In the labyrinthine corridors of information security, cryptography emerges as the unsung guardian of our digital life. Imagine, if you will, a grand castle fortified not merely by stone and mortar but by the artful cunning of its architect. This parallel encapsulates the essence of cryptography—it creates a refuge for our most sensitive data, ensuring that only those with the requisite keys may enter. Delving into the multifaceted realm of cryptography offers a fascinating glimpse into how we encode our secrets and safeguard them against unwelcome intrusions.
At its core, cryptography can be likened to an intricate language, rich in vocabulary and syntax that functions to obscure rather than reveal. In fact, the word “cryptography” itself is derived from the Greek “kryptos,” meaning hidden, and “grapho,” meaning writing. With this etymology in mind, one can appreciate that the very essence of cryptography lies in its ability to render information enigmatic. Such an endeavor, however, is not solely an act of concealment; rather, it embodies the delicate balance between the art of encoding and the science of decoding.
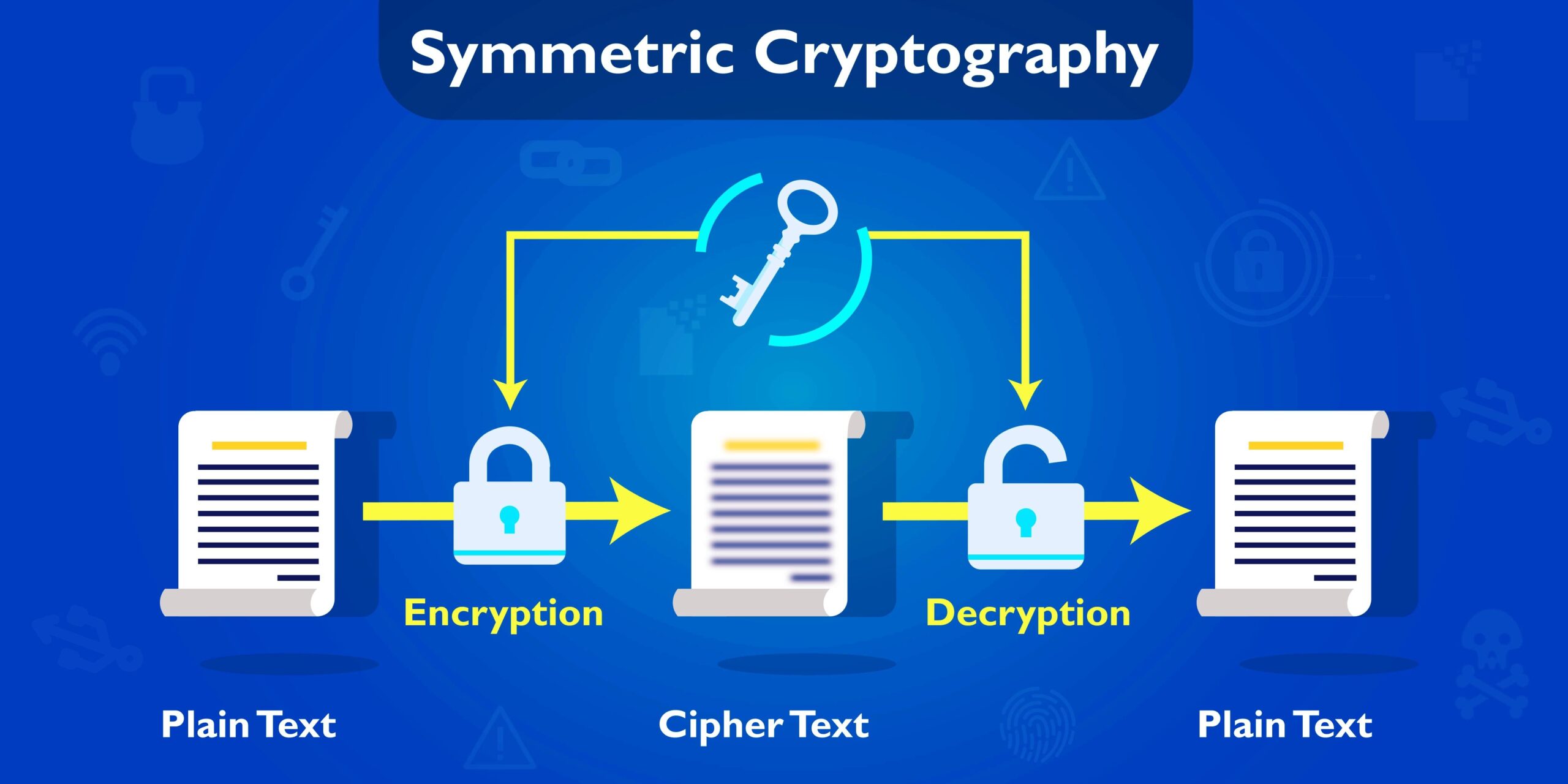
To understand the fundamentals of cryptography, it is essential to first familiarize ourselves with its primary components. Two principal methodologies stand at the forefront: symmetric and asymmetric cryptography. Symmetric cryptography relates to a scenario in which the same key is employed for both encryption and decryption. Picture this as a singular key unlocking both the door to the secret chamber and to the treasures within. The challenge here, however, is the secure distribution of that key to necessary parties involved, lest the encryption shroud be unraveled by unwarranted access.
On the other hand, asymmetric cryptography, often distinguished as public-key cryptography, introduces a novel twist to this security framework. In this paradigm, two keys are utilized: a public key, which may be openly shared, and a private key, kept securely in the possession of the owner. This divergence serves to facilitate a dynamic exchange of information, akin to sending a sealed letter with a lock that only the recipient can open. This duality is a winning formula, as it not only enhances security but allows for more symmetric interaction in an increasingly digital world.
Throughout the ages, cryptography has wielded considerable influence over both military and diplomatic affairs. Historical legends recount well-known figures, such as Julius Caesar, who resorted to rudimentary forms of cryptography to secure sensitive communications. The Caesar cipher, a relatively simple encryption technique, shifts letters by a predetermined number in the alphabet—much akin to a soldier advancing a certain number of paces before changing direction. Although trivial by today’s standards, this cipher set the stage for more sophisticated transformations as the requirement for robust security escalated.
Transitioning from classical to modern techniques, we witness the evolution to more complex encryption algorithms, such as the Data Encryption Standard (DES) and the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES). The latter has garnered significant acclaim within a plethora of applications—from secure communications to digital finance—owing much to its robustness and efficiency. In consideration of its digital fortifications, AES constructs layers of encryption akin to the thick walls surrounding an ancient citadel. Its complexity ensures that even the most determined adversary faces formidable opposition in unlocking its treasures.
However, while encryption stands as a critical complement to security, the efficacy of cryptography is inherently tied to the keystone of trust. Trust serves as the underlying fabric of any cryptographic endeavor. Without trust, encrypted communications can quickly devolve into a mire of skepticism, rendering it a futile exercise. In the evolving digital landscape, trust is essential for participation in e-commerce, secure communications, and confidential transactions. Blockchain technology, often lauded for its decentralized nature, epitomizes this concept by ensuring that every transaction is eternally recorded and verified, instilling trust across multifaceted platforms.
As enigmatic as it may appear, the field of cryptography also offers an invitation to explore its vulnerabilities. The history of secure communications is replete with tales of breakthrough methods to crack seemingly impregnable codes. The age-old arms race between cryptographers and cryptanalysts underscores this cat-and-mouse dynamic. The quest for ever-increasing security is counterbalanced by the relentless pursuit of breaking those complex systems. As computational power grows exponentially, so too does the potential for adversaries to breach cryptographic defenses.
In response, contemporary cryptographic practices continuously adapt, leveraging methods like quantum cryptography, which promises inherent security features through the laws of quantum mechanics. As we stand on the cusp of a technological revolution, the quest for absolute security may soon become a tangible reality. However, ethical considerations must not be overlooked. The rise of cryptography has serious ramifications beyond mere data security; it carries implications for privacy, surveillance, and civil liberties.
In conclusion, the journey into cryptography offers a veritable exploration of codes, keys, and secrets buried deep within the digital cosmos. As we navigate this intricate landscape, the metaphor of a fortress rings true, underscoring the inherent necessity for knowledge, vigilance, and trust. The richness of cryptographic history is not merely an academic pursuit; it represents a fundamental aspect of our lives, shaping how we communicate within the expansive corridors of the internet. Grasping the tenets of cryptography bestows individuals with the tools needed to navigate this brave new world of information, fortified by the layers of security crafted through centuries of necessity and ingenuity.






Leave a Comment