In the vast and intricate landscape of digital security, the concepts of public and private keys stand as monumental pillars, akin to the majestic columns of an ancient temple, safeguarding the sanctity of the realm of information. These cryptographic elements are not merely technical constructs; they embody the essence of trust and security in our increasingly interconnected world.
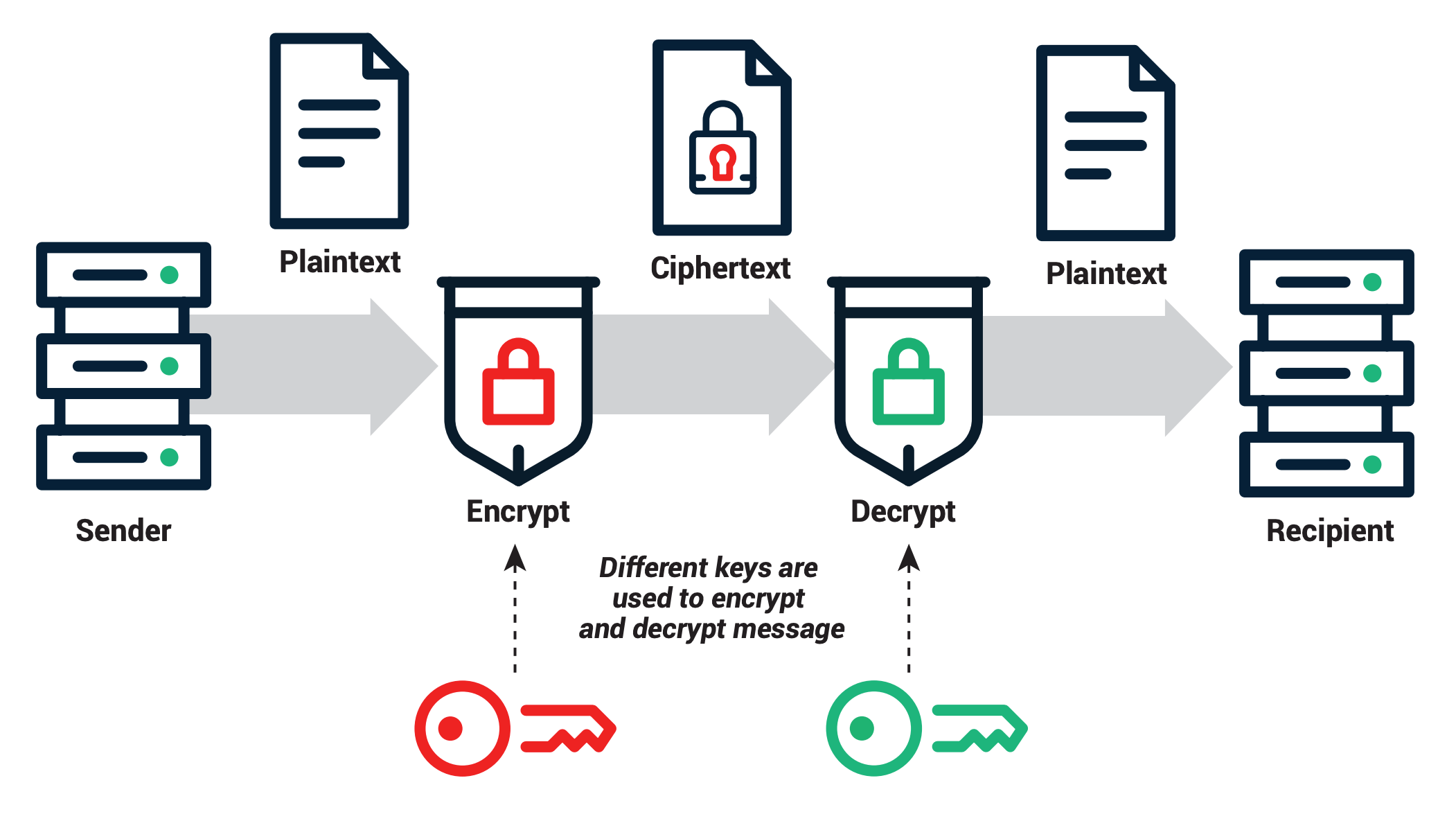
At the heart of public key cryptography lies a duality that mirrors the delicate balance between secrecy and transparency. The public key, as its nomenclature suggests, is open and accessible to anyone; it functions as a virtuous sentry, welcoming all who wish to communicate securely. Meanwhile, the private key remains shrouded in secrecy, akin to a knight’s cherished sword, guarded zealously and wielded only by its rightful owner. Together, they orchestrate a symphony of secure communication, allowing users to transmit sensitive information over otherwise perilous networks.
The Anatomy of Key Pairing
To truly understand the functionality of public and private keys, one must first comprehend the concept of key pairing. This pairing forms the bedrock of cryptographic protocols, such as RSA and ECC (Elliptic Curve Cryptography), which, much like a tightly clenched fist, holds the key to ensuring confidentiality and integrity.
Imagine a locked treasure chest filled with precious gemstones, where the public key serves as the lock visible to the world. Anyone can use this lock to secure their gems within, but only the owner of the private key possesses the key to unlock it. This metaphor illustrates the intrinsic nature of these keys: the public key encrypts messages, while the private key decrypts them, seamlessly ensuring that only the intended recipient can access the secured treasure.
The Guardians of Digital Communication
In a world rife with information breaches and cyber threats, public and private keys stand as vigilant guardians, employing their unique characteristics to protect sensitive data. The public key’s role as a gatekeeper allows it to facilitate ease of communication; it invites strangers to send encrypted messages without necessitating prior arrangements or exchanges, thus enhancing convenience.
Conversely, the private key is the ultimate protector, safeguarding the decrypted messages. Its influence is singular and cumulative, reiterating the importance of keeping it secure and known only to a select few. The cryptographic fortress built through this interplay between public and private keys ensures that even in the event of a breach, where the public key might be exposed, the sanctity of the private key remains intact, akin to a fortress with hidden chambers that repel invaders.
Signature, Authentication, and Non-repudiation
Furthermore, the functionality of public and private keys encompasses critical aspects of digital security, namely digital signatures, authentication, and non-repudiation. Just as a monarch’s seal serves to authenticate royal decrees, digital signatures harness the unique characteristics of asymmetric encryption to verify the authenticity of messages and documents. When a private key is used to sign a message, the corresponding public key can be employed to verify that signature, ensuring the integrity of the transmitted information.
This mechanism serves as an unwavering testament to the concept of non-repudiation. Within legal frameworks, non-repudiation stipulates that an individual cannot deny the authenticity of a signature or the transmission of a message. In such a way, the public and private key duo fortifies trust between parties, instituting a form of accountability that is paramount in various sectors, from finance to governance.
Real-World Applications and Implications
Public and private key cryptography permeates numerous real-world applications, each illustrating the dual nature of these keys. Take email encryption, for instance. Users leveraging systems like PGP (Pretty Good Privacy) utilize public keys to ensure that only designated recipients can access their messages, maintaining confidentiality and reducing the risk of interception by unwarranted third parties.
Additionally, blockchain technology epitomizes the compelling applications of public and private keys in securing transactions. Each transaction is signed with the sender’s private key, while the public key allows networks to validate the transaction’s authenticity. This intricate dance between visibility and invisibility fosters a decentralized yet secure environment, where trust is ensured through cryptographic proof rather than reliance on centralized authorities.
The Challenges on the Horizon
Despite their fundamental role in digital security, public and private keys are not without their vulnerabilities. As computational power burgeons, malicious actors may seek ways to exploit weaknesses or employ quantum computing as a formidable foe against traditional encryption methods. The horizon of cryptographic practices necessitates ongoing evolution and adaptation, prompting researchers and organizations to explore more robust cryptographic algorithms resilient against future threats.
Moreover, the management of keys presents its own array of challenges. The necessity for secure storage of private keys demands vigilance; a compromised private key can lead to catastrophic breaches. Organizations must invest in comprehensive key management solutions, employing hardware security modules (HSMs) and other protective measures that fortify the integrity of these cryptographic instruments.
Conclusion: The Enduring Landscape of Cryptographic Security
In summation, public and private keys serve as the two pillars supporting the edifice of digital security. They embody a sophisticated interplay between accessibility and protection, facilitating secure communication in a world fraught with uncertainty. As technology continues to advance and evolve, these cryptographic constructs must adapt to meet emerging challenges, preserving the integrity and confidentiality of data for individuals and organizations alike. The ongoing narrative of public vs. private keys remains as captivating as the quest for knowledge and security itself—a journey marked by innovation, vigilance, and unwavering resolve.






Leave a Comment