In an age where digital information flows as freely as water in a river, the necessity for secure transport mechanisms becomes imperative. Data in transit, akin to a ship laden with precious cargo, traverses a vast ocean of potential threats. Each packet of information is vulnerable to interception, manipulation, and misappropriation. Thus, encryption emerges as the sturdy vessel that shields this cargo from the tempestuous waters of the internet.
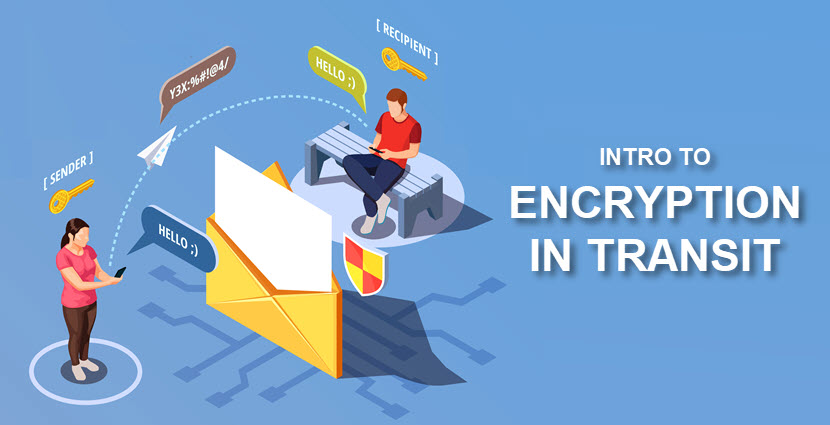
Imagine data in transit as a treasure chest filled with invaluable jewels, glistening under the sun. However, this treasure is not without risk, as it travels through jungles of malicious actors, prying eyes, and cyber threats. Without proper encryption, the jewels are exposed, begging to be snatched from their rightful owner. Encryption serves as the lock and key, ensuring that only authorized hands can unseal the treasure chest. It transforms plaintext into an indecipherable form, known as ciphertext, rendering the information utterly useless to any would-be scavengers.
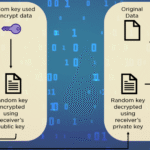
When discussing the mechanics of encryption, it is essential to grasp the fundamental concepts surrounding symmetric and asymmetric cryptography. Symmetric encryption utilizes a single key for both encryption and decryption operations, akin to a unique key that locks and unlocks the treasure chest. This simplicity offers speed and efficiency but raises vulnerabilities; if the key is compromised, the treasure is laid bare. Conversely, asymmetric encryption employs a pair of keys—a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption. This dual-key mechanism acts like a sophisticated vault, considerably enhancing the security of the transported data.
The implementation of encryption in data transmission manifests through various protocols, with Transport Layer Security (TLS) being one of the most prevalent. TLS operates as a secure layer built atop existing communication protocols, such as HTTPS. This layered approach mirrors the construction of a fortress: robust walls safeguard the inner sanctum, ensuring that intruders face formidable defenses. As data is transmitted over the internet, TLS encrypts the information to protect it during transit, much like a secure tunnel obscured from public view.
The significance of encryption cannot be overstated. Data breaches have increasingly become the bane of organizations, leading to financial loss, damage to reputation, and even legal ramifications. Every byte of compromised data represents potential identity theft, intellectual property theft, or financial fraud. By employing encryption in transit, organizations significantly mitigate these risks, offering a protective barrier that instills confidence among their clientele.
Beyond mere protection, encryption plays a vital role in maintaining data integrity. As information traverses networks, the risk of alteration looms omnipresent. An adversary might seek to manipulate the content before it reaches its final destination, potentially leading to disastrous consequences. Encryption incorporates mechanisms that safeguard against unauthorized modifications, preserving the sanctity of the information being conveyed. This assurance is paramount in sectors where accuracy is non-negotiable—think of the implications of tampered medical records or altered financial transactions.
Moreover, the allure of encryption extends beyond immediate security concerns; it fosters a culture of trust in a digitally interconnected world. Users engage with services, unaware of the intricacies involved in protecting their sensitive information. In essence, encryption becomes the guardian angel of the digital realm, instilling a sense of security and encouraging engagement. Trust is the currency of the digital age, and organizations that champion encryption establish themselves as reliable stewards of their users’ information.
However, the reliance on encryption also invites scrutiny and discussion about accountability. As encryption techniques advance, so too do the strategies employed by adversaries seeking to undermine the very systems designed for protection. This cat-and-mouse dynamic necessitates continual evolution in encryption methodologies and robust practices. In this regard, organizations must remain vigilant and proactive in adopting new encryption standards and practices to safeguard their data effectively.
As we delve deeper into the intricacies of encryption, it becomes clear that the consequences of neglecting data in transit are dire. The ramifications of data breaches extend beyond individual entities, rippling through economies and societies at large. The erosion of trust can lead to decreased participation in digital platforms and stifled innovation. Thus, the societal implication of robust encryption practices cannot be understated; it is fundamentally intertwined with the future of our digital existence.
In conclusion, encryption embodies the essence of data security during transit in an increasingly treacherous digital landscape. It transforms vulnerable information into a safeguarded treasure, protecting it from the clutches of unwelcome intruders. As technology evolves, so too must our commitment to robust encryption practices. The protective framework provided by encryption is essential, serving not just to shield data, but also to foster trust and maintain the integrity of our digital engagements. The challenge lies not only in adopting current practices but also in anticipating and adapting to the future of encryption in our interconnected world.




Leave a Comment