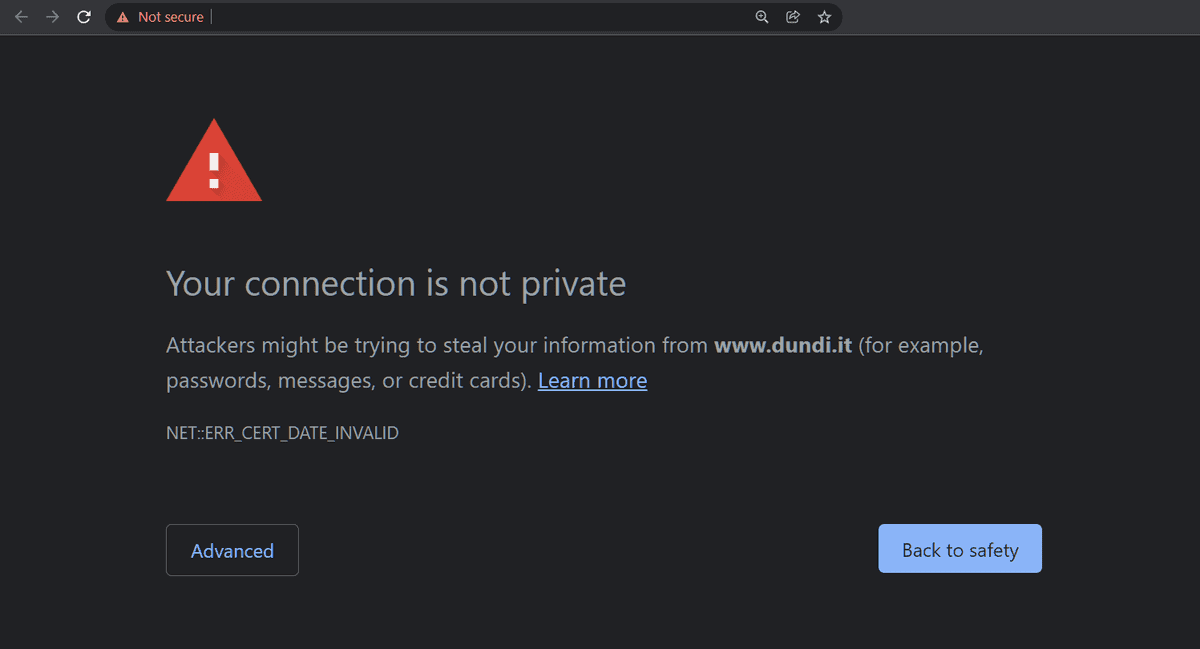
In today’s digitally interconnected world, the security of websites has emerged as a paramount concern for both users and developers. When we encounter a website that isn’t secure, indicated by an absence of HTTPS in the address bar or a conspicuous warning message, it prompts a cascade of questions regarding the implications of engaging with such a site. This article delves into the multifaceted consequences that arise when a website lacks adequate security measures, illustrating why this phenomenon warrants our attention.
To comprehend the ramifications of insecure websites, one must first grasp the mechanics of internet security. An unsecured website typically operates over HTTP rather than HTTPS. The inclusion of the ‘S’ in HTTPS signifies that the site utilizes Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) or Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocols to encrypt data between the user’s browser and the website’s server. When this layer of protection is absent, all transmitted data remains unencrypted and theoretically susceptible to eavesdropping by malicious actors.
The most immediate and tangible effect of visiting an insecure website is the risk to personal data. Users unwittingly expose sensitive information—such as passwords, credit card numbers, and personal identification details—while transmitting this data over public networks. This vulnerability opens avenues for cybercriminals to intercept communications through techniques such as man-in-the-middle attacks, whereby they position themselves between the user and the server to siphon off confidential information.
Beyond the personal risk, the credibility of an insecure website is severely undermined. Consumers and users are increasingly discerning; as they encounter the ubiquitous “Not Secure” warning, their trust in the website plummets. Research indicates that users are less likely to interact with websites that lack security. Consequently, businesses may experience diminished traffic, adversely impacting their bottom line. The perception of a brand is intricately linked to its online presence, and if a website is perceived as insecure, it can tarnish the overall reputation of the organization.
Moreover, search engines prioritize secure websites in their ranking algorithms. Google, for instance, has explicitly stated that HTTPS is a ranking factor. This means that an insecure website is not only at risk of being avoided by potential users but also risks being relegated to the lower echelons of search engine results pages (SERPs). In this manner, the compound effect of insecurity exacerbates the challenges of gaining visibility and attracting new visitors.
The repercussions extend further into regulatory territory. The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and other compliance requirements mandate that organizations safeguard personal data with requisite security measures. An insecure website may inadvertently expose businesses to legal ramifications, including hefty fines and damages, stemming from data breaches resulting from inadequate security. This gross oversight can lead to a domino effect, tarnishing not just the organization’s reputation but also straining relationships with partners, stakeholders, and customers.
In addition to these tangible risks, insecure websites foster an environment rife with cyber threats. Malware attacks are one of the most pernicious consequences. An unsecured site can serve as a breeding ground for malicious software that can compromise user systems and data integrity. Such malware can manipulate user devices, leading to severe consequences such as identity theft, financial loss, and the dissemination of further cyber threats.
Furthermore, there exists an insidious form of attack called phishing, where malicious actors construct look-alike websites intended to deceive users into entering their credentials. Insecure websites are often the first line of defense against such predatory tactics. Without robust security measures, users are more likely to fall prey to phishing attacks, which can propagate viral damage across their digital interactions.
Some may wonder about the remedies available to mitigate the risks associated with visiting insecure websites. While one could utilize virtual private networks (VPNs) for an added layer of abstraction, this does not eliminate the inherent risks posed by an unsecured site. That said, prudent measures such as employing browser extensions that signal website security status and cultivating habits of vigilance—such as checking for the presence of HTTPS—can empower users to navigate the web with greater awareness.
Nevertheless, the onus must also fall upon website administrators and developers to uphold security standards. Deployment of SSL certificates and strict adherence to secure coding practices are fundamental steps in establishing a secure online environment. Regular security audits, penetration testing, and user education campaigns can further bolster defenses and build trust between users and websites.
In conclusion, the implications of engaging with an insecure website are profound and multifarious. From compromising personal data to jeopardizing business credibility and incurring legal repercussions, the ramifications extend beyond individual experiences. They permeate organizational structures and wider digital ecosystems. The stakes are higher than ever as we continue to navigate the complexities of the online world. Awareness of these dangers underscores the necessity for robust security measures and critical user education, inviting a collective endeavor toward a more secure internet for everyone.






Leave a Comment