Cryptanalysis and security attacks form two distinct, albeit interrelated, components of the broader landscape of information security. Understanding the nuances that separate these two concepts is critical for developing robust defenses against potential threats. This article delineates the characteristics, methodologies, and implications of cryptanalysis in contrast to security attacks, providing readers with a comprehensive overview.
Defining Cryptanalysis
Cryptanalysis is the art and science of decoding or deciphering encrypted data without direct access to the decryption key. It utilizes various mathematical techniques and theoretical frameworks to breach cryptographic systems. The practice can be categorized into two primary modalities: deciphering and exploitation. Deciphering involves breaking the encryption directly, while exploitation refers to leveraging the inherent vulnerabilities within cryptographic algorithms.
Historically, cryptanalysis has evolved through numerous phases, often reflecting advancements in both computing technologies and cryptographic methodologies. For example, early forms of cryptanalysis heavily relied on frequency analysis, a technique predicated on the observation of letter patterns in classical ciphers. In contrast, contemporary cryptanalysis employs sophisticated tools such as linear and differential cryptanalysis which exploit specific weaknesses in modern cryptographic algorithms.
Understanding Security Attacks
Security attacks, on the other hand, encompass a wide array of malicious activities aimed at compromising the integrity, confidentiality, or availability of information systems. They can be classified into two broad categories: passive and active attacks. Passive attacks involve eavesdropping or monitoring transmissions without altering data, whereas active attacks entail manipulating or tampering with data in transit.
Within these categories, various methods are utilized, including brute-force attacks, man-in-the-middle attacks, and denial-of-service attacks. These attacks can target not only cryptographic algorithms but also other facets of information systems — such as network protocols, web applications, and even the physical hardware that supports these systems. The sheer diversity of security attacks necessitates a multifaceted approach to cybersecurity.
Differences in Objectives
The fundamental difference between cryptanalysis and security attacks lies primarily in their objectives. Cryptanalysis focuses on understanding and breaking cryptographic systems to unveil hidden information. In contrast, security attacks are broader in scope, often targeting the entire security infrastructure of an organization, with motives ranging from data theft to disruption of services.
While cryptanalysis may serve as a tactical component of a security attack — for instance, when an attacker employs cryptanalysis to garner information protected by encryption — it is but one strategy among many available to assailants. Security attacks exploit various vulnerabilities across multiple layers of an information system, reflecting a more comprehensive approach to inflicting harm.
Methodologies Employed
The methodologies of cryptanalysis include multiple techniques, suited to different types of algorithms and encryption standards. Some notable methods involve:
- Brute Force: This entails exhaustively attempting every possible key until the correct one is found.
- Known-Plaintext Attacks: In this scenario, the attacker possesses both the plaintext and its corresponding ciphertext, providing a foothold to deduce the encryption key.
- Chosen-Ciphertext Attacks: The cryptanalyst has the capability to choose any ciphertext and determine its decryption, allowing targeted analysis of algorithms.
- Side-Channel Attacks: These exploit information leakage from implementations, such as timing information, power consumption, and electromagnetic emissions.
Similarly, security attacks manifest through various tactics, including:
- Phishing: A social engineering tactic designed to trick individuals into divulging sensitive information.
- Exploitation of Software Vulnerabilities: Targeting flaws within applications or operating systems to execute arbitrary code.
- Insider Threats: Malicious actions taken by individuals within an organization who possess access to confidential data.
Consequences and Mitigation Strategies
Consequences of successful cryptanalysis can range from unauthorized access to sensitive data to severe breaches of trust in security protocols, potentially crippling organizations. The implications of security attacks extend even further, as they can result in financial loss, reputational damage, and legal ramifications. The breadth of impact warrants vigilance and readiness for both cryptanalysis and security attacks as aspects of comprehensive security planning.
Organizations can bolster their defenses through a combination of mitigation strategies. Effective measures against cryptanalysis include employing advanced cryptographic algorithms that incorporate robust keys and undergo thorough scrutiny through peer reviews. Security attacks, on the other hand, necessitate an integrative security model that involves employee training, constant monitoring of network activity, and incident response strategies to swiftly neutralize threats.
Conclusion
In summary, while cryptanalysis and security attacks share an intersection within the domain of information security, they serve distinct purposes and employ different methodologies. Cryptanalysis may be regarded as a specialized branch focusing on deciphering encoded messages, whereas security attacks embody a broader spectrum of malicious activities targeting overall system vulnerabilities. To navigate the complex terrain of digital threats effectively, a nuanced understanding of both concepts is essential.


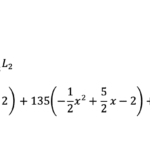
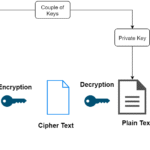
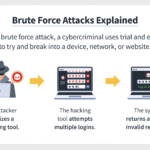




Leave a Comment