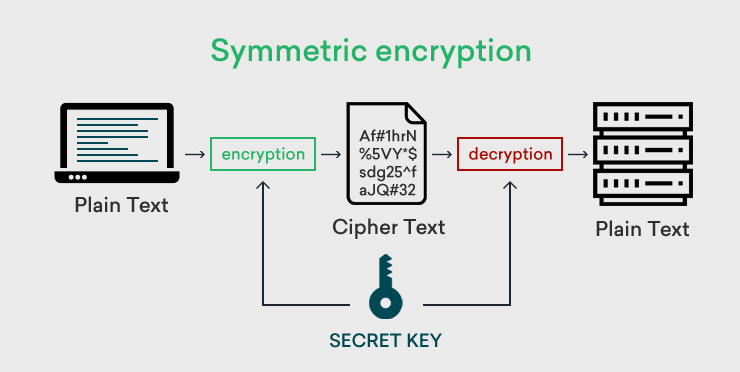
In the intricate landscape of cybersecurity, symmetry plays a vital role that often goes unnoticed. Symmetric encryption, a cornerstone of modern information security, encompasses a protocol where the same key is utilized for both encryption and decryption. As an efficient and robust method for safeguarding confidentiality, symmetric encryption finds application in numerous real-world scenarios. Its prevalence, notwithstanding the emergence of asymmetric counterparts, signifies a stronghold in cybersecurity practices. This exploration will illuminate various settings where symmetric encryption truly excels, shedding light on its indispensable role in our data-driven society.
One of the most compelling realms where symmetric encryption shines is within the domain of data storage. Organizations, from large corporations to small entities, accumulate colossal amounts of sensitive information ranging from customer data to proprietary algorithms. Encrypting this data at rest is paramount. Take, for instance, a financial institution that could face catastrophic consequences if hackers accessed confidential account information. Symmetric encryption algorithms such as AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) offer a formidable solution. They employ a shared secret key, ensuring that information remains unintelligible to unauthorized parties while still being accessible to those who possess the necessary key. This dual-purpose capability illustrates symmetric encryption’s critical function in safeguarding sensitive data against potential breaches.
Moreover, in the pervasive realm of cloud computing, symmetric encryption emerges as a quintessential guardian of digital assets. As businesses increasingly migrate operations to cloud infrastructures, securing sensitive data uploaded to public or private clouds is imperative. The cloud environment, while offering flexibility and scalability, presents unique challenges related to data security and privacy. Symmetric encryption serves as a bulwark against unauthorized access. By encrypting files before they traverse the internet, organizations ensure that even if a data breach were to occur, intercepted data would remain close to indecipherable, acting as a deterrent. As a result, users can confidently utilize cloud services without sacrificing data integrity.
In addition, symmetric encryption finds its most elegant application in securing network communications. In an era dominated by digital connectivity, ensuring the safety of data exchanged over networks is crucial. Consider the application of symmetric encryption within a Virtual Private Network (VPN). Here, data packets sent over the internet undergo encryption using a shared key, ensuring that even if the information is intercepted, it would remain unreadable. The efficiency of symmetric encryption allows for swift execution, enabling real-time communication without noticeable lag. This makes it particularly viable for high-speed applications such as video conferencing, VoIP calls, and online gaming. The sheer robustness and speed of symmetric encryption render it a preferred choice in circumstances demanding both security and performance.
The corporate world also leverages symmetric encryption in securing software applications. As businesses develop and distribute applications embedded with sensitive functionalities—think online banking apps—they face the pressing need to safeguard the underlying code and user data. Symmetric encryption becomes instrumental in this realm, where encryption keys can secure critical data paths within the application itself. Through the act of encrypting sensitive information such as user credentials and financial transactions within the app, developers can thwart attempts at data theft, thus fostering greater user trust. The reliance on symmetric encryption in software development highlights its pivotal role in the operational defense strategy of organizations.
In the field of electronic payments, symmetric encryption plays a crucial role in ensuring transactional security. When a consumer engages in online transactions, a myriad of sensitive data, including credit card numbers and personal identification information, is transmitted across networks. Symmetric encryption protocols encrypt this data using a shared key that both the merchant and the consumer know, offering assurance that confidential information cannot be easily accessed by malicious actors. This practice not only fortifies the payment process but also cultivates consumer confidence in digital financial systems. The unyielding reliability of symmetric encryption retains its stature amid a backdrop of increasing cyber threats in the payment industry.
Turning towards the realm of Internet of Things (IoT), symmetric encryption aids in securing communication between devices. With the proliferation of interconnected devices, the potential for vulnerabilities has escalated. Consider smart home devices, which frequently manage personal data. Implementing symmetric encryption ensures that any data exchanged between a smartphone and a smart thermostat, for instance, is securely transmitted. Each device operates using a shared key, making unauthorized access increasingly arduous. The application of symmetric encryption thus optimizes functionality while simultaneously addressing data privacy concerns. The imperative security mechanism becomes fundamental in a landscape defined by digital interdependence.
While exploring these scenarios, it is crucial to acknowledge the balance between security and performance that symmetric encryption strikes. The fundamental nature of using a single key not only simplifies the encryption and decryption processes but also demands less computational power than asymmetric schemes. This efficiency permits organizations to secure extensive datasets without incurring prohibitive resource costs, making symmetric encryption not only a secure choice but also a practical one.
In conclusion, symmetric encryption’s versatility and efficiency position it as an essential tool in a myriad of real-world applications. From data storage and cloud computing to secure communications and electronic payments, its ability to safeguard sensitive information against potential breaches reflects its indispensable value. As the digital landscape continues to evolve, the relevance of symmetric encryption remains profound, underscoring its capability to adapt and flourish in various settings. Through this examination, one can appreciate the pivotal role that symmetric encryption plays in maintaining the sanctity of our data, illuminating the path for a secure digital future.






Leave a Comment