Cryptography, a word that often evokes intrigue and fascination, plays a paramount role in the intricate dance of modern cyber defense. In a world increasingly governed by digitized communication, the safeguarding of sensitive information has ascended to the forefront of cybersecurity strategies. Delving into the cryptographic realm unveils not merely the techniques employed to obfuscate data, but rather an expansive field that encompasses historical roots, pivotal technologies, and a commitment to confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
To comprehend the significance of cryptography in cyber defense, one must first explore its historical evolution. The origins of cryptographic methods can be traced back to ancient civilizations where covert communication held strategic advantages. From Caesar’s simple cipher to the complex enigmas used during World War II, such as the German Enigma machine, each era shaped the field, refining techniques for encrypting messages. These early examples laid the groundwork for contemporary practices, highlighting the enduring human desire for secrecy and security.
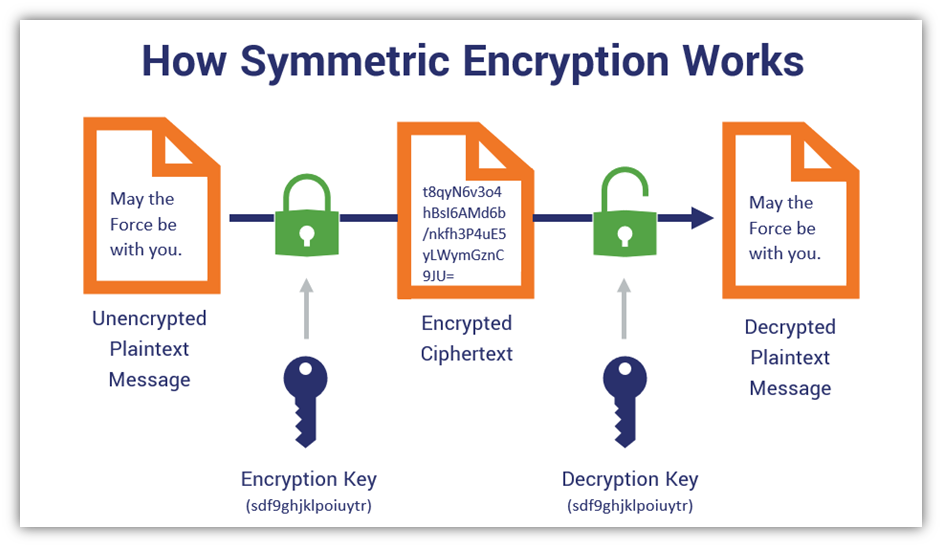
As we transition into the digital age, the stakes have escalated remarkably. Today, the proliferation of personal data, financial transactions, and confidential communications necessitates robust encryption practices. Modern cryptography manifests in two primary forms: symmetric and asymmetric encryption. Symmetric encryption, characterized by a shared key for both encryption and decryption processes, functions swiftly and is often employed for encrypting vast datasets. Conversely, asymmetric encryption utilizes a pair of keys, a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption, thus embodying a more complex and secure mechanism, essential for applications like secure email communication and digital signatures.
The contrasting methodologies of symmetric and asymmetric encryption reveal a profound dichotomy, yet they work synergistically within expansive cybersecurity frameworks. For instance, symmetric encryption’s speed proves advantageous for real-time data protection, while asymmetric encryption grants a formidable layer of security when identity verification is paramount. These dualistic approaches form the bedrock of cryptographic practices in sectors ranging from e-commerce to government communications, each necessitating tailored strategies to withstand an array of cyber threats.
In the digital landscape, where vulnerabilities are omnipresent, threats such as data breaches, ransomware attacks, and identity theft loom ever larger. Herein lies cryptography’s formidable defensive stance. By employing encryption, organizations can render data indecipherable to unauthorized actors. This encumbrance acts as a sentinel, mitigating the impact of breaches and preserving the sanctity of sensitive information. For instance, even if a database is compromised, the information encoded within it remains inaccessible without the appropriate decryption keys.
Yet cryptography does not merely shield organizations but also fosters trust among users. The concept of public key infrastructure (PKI) epitomizes this trust model, allowing users to confidently engage in digital transactions. When a website employs SSL/TLS certificates, integrating cryptographic techniques, users can ascertain that their connections are secure, cultivating a sense of safety that is paramount in building lasting online relationships. This trust extends to various domains, from casual online interactions to high-stakes financial exchanges, underscoring a fundamental tenet of cryptography—it is as much about user trust as it is about technical sophistication.
However, the landscape of cryptography is not devoid of challenges. One of the most pressing concerns involves the advent of quantum computing, a nascent technology poised to disrupt traditional cryptographic algorithms. Quantum computers possess the potential to unravel the complexities of widely used encryption methods, posing an existential threat to current defense mechanisms. To combat this impending challenge, researchers are diligently exploring post-quantum cryptographic algorithms designed to withstand the computational prowess of quantum machines. This realm of research represents a critical frontier, one that mandates the adaptation and evolution of cryptographic practices to preserve virtual security.
Moreover, as the internet of things (IoT) proliferates, the necessity for robust cryptographic protocols becomes increasingly urgent. IoT devices—often characterized by their interconnectedness and inherent limitations in processing power—present unique challenges for encryption. The deployment of lightweight cryptographic techniques is vital to secure these devices, which, if left unprotected, open a Pandora’s box of vulnerabilities that can be exploited by malicious actors. The discourse around IoT security exemplifies the ongoing adaptation of cryptographic practices in response to evolving digital landscapes.
In conclusion, the crucial role of cryptography within cyber defense cannot be overstated. It serves as both shield and sword, equipping individuals and organizations alike with the tools necessary to navigate the shadows of cyberspace. As technology continues to advance at an unprecedented pace, the field of cryptography must evolve correspondingly. From the ancient ciphers that historically safeguarded communication to the sophisticated algorithms that protect modern data, cryptography remains an indispensable ally in the quest for privacy and security in an increasingly interconnected world. The challenges ahead may be formidable, but with innovation and resilience, cryptography stands poised to ensure that secrets remain safely nestled in the shadows, ever vigilant against those who would seek to unveil them.






Leave a Comment