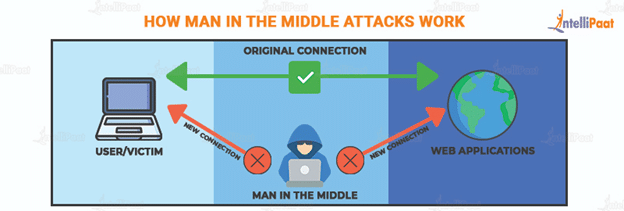
In the digital realm, where currents of data flow effortlessly across invisible networks, there lies a lurking danger known as the Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) attack. Imagine, if you will, two parties engaging in a clandestine conversation, unaware that an eavesdropper is skillfully manipulating the dialogue. As technology evolves, so too does the sophistication of these attacks. Thus, countering MitM attacks becomes not just prudent, but paramount. Below, we delve into a tapestry of best practices to fortify one’s defenses against these insidious threats.
1. Understanding Man-in-the-Middle Attacks
Fundamentally, a MitM attack occurs when a nefarious third party intercepts communication between two entities. This could be a strategic business negotiation or a simple transaction; the malevolent actor can listen, alter, or inject erroneous information. There are various vectors for such attacks—including unsecured Wi-Fi networks, phishing attempts, and DNS spoofing—each requiring tailored defenses.
2. Employing Strong Encryption Protocols
The first bastion of defense lies in implementing robust encryption protocols. Just as a fortress stands impervious against the onslaught of enemy forces, strong encryption shields data in transit. Utilize Transport Layer Security (TLS) to encrypt communications between clients and servers. This ensures that any data exchanged is rendered incomprehensible to unauthorized entities. Moreover, employing end-to-end encryption provides an additional layer of security, particularly in messaging applications, where messages are encrypted before they leave the sender and only decrypted by the recipient.
3. Utilizing Secure Wi-Fi Networks
Public Wi-Fi is often regarded as a double-edged sword; while it provides convenience, it also serves as a breeding ground for MitM attacks. One should treat public Wi-Fi networks with suspicion. Whenever possible, connect to secure, password-protected networks. Utilizing a Virtual Private Network (VPN) when accessing the internet over public Wi-Fi is akin to donning a suit of armor. A VPN encrypts all your internet traffic, rendering it unintelligible to any eavesdroppers.
4. Implementing Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Authentication, in the digital context, serves as a gatekeeper to invaluable information. The implementation of multi-factor authentication fortifies this barrier. MFA requires users to provide multiple forms of verification before granting access, which significantly mitigates the risk of unauthorized entry—much like requiring both a key and a passphrase to unlock a treasure chest. Common forms of MFA include SMS codes, authentication apps, or biometric scans.
5. Watching for Phishing Schemes
Phishing is another pawn in the MitM playbook. This tactic relies on deception, enticing users to divulge personal information or credentials through fraudulent emails or websites. One must cultivate a vigilant mindset, scrutinizing URLs and email addresses to ensure their authenticity. Employing tools such as browser extensions that flag suspicious links can also serve as an additional line of defense against this form of attack.
6. Regularly Updating Software and Devices
In the intricate dance of cybersecurity, one must remain nimble and adaptive. Regular updates to software and devices are essential to patch vulnerabilities that may be exploited by attackers. Manufacturers frequently release updates that rectify security flaws, thus keeping defenses robust. An unpatched system can be likened to a ship with leaks allowed to fester—eventually, it will sink under the weight of its vulnerabilities.
7. Utilizing Strong Password Policies
Passwords serve as the sentinels of one’s digital realm. However, weak and easily guessable passwords can be breached in the blink of an eye. Enforce policies that mandate the use of strong passwords: at least 12 characters long, integrating letters (both uppercase and lowercase), numbers, and special characters. Furthermore, encourage users to change their passwords regularly and avoid reusing them across multiple platforms—a practice akin to leaving the back door to one’s home unlocked.
8. Employing Security Certificates
Security certificates play a crucial role in establishing the identity of websites. When a user connects to a site, they should always verify the presence of a valid certificate. This is akin to checking the credentials of a stranger before trusting them with sensitive information. Organizations are urged to utilize SSL/TLS certificates to bolster users’ trust in their websites and transactions, thus reducing the risk of MitM attacks.
9. Education and Awareness
The most potent weapon against MitM attacks is an informed user base. Education plays an instrumental role in bolstering defenses. Regular training sessions tailored to recognize the signs of MitM attacks can instill a culture of security awareness. By promoting good digital hygiene practices—such as recognizing suspicious emails or using secure connections—organizations can transform their personnel into vigilant sentinels against potential threats.
10. Monitoring Network Traffic
A proactive approach to security involves monitoring and analyzing network traffic for anomalies. Various tools allow organizations to gain insights into traffic patterns, making it possible to detect irregularities that may signify a MitM attack. Like a vigilant watchman observing the horizon for intruders, this continual assessment can preemptively thwart attempts to intercept sensitive communications.
In summation, countering Man-in-the-Middle attacks necessitates a multifaceted approach, weaving together strong encryption, vigilant practices, and continuous education. Just as an architect crafts a building with layers of protective measures, so too must one build a resilient digital fortress. By disseminating these best practices throughout their organization, individuals and businesses can foster a robust cybersecurity environment, ensuring that their communications remain secure and their information safeguarded against the specter of the MitM threat.






Leave a Comment