In today’s digital landscape, the sanctity of data privacy has emerged as an inevitability. The prospect of aligning weakened data security protocols with escalating cyber threats calls for rigorous methodologies. One such strategy is to employ encryption—a process that encodes information in a manner that renders it inaccessible without the appropriate decryption key. Particularly, using Python for this task presents a versatile and efficient approach, given the language’s extensive libraries, straightforward syntax, and growing community support.
This discourse will delineate the procedure for encrypting all files within an operating system using Python scripts. By elaborating on the salient components involved and the steps necessary for implementation, readers will be equipped with both the theoretical underpinnings and practical execution required for effective file encryption.
Understanding Encryption
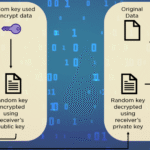
Encryption is fundamentally subdivided into two predominant types: symmetric and asymmetric cryptography. Symmetric encryption employs a singular key for both encryption and decryption processes, while asymmetric encryption utilizes a pair of keys—one public and one private. For the purpose of encrypting files on a personal computer, symmetric encryption is generally favored due to its efficiency when processing large volumes of data.
Choosing the Right Libraries
Python, acclaimed for its vast repository of libraries, provides several options for file encryption. Notably, libraries such as cryptography and PyCryptodome come equipped with robust functionalities. The cryptography library facilitates the implementation of both symmetric and asymmetric encryption methods, while PyCryptodome offers extensive support for various cryptographic algorithms. Given their ease of use and documentation, either library can serve as a proficient tool for encrypting files.
Installation Requirements
Before embarking on the encryption process, it is imperative to install the requisite libraries. This can be accomplished via the Python package manager. Executing the command pip install cryptography or pip install pycryptodome in a terminal or command prompt will retrieve the latest versions of these libraries, granting access to their functionalities.
Developing the Encryption Script
The heart of the encryption process lies in the script itself. Here is a comprehensive outline of the core functionalities one would generally include:
- Key Generation: The first step involves generating a secure key, typically accomplished using a method such as
os.urandomfor random byte generation. This key must remain secure and undisclosed. - File Identification: Subsequently, scripts must identify files to be encrypted. This often involves traversing directory structures and filtering file types based on user preferences.
- Encryption Process: The core encryption function would utilize the chosen algorithm to encode files. Utilizing the
Fernetclass from thecryptographylibrary exemplifies a straightforward application of symmetric encryption. - Error Handling and Logging: Robust error handling and logging enhance script reliability. Including try-except blocks allows for graceful exits in the face of unforeseen errors during file access or encryption failures.
- Decryption Functionality: Retaining the ability to reverse the process is essential. Implementing a complementary decryption function reinforces the system’s holistic design, ensuring that users can restore access to their files when necessary.
Practical Script Example
Within the context of employing the cryptography library, a basic script may appear as follows:
from cryptography.fernet import Fernet
import os
def generate_key():
return Fernet.generate_key()
def encrypt_file(file_path, key):
fernet = Fernet(key)
with open(file_path, 'rb') as file:
file_data = file.read()
encrypted_data = fernet.encrypt(file_data)
with open(file_path, 'wb') as file:
file.write(encrypted_data)
def encrypt_all_files(directory, key):
for root, _, files in os.walk(directory):
for file in files:
encrypt_file(os.path.join(root, file), key)
directory = 'path_to_your_directory'
key = generate_key()
encrypt_all_files(directory, key)
This script represents a rudimentary yet functional approach to the encryption task. The flexibility of Python allows for extensive customization, including refining the selection of files based on individual needs.
Security Considerations
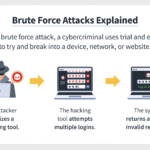
While implementing encryption enhances data security, several pivotal considerations must be acknowledged. Storing the encryption key in a secure location, separate from encrypted files, is paramount. Moreover, employing a strong passphrase for the key reinforces security against bruteforce attacks. It is also prudent to periodically assess encryption protocols, adapting to evolving security standards and practices.
Frequently Encountered Challenges
Conclusion
In summation, utilizing Python scripts for encrypting files across an operating system presents a methodological approach to enhancing data security. By leveraging available libraries, understanding encryption fundamentals, and proactively addressing challenges, individuals and organizations can significantly bolster their data protection strategies. The oscillation between convenience and security is a delicate balance, but through diligent application of the techniques discussed, one can elucidate a path toward securing personal information against insidious threats.




Leave a Comment