In the realm of cybersecurity, the term “brute force attack” evokes images of tenacious hackers seated in dimly lit rooms, relentlessly typing strings of characters in an effort to infiltrate secure systems. Yet, beneath the surface of this seemingly straightforward concept lies a labyrinthine intersection of methodology, tenacity, and technological adeptness. The distinction between brute force hacking and mere guesswork is often nebulous, cloaked in the complexity of evolving cyber threats and defense mechanisms. This article seeks to delineate the nuances that separate cunning cybercriminals from mere amateurish attempts at digital trespassing.
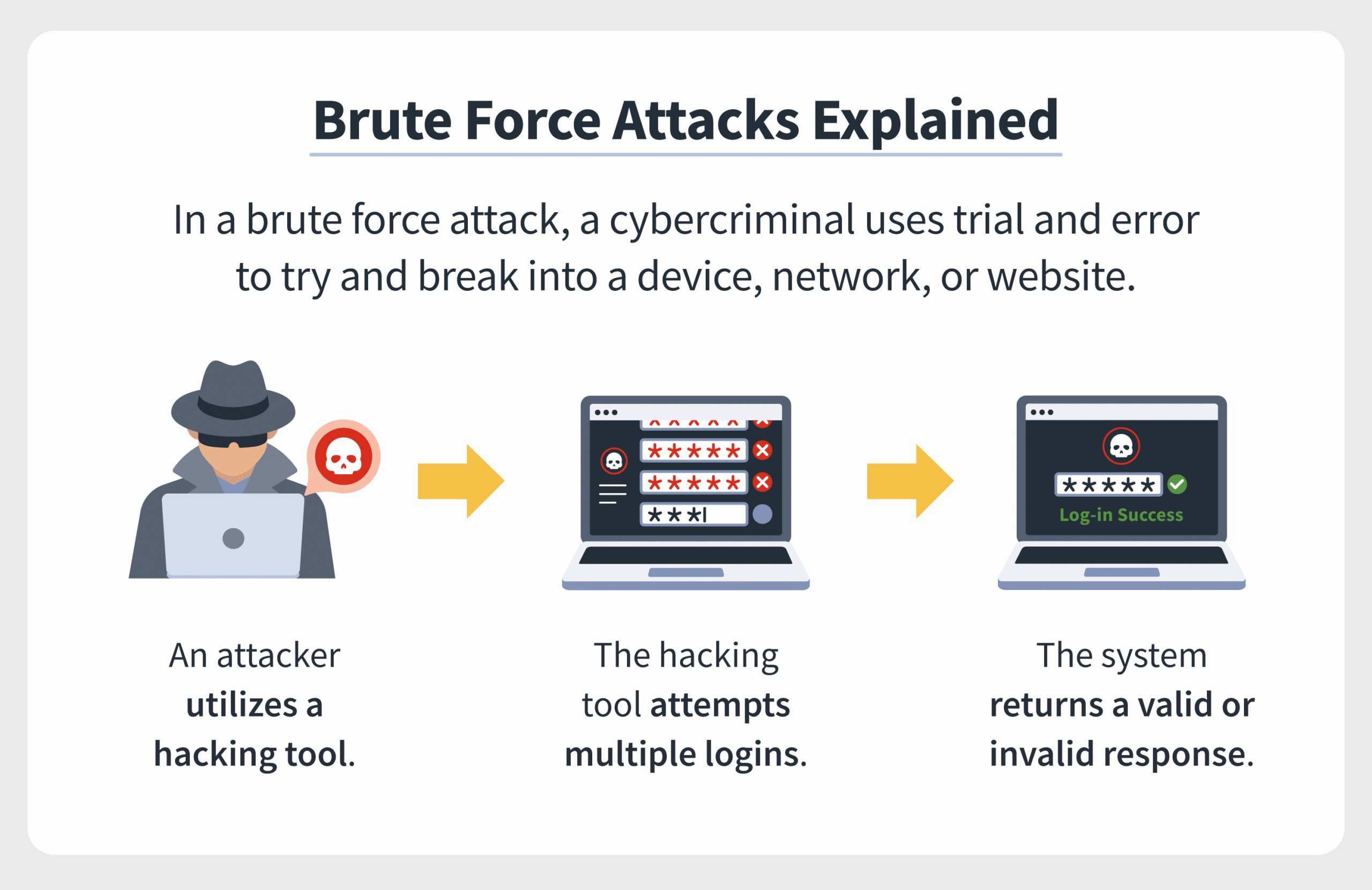
At its core, a brute force attack is analogous to a determined locksmith armed with a set of tools aimed at severing the intricate series of tumblers within a lock. It relies on the straightforward premise of trial and error with the computational muscle to back it up. By systematically trying every conceivable combination until the lock yields, the brute force method exposes vulnerabilities present in weak password systems. However, a stark contrast lies in the approach; while the locksmith methodically engages with each combination, the hacker operates at an accelerated pace, leveraging algorithms to spit out thousands, if not millions, of possible passwords in mere moments.
The proverbial ‘lock’ in this metaphor is often a password or encryption which stands as the first line of defense against unauthorized access. Intriguingly, the sophistication of these defenses has evolved dramatically. Contemporary systems increasingly implement layered security protocols, including multifactor authentication, which complicates the brute force hacker’s task and necessitates ingenuity. Nevertheless, certain short and weak passwords remain the Achilles’ heel of countless networks, rendering them susceptible to brute force attacks.
Moreover, the landscape of passwords reveals a captivating sociological phenomenon. Human behavior impacts password selection patterns, further illuminating the chasm between brute force attacks and guesswork. Many users gravitate towards predictable choices—birthdays, common words, or sequential numbers. These habits create a fertile ground for threat actors. In essence, the hacker’s guesswork often finds its success not merely in computational prowess but in cognitive insight into human psychology.
Further complicating this discourse is the advent of advanced technologies such as machine learning and artificial intelligence. Cybercriminals harness these tools to refine their attacks, blending brute force techniques with sophisticated social engineering tactics. AI algorithms can analyze vast databases of leaked credentials, allowing hackers to prioritize attempts based on likelihood rather than random selection. This ability to discern patterns elevates the act from guesswork to an orchestrated endeavor, bridging the gap between tenacity and methodical calculation.
As one delves deeper into the mechanics of brute force attacks, the advent of tools such as “hashcat” and “John the Ripper” becomes apparent. These applications transform the art of hacking into a science, bringing unprecedented efficiency to the guessing game. Equipped with these tools, hackers can execute dictionary attacks alongside brute force methods, harnessing precomputed hash tables of common passwords. This convergence of techniques exemplifies the unique appeal of this field: the harmony between technological advancement and human cunning.
Yet, it is vital to recognize the psychological elements that govern the relationship between humans and their passwords. The allure of convenience often overshadows security implications. In a world increasingly dominated by instant access and seamless user experiences, the tendency to create banal yet memorable passwords proliferates. As such, the line between brute force hacking and guesswork becomes increasingly blurred. In seeking to gain an advantage, the cybercriminal often dances on the edge of psychological manipulation, exploiting user tendencies and behaviors to maximize their success rate.
Conversely, defenders are not idle spectators in this grand contest. The cybersecurity landscape is marked by an arms race, where the cat-and-mouse dynamic unfolds. Security experts dedicate countless hours to developing robust methods to counteract brute force endeavors, employing measures such as account lockouts and randomized delays after multiple failed attempts. These proactive interventions represent a significant shift in strategy, transforming the battlefield where attackers and defenders engage in this eternal dance of wits.
As brute force attacks continue to permeate the digital space, more sophisticated forms emerge. For instance, credential stuffing exploits the recycling of usernames and passwords across multiple platforms. This method amplifies the effectiveness of brute force because attackers leverage previously breached credentials to gain access to other accounts. Thus, the nuances of human behavior and systemic vulnerabilities further blur the lines between hacking and guesswork.
In conclusion, the domain of brute force attacks encapsulates a compelling juxtaposition characterized by the confluence of technology, human psychology, and evolving defense mechanisms. Hacking, when dissected, reveals a landscape where systematic methodologies intermingle with gambit-like guesswork, intertwined by the common thread of human interaction. As defenders devise increasingly resilient barriers, the dance between brute force and guesswork will persist, forever shaping the cybersecurity landscape. This intricate relationship prompts a reflective inquiry into our digital habits and the structural robustness of our defenses—a contemplation essential in navigating the complexities of an increasingly connected world.






Leave a Comment