In an age characterized by rapid technological advancement, the threats posed by cyber adversaries have burgeoned, creating a critical need for robust cybersecurity measures. One of the cornerstones of these protective strategies is encryption. This crucial technique serves as a formidable bulwark against a myriad of threats, safeguarding sensitive information in an ever-evolving digital landscape. Understanding the multifaceted role of encryption in cybersecurity is essential for grasping the intricacies of contemporary digital safety protocols.
Encryption is a method of converting plaintext into a coded format, known as ciphertext, rendering it unintelligible to unauthorized users. This conversion is executed through complex algorithms that require a specific key for decryption. The fundamental essence of encryption lies in its ability to conceal data, creating an impenetrable layer that deters potential breaches. In this paradigm, encryption not only serves a defensive purpose but also sparks intriguing inquiries into the underlying motivations for its adoption.
A prevalent observation is that the mere presence of encryption can instill a sense of security among users. However, this perception can mask a more profound understanding of how encryption functions within the wider context of cybersecurity. On a superficial level, encryption may be viewed simply as a technical safeguard. Yet, it embodies a philosophical commitment to privacy and data integrity that resonates with users, businesses, and governments alike.
One compelling reason for the widespread implementation of encryption practices is the staggering increase in data breaches and identity theft incidents. With the proliferation of sophisticated hacking techniques, sensitive information is perpetually at risk. Statistical data illuminates this phenomenon; for instance, thousands of distinct attempts to compromise data are made each day across the web. In such an environment, the importance of encryption becomes increasingly evident. By obfuscating data, enterprises can not only protect their clientele but also foster trust, an invaluable currency in today’s digital commerce.
Moreover, the ramifications of compromised data extend beyond immediate financial loss. Reputational damage and the erosion of customer trust can have far-reaching consequences for organizations. Encryption acts as a form of insurance, creating an assurance that even in the event of a breach, data remains protected and unusable. This capability highlights encryption’s role as a strategic asset rather than merely a technical measure.
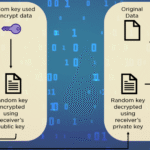
Another layer of complexity is introduced by the different types of encryption methodologies. Symmetric encryption, wherein the same key is used for both encryption and decryption, offers efficiency and speed but raises concerns regarding key distribution and management. Conversely, asymmetric encryption employs a pair of keys—one public and one private—offering an elegant solution to key exchange issues. This distinction emphasizes the continuous evolution and refinement of encryption techniques, drawing interest from encryption specialists and cybersecurity professionals who strive to balance performance with security.
The integration of encryption into various facets of daily operations showcases its indispensable nature. For instance, in online communications, encryption protocols like TLS (Transport Layer Security) and SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) play pivotal roles in securing data transmitted over networks. E-commerce platforms similarly utilize encryption to protect transaction data, thereby ensuring confidentiality and fostering consumer confidence. These applications accentuate not just the technical proficiency of encryption but also its societal implications, as they directly impact user experiences and the integrity of digital interactions.
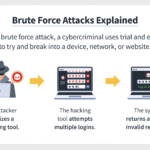
Despite the manifold benefits encryption affords, it is crucial to acknowledge its limitations. No system is infallible; encryption can be compromised through various means, including brute-force attacks or social engineering tactics. Additionally, the question of key management looms large, as the security of an encrypted system hinges upon the efficacy of its key storage and retrieval processes. This complexity invites a deeper examination of the interplay between technology and human factors, culminating in an understanding that effective cybersecurity requires not only advanced encryption techniques but also user education and vigilance.
As cyber threats continue to evolve, so too must encryption strategies. The emergence of quantum computing poses an existential challenge to traditional encryption algorithms. Quantum computers leverage the principles of quantum mechanics to perform calculations at unprecedented speeds, potentially undermining the very foundations of current cryptographic practices. This looming threat propels a vibrant discourse in the cybersecurity community as researchers and technologists work tirelessly to develop quantum-resistant algorithms. Such initiatives underscore the necessity for continual adaptation in the realm of encryption, driven by a commitment to preserving data integrity against advancing technologies.
The fascination with encryption extends beyond its technical capabilities; it embodies an ideological stance on data privacy and security. As individuals increasingly recognize the value of personal information, there is a growing demand for transparency in how data is handled. Encryption serves as a vital tool in this dialogue, supporting the principles of data ownership and autonomous control. In a world saturated with cyber risks, the conversation surrounding encryption is not merely about technology, but rather, it reflects broader societal concerns regarding privacy and ethical data stewardship.
In conclusion, encryption is an indispensable element of modern cybersecurity frameworks. Beyond its technical applications, encryption intertwines with philosophical questions of privacy, trust, and data governance. The intricate layers of encryption underscore its role as both a defense mechanism against external threats and a foundation for ethical interactions in the digital era. As threats continually evolve, so too will the strategies for encryption, ensuring its pivotal role in securing the future of our digital landscape.





Leave a Comment