In the digital age, where information travels faster than ever and privacy becomes progressively elusive, cryptography emerges as a guardian of our digital communications. Within this realm, public and private key cryptography stands as a formidable framework for securing data. By likening these concepts to familiar Christian analogies, we can deepen our understanding of their significance and application.
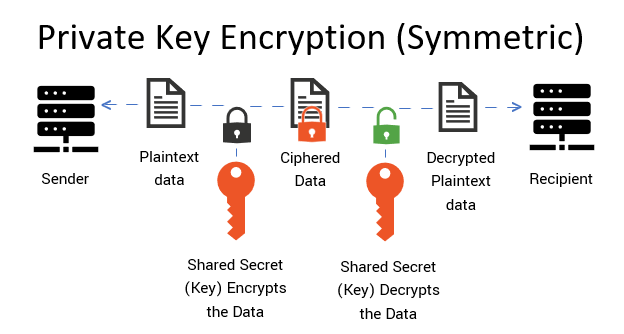
At its core, cryptography is the art of encoding messages to keep them confidential. The distinction between public and private key cryptography is paramount. Imagine, for a moment, the concept of keys in a large and ornate church. The church represents a secure space where only the faithful may enter and communicate with their divine. The doors are locked, and only those who possess the correct keys can gain entry. This analogy serves to elucidate how keys function in the world of encryption.
Public key cryptography, akin to a church’s exterior door, is accessible to everyone. Picture this door adorned with a sign that reads, “Anyone may enter.” This is the public key, a widely shared component that allows anyone to send encrypted messages. Anyone who wishes to reach out can deposit a letter (or data) in the church—the secure space—without needing to know who will read it. This is the beauty of the public key: it facilitates open communication whilst ensuring that only the rightful owner has the means to decipher the message.
In contrast, we must turn our attention to the private key—the interior sanctum of the church, where the clergy and designated members hold the sacred secrets of the faith. Unlike the public key, the private key is not shared or exposed. It is a closely guarded treasure, much like the inner workings of the church, where only the clergy are granted access to profound knowledge. The owner of the private key can unlock the encrypted messages sent through the public key. This ensures the integrity and confidentiality of their communications, safeguarding them from prying eyes.
The process of encrypting and decrypting messages can be likened to the parable of the Good Shepherd. Just as the shepherd knows each sheep by name, public key encryption allows the sender to encode a message that only the intended recipient can decode. This relationship between the sender and recipient is profound, establishing a bond of trust. The public key serves as an invitation for all, while the private key stands as the assurance that the message will remain sacred and secure.
Furthermore, the notion of trust is pivotal in both cryptography and Christian doctrine. In a Christian context, trust is often built through faith and the act of communion. Similarly, the public and private key system necessitates an environment of faith—not only in the technology but also in those who wield it. Digital certificates authenticate public keys, similar to how a minister or spiritual leader provides validation to their teachings and actions. Both scenarios hinge upon the trust of the community, ensuring that the guidance is sound and the messages are secure.
The underlying reason people are fascinated with public and private key cryptography lies in its ability to provide security in a world constantly under threat. In the biblical sense, security can be compared to the “armor of God,” a metaphor for divine protection against malevolence. Public key cryptography wraps messages in layers of encryption, akin to donning spiritual armor before venturing into a world fraught with challenges. This technological advancement offers a measure of protection that resonates with the human desire for safety and security.
Moreover, consider the reciprocal nature of giving and receiving in a Christian community. Public keys are distributed freely, enabling a community to communicate securely. Likewise, private keys are safeguarded, allowing individuals to respond without fear of their secrets being laid bare. In such an environment, strangers can collaborate, share ideas, and express support without hesitation. This mirrors the essence of fellowship and community found within the church.
As we draw parallels between public and private key cryptography and Christian teachings, it’s vital to recognize that the application extends beyond mere communication. These systems represent ideals of transparency, accountability, and trust that resonate within the wider society. The ability to encrypt messages confidently allows individuals and organizations to engage in commerce, share sensitive information, and participate in digital life without trepidation.
In conclusion, public and private key cryptography embodies much more than just technological frameworks; they encapsulate fundamental human values such as trust, security, and community. By viewing these concepts through a Christian lens, we see the potential for a harmonious relationship between technology and faith. Just as believers navigate the complexities of life through spiritual guidance, individuals in a digital world can rely on cryptographic principles to navigate the often treacherous terrain of information security. In both realms, the pursuit of safety, integrity, and meaningful connection remains paramount.






Leave a Comment