In the modern digital landscape, cryptography has become a cornerstone of data security, extending far beyond the realm of mundane password protection. As our lives become increasingly intertwined with technology, the implications of encryption on personal, corporate, and national security cannot be overstated. This expansive exploration of cryptography will enlighten readers about its multifaceted applications, illustrating its vital role across various sectors.
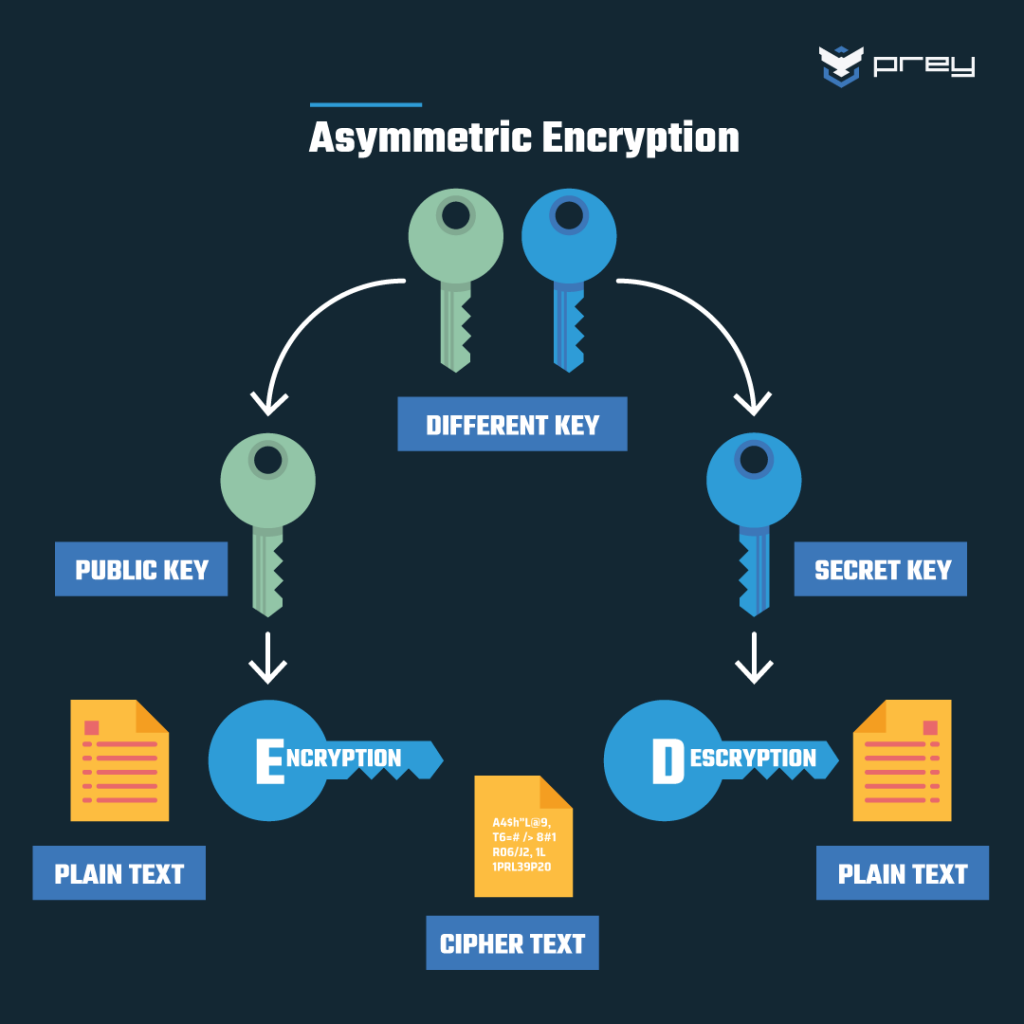
To understand the essence of cryptography, it is imperative to comprehend the fundamental mechanisms that underpin it. At its core, cryptography is the art of enciphering and deciphering information to prevent unauthorized access. The methods of encryption can be categorized into two primary types: symmetric encryption and asymmetric encryption. Symmetric encryption employs a single shared key for both encryption and decryption. This key must remain confidential, as anyone privy to it can access the secured data. Conversely, asymmetric encryption utilizes a pair of keys—public and private keys—rendering it a more robust solution in scenarios such as secure communication and digital signatures.
One of the principal applications of cryptography is in ensuring the confidentiality of sensitive information. Financial institutions rely heavily on encryption to safeguard customer data during transactions. When consumers input their personal information on e-commerce platforms, cryptography encrypts this data, rendering it unintelligible to potential eavesdroppers. Techniques such as Secure Socket Layer (SSL) encryption are employed to create an encrypted connection between users and websites, fostering trust and encouraging online commerce.
The implications of cryptography extend into healthcare, where patient confidentiality is of the utmost importance. Medical records contain sensitive information accessible to authorized healthcare professionals only. Encryption ensures that patient data remains secure from potential breaches, adhering to stringent regulations such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States. Unauthorized access to this information can lead to identity theft and other grave consequences, emphasizing the necessity of robust security measures.
Moreover, organizations utilize cryptography to maintain the integrity of data. This means ensuring that information remains unaltered during storage and transmission. Hash functions play a critical role in this aspect, converting data into a fixed-length string of characters that uniquely represents the original input. Any alteration in the data will produce a drastically different hash, alerting stakeholders to potential tampering. This capability is essential for sectors such as finance, where discrepancies in transaction records can lead to significant losses and legal liabilities.
In addition to confidentiality and integrity, authentication is another pivotal component of cryptographic systems. Users must be assured that they are communicating with legitimate parties. Cryptographic protocols like Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) facilitate this through digital certificates, which vouch for the authenticity of entities. This aspect is particularly crucial in the realm of email communications, where phishing attacks are rampant. Encrypted emails that utilize digital signatures provide recipients with the assurance that the content originates from a verified source.
Furthermore, the digital age has ushered in an era of complex data-sharing environments. The concept of cloud computing, for instance, has revolutionized how data is managed and stored. However, this innovation brings with it concerns about data sovereignty and security. Cryptography enables organizations to maintain control over their data, even when stored in external environments. End-to-end encryption, for example, ensures that only authorized users can access information stored on cloud servers, thwarting unauthorized third-party access.
With the rapid evolution of technology, the emergence of the Internet of Things (IoT) has presented unique challenges. Smart devices, ranging from household appliances to industrial sensors, often transmit sensitive information. Cryptographic solutions are imperative in securing these devices against cyber threats. As these interconnected systems proliferate, robust encryption measures must be implemented to protect user data and ensure the reliable functioning of critical infrastructure.
As individuals become increasingly aware of their digital footprint, personal privacy has shifted to the forefront of public discourse. With governments collecting vast amounts of data, the call for enhanced privacy measures has become louder. Encryption serves as a tool for individuals seeking to preserve their personal communications and data security. Applications employing end-to-end encryption, such as messaging platforms, exemplify the growing demand for privacy-centric solutions. By utilizing cryptography, users can engage in conversations without fear of interception or surveillance, reinstating a sense of autonomy in an age dominated by information sharing.
Recently, discussions surrounding encryption have been underscored by debates about surveillance versus privacy. Law enforcement agencies advocate for access to encrypted communications in the interest of national security. Conversely, cybersecurity experts warn that backdoors in encryption weaken the overall security framework and expose individuals and organizations to risk. This ongoing dialogue illustrates the delicate balance between ensuring public safety and protecting personal freedoms, emphasizing the complex nature of cryptographic practices.
In conclusion, the realm of cryptography is intricate and essential, safeguarding not merely passwords but the very foundation of digital security across diverse sectors. By understanding the various dimensions of cryptography, including confidentiality, integrity, authentication, and the implications of emerging technologies, stakeholders can better appreciate the weighty significance of encryption in contemporary society. As we navigate a world that increasingly relies on the digital domain, the importance of robust cryptographic measures will only magnify. The evolution of encryption is not merely a technical consideration; it is central to fostering a secure, privacy-respecting digital future.






Leave a Comment