In the digital age, the authenticity of signatures has transcended the traditional pen-and-paper concept, evolving into a sophisticated technical mechanism known as digital signatures. This method harnesses cryptographic algorithms to ensure the integrity and non-repudiation of electronic messages and transactions. But the pressing question remains: are digital signatures truly authentic? To dissect this inquiry, it is imperative to traverse the intricate workings, varying types, and the compelling benefits of digital signatures.
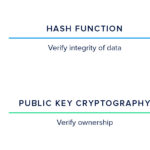
At its core, a digital signature is a mathematical scheme for verifying the authenticity and integrity of a message or document. The primary goal is to ensure that the signee is indeed who they profess to be and that the message has remained unaltered during transmission. Fundamental to this process is public key cryptography, also referred to as asymmetric cryptography. This framework employs two keys: a public key, which can be shared widely, and a private key, which must remain confidential.
The process begins with the sender creating a hash—essentially a digest—of the document intended for signature. This cryptographic hash function generates a unique fixed-size output for the variable-size input (the document). The digital fingerprint produced by this hash function serves as a concise representation of the original content. Next, the sender encrypts this hash using their private key. The resultant encrypted hash, along with the original document, constitutes the digital signature.
Upon receipt, the receiver utilizes the sender’s public key to decrypt the hash. If this decrypted hash matches the hash they generate from the received document, it confirms the authenticity of the signature and asserts that the document has not been adulterated. Conversely, if the hashes do not correspond, there exists a possibility of tampering or misrepresentation, lifting the veil on the document’s integrity.
There are various types of digital signatures that cater to diverse needs. The simplest form is the basic digital signature, which adheres to a rudimentary authentication model. While suitable for personal use, such signatures may lack the robust legal standing required in professional domains.
Further up the spectrum are **standardized digital signatures**, used in secure email platforms and other transactional systems. These signatures function in conjunction with digital certificates issued by Certificate Authorities (CAs). The CA vouches for the users of the digital signatures by validating their identity, thus enhancing trust significantly. This framework operates under the **Public Key Infrastructure (PKI)**, establishing a comprehensive model for secure electronic transactions.
For high-stakes environments, **advanced electronic signatures (AES)** are often requisite. AES are more sophisticated signatures that meet stringent regulatory compliance, as seen in industries such as finance, healthcare, and government. These signatures offer complex verification techniques and are recognized legally as equivalent to handwritten signatures in many jurisdictions.
Nevertheless, the efficacy of digital signatures is predicated on various factors, particularly the security of the private key. If a malicious actor gains access to this key, they acquire the capability to forge signatures, thus undermining the authenticity guarantee that digital signatures provide. It’s prudent to employ strong passwords and multi-factor authentication to mitigate the risk of key compromise.
Digital signatures also foster a plethora of benefits that accelerate contemporary business practices. One significant advantage is the expeditious nature of verifying authenticity. Unlike traditional signatures, which require physical presence and lengthy procedures, digital signatures allow for instant authentication across vast distances with unwavering precision.
Moreover, the automated nature of digital signature systems streamlines workflows, reducing operational costs and enhancing efficiency through the reduction of paper-based processes. Organizations can save time, manage compliance more effectively, and ensure legal enforceability without the cumbersome documentation associated with traditional signatures.
Despite their merits, skepticism surrounding the authenticity of digital signatures persists in certain circles. This is predominantly due to a lack of understanding about the underlying technology and the complexities involved in cryptography. Misinformation can breed mistrust, leading stakeholders to question the reliability of this evolving method of verification.
Moreover, the digital landscape is fraught with threats, from phishing attacks to advanced cyberintrusions. Regular audits and ongoing education about identifying secure communications could ameliorate these concerns, reinforcing trust in digital signature technologies.
In conclusion, digital signatures present an innovative solution for ensuring authenticity in the digital realm. Built upon cryptographic principles, their operational integrity depends on proper management of asymmetric keys and robust infrastructure. Various formats exist, catering to a spectrum of demands, from personal use to stringent industry standards. While challenges persist, the proactive management of security and continuous education can bolster trust in this technology, affirming that, indeed, digital signatures can be authentically reliable instruments in the digital age.






Leave a Comment