In an increasingly digital world, ensuring the authenticity of documents is paramount. Digital signatures provide a method for verifying the integrity and origin of electronic messages or documents. This article delves into the intricacies of authenticating a digital signature the easy way while examining various methodologies and tools available. Readers can expect a comprehensive overview of the subject matter, complete with nuanced discussions of technology trends and practical applications.
To begin, understanding what a digital signature is can aid in comprehending its authentication. A digital signature is akin to a handwritten signature or a stamped seal, but it offers far more inherent security. It utilizes cryptographic techniques to validate the authenticity and integrity of a message or document, thereby ensuring that the content has not been altered after signing. This mechanism typically involves public key cryptography, where a signing key creates the signature and a corresponding verification key confirms its authenticity.
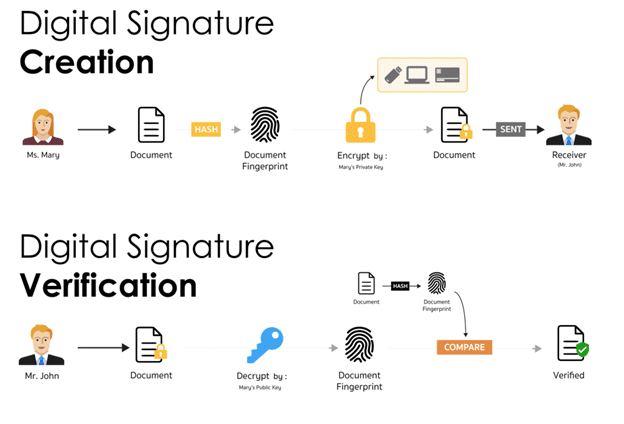
The process of creating a digital signature involves several steps: hashing the document, encrypting the hash with the signer’s private key, and attaching this encrypted hash to the document. To authenticate a digital signature, the recipient of a signed document uses the signer’s public key to decrypt the hash. The recipient then hashes the original document again and compares the two hashes. If they match, it affirms both the document’s integrity and the authenticity of the signer.
There are several methods for authenticating digital signatures, each with varying degrees of complexity and technological requirements. Understanding these can assist users in selecting the method that best fits their needs.
One straightforward approach involves using software that automatically verifies digital signatures. This approach is particularly beneficial for users unfamiliar with the underlying cryptographic principles. Software tools such as Adobe Acrobat Reader, for instance, come equipped with built-in capabilities to check digital signatures. Upon opening a signed document, the software alerts the user to the document’s signature status, providing a visual representation of the verification, which can be an assurance of authenticity for the average user.
A more manual method requires users to engage with public key infrastructure (PKI). In this scenario, gaining access to the public key of the signer is crucial. Trusting the public key source is paramount, as a compromised or counterfeit public key can lead to devastating consequences. Utilizing certificate authorities (CAs) enhances this aspect, as these entities vouch for the authenticity of public keys, thus facilitating trust in the verification process.
An additional layer to the verification process is the understanding of timestamping. Timestamping services act as third-party witnesses in the digital signature process. These services generate a time-stamped record certifying when the document was signed, providing a chronological context to the authenticity claims. This is particularly beneficial in legal situations where establishing a timeline can be critical.
As users venture further into the authentication realm, it’s important to consider the nuances of signature types. There are primarily three types of digital signatures: simple, advanced, and qualified. Simple digital signatures offer minimal security features and are generally suitable for non-sensitive documents. Advanced digital signatures incorporate a higher level of encryption and are linked to the signer’s identity, utilizing a secure signature creation device. Qualified digital signatures take this a step further by adhering to legally recognized protocols, providing a maximum level of security and authenticity.
A point of contention that deserves attention is the role of Electronic Signatures in relation to digital signatures. It is crucial to delineate between the two. While all digital signatures are electronic signatures, not all electronic signatures qualify as digital signatures. The latter employs cryptographic methods to ensure integrity, while electronic signatures may not offer the same level of security. As such, users must ascertain the appropriate classification for their document needs and the applicable legal standards in their jurisdiction.
In practice, the authentication of a digital signature can extend beyond software verification and the use of PKI. Users may need to engage with legislative frameworks surrounding digital signatures. Various regions have implemented regulations to govern the use of digital signatures, ensuring they are recognized legally. Familiarizing oneself with these regulations is essential for professionals who wish to leverage digital signatures for contractual obligations or official documents.
One must also remain cognizant of the evolving landscape of technology. With emerging threats in cybersecurity, such as spoofing and phishing attacks, it becomes imperative to ensure that the signature verification process is robust and up-to-date. Regular software updates, the adoption of advanced encryption standards, and comprehensive cyber hygiene practices are the stalwarts of maintaining a secure digital signature environment.
In conclusion, the process of authenticating a digital signature does not necessitate a complex understanding of cryptographic algorithms for every user. Employing user-friendly software tools and leveraging third-party services such as CAs can simplify the process, making it accessible. By recognizing the different types of digital signatures, the significance of compliance with legal frameworks and staying attuned to technological advancements, individuals can navigate the digital signature landscape with confidence. In sum, ensuring document integrity and authenticity is vitally important in today’s digital ecosystem and can be achieved effectively and efficiently.






Leave a Comment