In an increasingly digital landscape, the protection of sensitive information has become paramount. One of the most effective methodologies for safeguarding this data is the practice of encrypting data at rest. This concept addresses a critical aspect of data security and reveals inherent vulnerabilities associated with unprotected data. But what does encrypting data at rest actually protect against? To fully comprehend this, one must first delve into the nature of data at rest, the threats it faces, and the implications of encryption.
Data at rest refers to inactive data stored physically in any digital form (such as databases, data warehouses, and file systems). Unlike data in transit, which is being sent across networks, data at rest remains dormant until it is accessed or altered. However, this state of inactivity does not render it impervious to threats; rather, it becomes an inviting target for unauthorized access. The significance of this distinction cannot be understated—data at rest is often more vulnerable to attacks than one might assume.
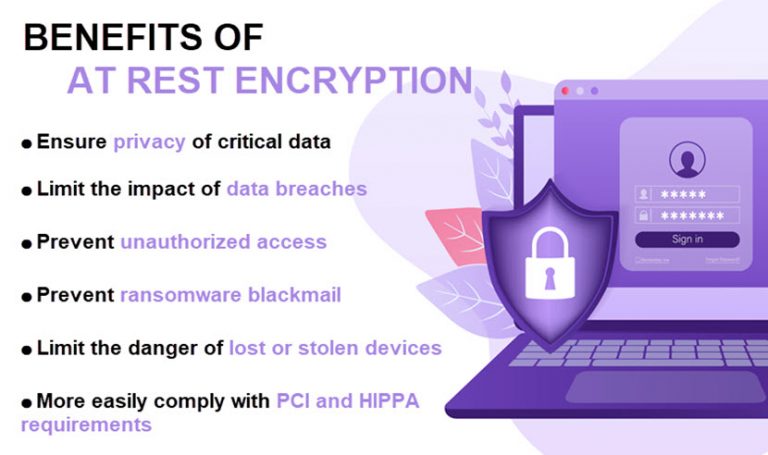
First and foremost, encrypting data at rest acts as a formidable barrier against unauthorized access. Cybercriminals consistently seek to exploit weaknesses in systems to access sensitive information, whether for personal gain, corporate espionage, or other nefarious purposes. Plaintext data, without encryption, can easily be intercepted or accessed through physical theft, unauthorized network intrusions, or through exploitation of software vulnerabilities. Encrypting data transforms it into a garbled format that is incomprehensible without the appropriate decryption keys, effectively safeguarding it against unauthorized eyes.
Moreover, one must consider the risk posed by insiders. Malicious or negligent employees can inadvertently compromise data security by misappropriating sensitive information. This scenario becomes particularly pertinent within organizations where privileged access to data can lead to potential misuse. Encrypting data at rest significantly mitigates this risk; even if an insider were to access this data, it would remain protected and unreadable without the appropriate encryption keys. This layer of security ensures that sensitive information remains out of reach, preserving the integrity of the organization’s data.
Another insidious threat comes from physical breaches. Despite having robust digital security measures, an organization may still fall victim to physical theft. Laptops, hard drives, or entire servers can be stolen, exposing the sensitive data they contained. If that data is not encrypted, it presents a straightforward opportunity for attackers. However, with encryption in place, the stolen data is rendered useless, offering no value to the thief. This critical protective measure underlines an often-overlooked aspect of data security: physical safeguards alone are inadequate in a comprehensive security strategy.
The repercussions of data breaches can be staggering—not merely in terms of immediate financial losses but also through long-term reputational damage and potential legal consequences. Organizations that fail to protect sensitive data risk substantial penalties under various data protection regulations, such as GDPR or HIPAA. Encrypting data at rest can demonstrate due diligence and compliance with these regulations, potentially alleviating some liability in the event of a breach. By adopting encryption as a best practice, organizations reinforce their commitment to data protection and accountability.
In addition to safeguarding against unauthorized access, insider threats, and physical breaches, encrypting data at rest also enhances data integrity. Encryption algorithms incorporate checks that can help ensure that data has not been tampered with during its dormant state. Any alteration to the encrypted data will render it unrecognizable, thereby alerting administrators to potential compromises. This aspect of encryption serves to bolster not only the security of the data but also its reliability, providing further reassurance to stakeholders regarding the integrity of critical organizational information.
Cultural and psychological dimensions of data security also play a crucial role in the fascination surrounding data encryption. As society places increasing importance on privacy and the control of personal information, encryption has emerged as a means of empowering individuals and organizations. By encrypting data at rest, entities can foster a culture of trust wherein stakeholders feel confident that their information is secure. This proactive approach to security fosters a sense of responsibility and transparency, reinforcing sentiments about data ethics in the digital age.
Furthermore, as data continues to proliferate exponentially, the volume of information requiring protection will only grow. Encrypting data at rest provides scalability as organizations expand and accumulate larger datasets. With efficient encryption mechanisms in place, entities can adapt to increasing security demands without compromising their core operations. This adaptability ensures that security measures evolve in tandem with technological advancements, preserving the safety and confidentiality of sensitive information.
In conclusion, encrypting data at rest serves as a multifaceted shield against a plethora of threats, including unauthorized access, insider malfeasance, physical security breaches, and regulatory scrutiny. It enhances data integrity and fosters trust within the organizational ecosystem. As we navigate an ever-changing digital landscape, the imperative nature of protecting sensitive information through encryption becomes more pronounced. In a world rife with complexities and vulnerabilities, upholding the sanctity of data is of utmost importance. The practice of encrypting data at rest is not merely a technical requirement; it is an ethical obligation in the preservation of privacy, integrity, and trust in the digital realm.





Leave a Comment