Encryption stands as a stalwart guardian of data in today’s digital era, shielding sensitive information from prying eyes and malicious entities. Two predominant forms of encryption, symmetric and asymmetric, each serve unique purposes and have distinct methodologies. Understanding the nuances of each type allows individuals and organizations to make informed decisions regarding the appropriate encryption method based on their specific requirements. This analysis delves into the characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages of symmetric and asymmetric encryption, ultimately guiding you towards the right choice.
Understanding Symmetric Encryption
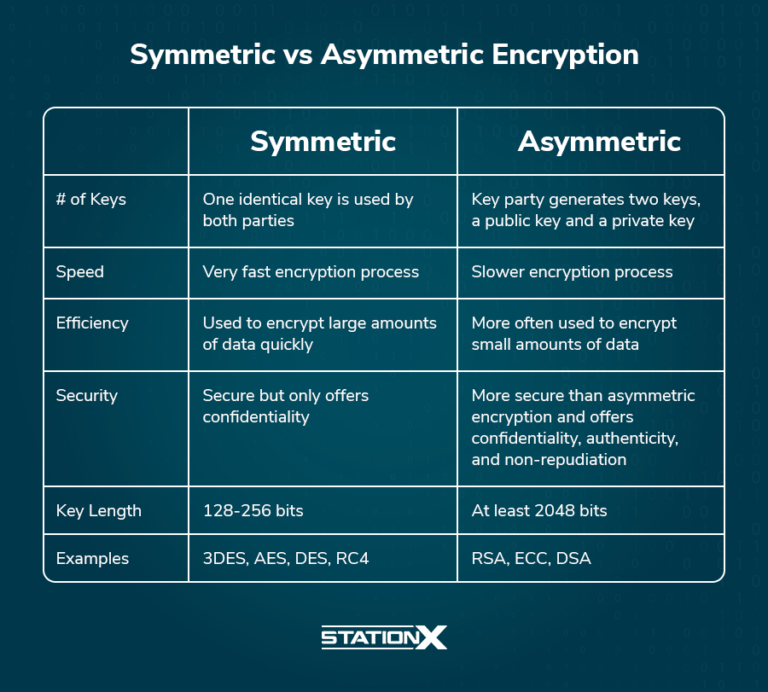
Symmetric encryption employs a single secret key for both the encryption and decryption processes. This shared key ensures that data can be cloaked and later unveiled by anyone possessing the same key. Prominent algorithms embodying this approach include the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), Data Encryption Standard (DES), and Blowfish.
One salient characteristic of symmetric encryption is its efficiency. The speed at which it encrypts and decrypts data is considerably higher than that of asymmetric encryption. This efficiency makes symmetric encryption the preferred choice for large volumes of data, such as the encryption of databases or large files during data transfer.
However, the reliance on a shared secret key introduces vulnerabilities. The primary challenge lies in the key distribution; securely transmitting the key to the intended recipient without interception can be complicated. Additionally, if the key is compromised, the entire encryption becomes moot. The intricacies of key management necessitate robust security protocols to mitigate potential threats.
Exploring Asymmetric Encryption
As opposed to symmetric encryption, asymmetric encryption utilizes a pair of keys: a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption. This method is particularly advantageous for secure data transmission over an untrusted network. Notable algorithms include RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman), DSA (Digital Signature Algorithm), and elliptic curve cryptography (ECC).
The public key can be disseminated widely without compromising security, rendering asymmetrical methods suitable for scenarios such as digital signatures and secure email communication. This paradigm shifts the burden of key management, as the private key remains confidential and is only known to the recipient. As a result, asymmetric encryption mitigates the risks associated with key distribution, enhancing overall security.
Nevertheless, the trade-off for this enhanced security comes in the form of performance. Asymmetric encryption is computationally intensive and generally slower than symmetric encryption, making it less ideal for encrypting large swathes of data. It is commonly used in conjunction with symmetric encryption, wherein asymmetric methods secure a symmetric key that is subsequently used for data encryption.
Use Cases and Applications
The selection between symmetric and asymmetric encryption often hinges on the specific use case. Symmetric encryption excels in environments where speed and efficiency are paramount. For instance, cloud storage services and enterprise-level VPNs frequently employ symmetric algorithms to encrypt vast amounts of data rapidly. Additionally, it is commonly adopted in disk encryption for personal devices, ensuring that sensitive files remain protected from unauthorized access.
In stark contrast, asymmetric encryption is indispensable for ensuring secure communications over the Internet. Protocols such as SSL/TLS rely on asymmetric cryptography to establish a secure connection between clients and servers. This mechanism not only authenticates the parties involved but also establishes a secure channel for symmetric key exchange, capitalizing on the strengths of both encryption types.
Moreover, asymmetric encryption plays a crucial role in blockchain technology and cryptocurrencies. Digital signatures, facilitated by asymmetric encryption, authenticate transactions and generate trust without necessitating a central authority. This fosters a decentralized model wherein integrity is paramount.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Each cryptographic method possesses inherent advantages and drawbacks that merit consideration. Symmetric encryption’s efficiency is a notable strength; however, its reliance on key secrecy poses a significant risk. On the other hand, while asymmetric encryption enhances security through the utilization of key pairs, its slower processing speed may inhibit performance in high-demand scenarios.
It is essential to recognize that while each encryption type has its merit, they are not mutually exclusive. The hybridization of symmetric and asymmetric encryption often provides a more robust security framework. By marrying the efficiencies of symmetric encryption with the security benefits of asymmetric techniques, organizations can harness the strengths of both to create resilient data protection strategies.
Evaluating Your Needs
Deciding which encryption method is right for you involves a thorough assessment of your specific needs. If quick and efficient encryption is your primary requirement, and you possess the means to manage secure key distribution, symmetric encryption may be your best choice. Conversely, if secure communication over an insecure network is your goal, asymmetric encryption stands out as the more suitable option.
Ultimately, the choice of encryption method should never be made lightly. The landscape of cybersecurity is ever-evolving, with threats becoming increasingly sophisticated. Adopting a layered approach to encryption that combines both symmetric and asymmetric methods can bolster defenses against myriad cybersecurity risks. In an age where data breaches are all too common, investing time and resources into understanding and implementing the right encryption methods is not just prudent; it is imperative.






Leave a Comment