In the digital age, our data is compared to gold. From personal photographs to sensitive financial information, every byte of data carries an intrinsic value. However, this treasure trove of information is continually threatened by an ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats. This is where the paramount importance of encryption comes into play. Encryption serves as an imperative mechanism, acting as a shield that guards our most vital digital assets against unauthorized access and malevolent actors.
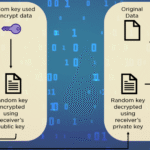
To understand encryption’s formidable role in safeguarding data, we first need to demystify what encryption actually entails. At its core, encryption is a cryptographic technique that transforms readable data, known as plaintext, into an unreadable format known as ciphertext. This transformation employs algorithms that utilize keys—small pieces of information that unlock the code and convert ciphertext back into plaintext. This intricate dance of encoding and decoding is what keeps data secure from prying eyes.
However, beyond its technical definition, encryption promises a remarkable shift in perspective regarding data security. It invites individuals and organizations alike to consider the paradigm of privacy, confidentiality, and trustworthiness in a vastly interconnected world. Gone are the days when information was simply stored in physical vaults. Today, we must consider the digital vaults where our sensitive data resides, and whether they are adequately secured.
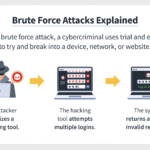
As we delve deeper, the significance of encryption becomes increasingly evident. For individuals, the potential risks of having personal data exposed can be catastrophic. Consider identity theft, a phenomenon that has spiraled into a nightmare of rampant data breaches. The repercussions can lead to financial ruin, damaged reputations, and long-lasting psychological distress. Encryption emerges as a formidable weapon in this battle. By encrypting personal data, individuals can ensure that even in the event of a breach, their information remains inscrutable and, therefore, useless to unauthorized users.
For businesses, the stakes are even higher. A company’s data—including customer information, proprietary algorithms, and financial records—can be an inviting target for cybercriminals. The implications of a data breach may result in a loss of customer trust, legal ramifications, and severe financial penalties. Implementing robust encryption strategies not only provides a safeguard but also signifies to customers and stakeholders a steadfast commitment to privacy and data protection. This commitment builds trust, a currency as valuable as the data itself.
Moreover, encryption plays a crucial role in regulatory compliance. With laws such as GDPR and HIPAA placing stringent requirements on data protection, organizations are compelled to upgrade their security manners. Encryption acts as both a safeguard and a compliance tool, ensuring that sensitive information is appropriately masked and protected, thus mitigating the risk of costly fines and legal disputes.
Yet, the path to implementing encryption is not devoid of complexity. Businesses may encounter challenges in determining which data requires encryption, as not all information holds the same level of sensitivity. Prioritizing what to encrypt necessitates a thorough risk assessment, identifying which assets, if compromised, could lead to significant harm. This analytical approach is crucial—the information landscape demands an informed and strategic approach to data protection.
Another consideration is the ongoing management of encryption keys. As pivotal elements of the encryption process, keys must be rigorously protected themselves. Losing a key can lead to irreversible loss of data, while weak key management can open vulnerabilities. Therefore, a comprehensive strategy for key generation, storage, and rotation is paramount. Tools like hardware security modules (HSMs) can be employed to bolster key management practices, providing a fortified environment for safeguarding these crucial pieces of information.
As encryption gradually becomes an industry standard, the techniques employed to crack these defenses also evolve. Cybercriminals are perpetually honing their skills, employing increasingly sophisticated methods to exploit vulnerabilities. Consequently, encryption mechanisms must remain agile as well. Implementing advanced encryption protocols, such as AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) or RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman), should be a non-negotiable aspect of any organization’s security protocol. Moreover, regularly updating encryption methods in tandem with technological advancements creates an adaptive defense against potential threats.
As we contemplate the broader implications of encryption, it becomes clear that the act of safeguarding data transcends individual or organizational concerns. It ties into societal values of privacy, ethics, and trust. When individuals take steps to encrypt their data, they are not only protecting themselves; they are contributing to a culture that respects and upholds privacy rights in the digital realm.
In conclusion, encryption serves as an indispensable shield for what matters most in the digital age. It transforms the landscape of data security from one of vulnerability to a stronghold of resilience. By embedding encryption into everyday practices—whether for personal use or within organizational frameworks—we can cultivate a secure environment, protecting invaluable data from the clutches of cybercriminals. As the digital realm continues to expand, our collective responsibility towards safeguarding information becomes paramount. By prioritizing encryption, we not only protect our own assets but also reinforce the fundamental principles of privacy and integrity that underpin our society.






Leave a Comment