Cryptography, the art of securing communication in the presence of adversaries, has fascinated humanity for centuries. The myriad of possibilities for exploration and experimentation in this field makes it an enticing subject for both amateurs and seasoned professionals alike. Engaging hands-on projects not only solidify theoretical knowledge but also cultivate a nuanced appreciation for the complexities of security and privacy. Below is a detailed account of intriguing project ideas designed to enhance learning in cryptography.
1. Building a Basic Encryption Tool
Starting with a simple encryption tool is a prudent first step. Select a user-friendly programming language like Python or JavaScript. Implement a classical cipher, such as the Caesar or Vigenère cipher. This project will introduce essential concepts like key management and plaintext-ciphertext transformation. Once comfortable, gradually introduce enhancements—such as creating a user interface, adding multiple cipher options, or implementing brute-force attack simulations. This evolution will illuminate the limitations of classical methods while emphasizing the importance of modern cryptographic techniques.
2. Cryptanalysis of Historical Ciphers
Cryptanalysis, the study of breaking encryption, allows one to comprehend the vulnerabilities of various cryptographic systems. Choose a historical cipher—like the Enigma machine used in World War II or the simple substitution cipher used in ancient Rome. Research the historical context of the cipher and then try to decode various messages without the key. This project is a confluence of history and mathematics, revealing why certain methods fell from use. Understanding these breakdowns underscores the necessity for robust encryption in contemporary society.
3. Secure Messaging Application
Creating a secure messaging application can be both challenging and enlightening. Utilize libraries that facilitate encryption, such as OpenSSL or Libsodium, to ensure messages are properly encrypted. Implement end-to-end encryption protocols to safeguard user communications. Furthermore, consider adding features like ephemeral messages that self-destruct after a set period. This project will deepen your knowledge of secure channels, authentication, and the principles of confidentiality and integrity, all of which are vital in today’s digital landscape.
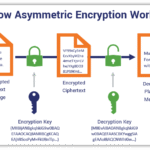
4. Implementing Public Key Infrastructure (PKI)
Engage in the construction of a rudimentary PKI system, which forms the backbone of modern secure communications. Create a Certificate Authority (CA) capable of issuing digital certificates. Explore the intricacies of asymmetric cryptography, focusing on the roles of public and private keys. This project may include creating certificates for various applications, such as email or website authentication. By understanding PKI, you’ll grasp its critical role in establishing trust between parties in a digital environment.
5. Blockchain and Cryptographic Hash Functions
Delve into the world of blockchain technology by developing a simple blockchain from scratch. Focus on the importance of cryptographic hash functions, which ensure data integrity. Begin with hashing algorithms like SHA-256, then build the chain of blocks linking each one securely. Explore how this technology forms the foundation for cryptocurrencies and its implications for various sectors increasingly reliant on distributed ledger technology. This project will illuminate how cryptography can be harnessed for more than just securing messages.
6. Creating a Password Manager
Develop a password manager to solidify understanding of secure storage and retrieval techniques. Use principles of hashing and salting to ensure passwords are stored safely. This project will involve creating a user interface for adding, deleting, and retrieving passwords while maintaining security protocols. The endeavor highlights the significance of strong password practices and urges the exploration of vulnerabilities commonly associated with password management.
7. Exploring Digital Signatures
Digital signatures are paramount in ensuring authenticity and integrity in electronic communications. Construct a project that demonstrates how digital signatures work using asymmetric cryptography. Create a simulated document signing process, whereby a message is “signed” using a private key and subsequently verified with a public key. This exercise will elucidate not only the technical aspects of digital signatures but also their implications for electronic contracts, software distribution, and more.
8. Designing a Secure File Transfer Protocol
Securely transferring files over insecure networks is a daunting task. Embark on a project to create a secure file transfer protocol using established encryption standards such as SSL/TLS. Focus on the underlying principles of confidentiality, integrity, and authentication during data transmission. This project will offer insight into the broader implications of secure transfers in sector-specific applications like healthcare or finance, where data sensitivity is paramount.
9. Implementing Secure Cookies in Web Applications
As web applications proliferate, the need for secure cookie management becomes apparent. Create a project that focuses on implementing secure cookies, ensuring they are set with proper flags like HttpOnly and Secure. This project will enhance understanding of web security practices and demonstrate how cookie vulnerabilities can be exploited. Engaging with this aspect of cryptography reinforces the importance of maintaining user privacy and data integrity.
10. Conduct a Security Audit on an Existing Application
Finally, undertaking a security audit on an existing software application can yield significant insights. Select an open-source project and analyze its security features, focusing on areas like data encryption, authentication protocols, and overall resilience against threats. This investigative approach will nurture critical thinking about security practices, allowing for thorough understanding and application of cryptographic principles in real-world scenarios.
Engaging with these hands-on projects not only equips learners with practical skills but also fosters a deeper appreciation for the intricate dance between cryptography and security. Through exploration and experimentation, the fascination with cryptography transforms from a mere academic interest into a compelling journey toward mastering the subtleties and nuances of the discipline. As we continue to navigate a digitally interconnected world, such knowledge remains not just valuable, but imperative.







Leave a Comment