of encoding data, transforming it into an unreadable format unless accessed with the correct decryption key. At its core, this technique ensures that even if malicious actors intercept data, the information remains indecipherable and, thus, secure. Consider a scenario in which sensitive documents are transmitted over a network without encryption. Any potential intruder could easily access and exploit this information, leading to breaches of privacy and significant damages. Here, the efficacy of encryption becomes abundantly clear.
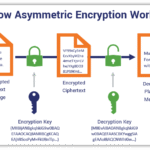
One of the most common forms of encryption is symmetric encryption. This involves the use of a single key for both encryption and decryption processes. While this technique may be computationally efficient, its primary drawback lies in key management. If the key falls into the wrong hands, the entire encryption system is compromised. Counterbalancing these challenges is the asymmetric encryption method, which employs a pair of public and private keys. In this paradigm, the public key encrypts the data, while the private key, kept secret, decrypts it. This duality exemplifies the intricate dance of security wherein both accessibility and protection play pivotal roles.
As organizations continue to implement encryption across their networks, a critical question arises: how can they effectively safeguard their encryption keys? Even the most robust encryption relies on the security of its keys. Solutions range from hardware security modules (HSMs) to advanced key rotation policies that limit the exposure of any given key over time. Failure to adequately protect these keys could result in catastrophic breaches, nullifying the benefits of encryption.
Furthermore, it is essential to highlight the growing sophistication of cyber threats. Ransomware attacks, for instance, involve encrypting a victim’s files, locking them out until a ransom is paid. This not only showcases how encryption can be wielded against innocents, but it also reinforces the necessity for proactive measures in digital defense. Regularly updating encryption protocols, employing multi-layered defense strategies, and maintaining vigilant monitoring systems are indispensable in fortifying networks against such crimes.
Moreover, the advent of quantum computing poses an emerging challenge to current encryption methods. Quantum phenomena enable attackers to leverage incomprehensibly powerful computational capabilities, potentially rendering traditional encryption ineffective. As a consequence, researchers are exploring quantum-resistant algorithms, anticipating a future where encryption must evolve to outpace these groundbreaking advancements. The landscape of digital security is indeed fluid; organizations must remain cognizant of these shifts and adapt accordingly.
Additionally, regulatory requirements add another layer of complexity to the encryption conversation. With data privacy laws swirling around the globe—from the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe to the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA)—organizations are compelled to adopt rigorous encryption measures to remain compliant. Non-adherence not only invites legal repercussions but also damages consumer trust, illustrating that encryption is pivotal not just for security, but for foundational business integrity.
In practical terms, implementing encryption goes beyond merely selecting a protocol. It entails comprehensive training for employees to recognize and thwart potential threats. Even the most advanced encryption systems can be ineffective against human error. Cultivating a culture of cybersecurity through ongoing education, simulated phishing exercises, and transparent communication is essential in creating a formidable defense mechanism that complements technological solutions.
As we develop these fortified systems, the question persists: can we ever achieve an unbreachable digital fortress? While total invulnerability may be an unrealistic target, the continuous pursuit of enhanced encryption practices, coupled with robust security protocols, positions organizations to mitigate risks effectively. Incremental improvements, informed by ongoing research and development, hone our defenses against a landscape fraught with digital perils.
In conclusion, encryption stands as a paramount element in the constellation of cybersecurity. By transcending traditional boundaries, it presents a strategic advantage that insulates networks from evolving threats. The complexities inherent in encryption—from key management to regulatory compliance—underscore the necessity of a comprehensive approach to augmenting digital defense. As we progress further into a digitally empowered epoch, the onus remains upon us to embrace encryption not just as a reactive measure, but as an integral component of proactive cybersecurity strategy. In doing so, we can safeguard our information, assure stakeholder confidence, and fortify the digital domain against the encroaching shadows of cybercriminality.







Leave a Comment