In today’s digital landscape, the importance of safeguarding personal information has never been more pronounced. With the proliferation of cybercrime and data breaches, individuals and organizations alike are seeking innovative solutions to protect sensitive data. One such innovation is the rise of cryptographic methods that eliminate the need for traditional passwords. This article delves into how Clef’s unique approach to cryptography secures user information without the reliance on passwords, examining the underlying mechanics of this technology while addressing the broader implications of its adoption.
Passwords have long been the cornerstone of digital security, but they are inherently flawed. They are often weak, easily forgotten, or susceptible to brute-force attacks. As a result, security experts have long advocated for alternatives. Clef, a pioneer in passwordless authentication, has developed a revolutionary system that leverages cryptographic principles to keep data secure without the cumbersome password regime.
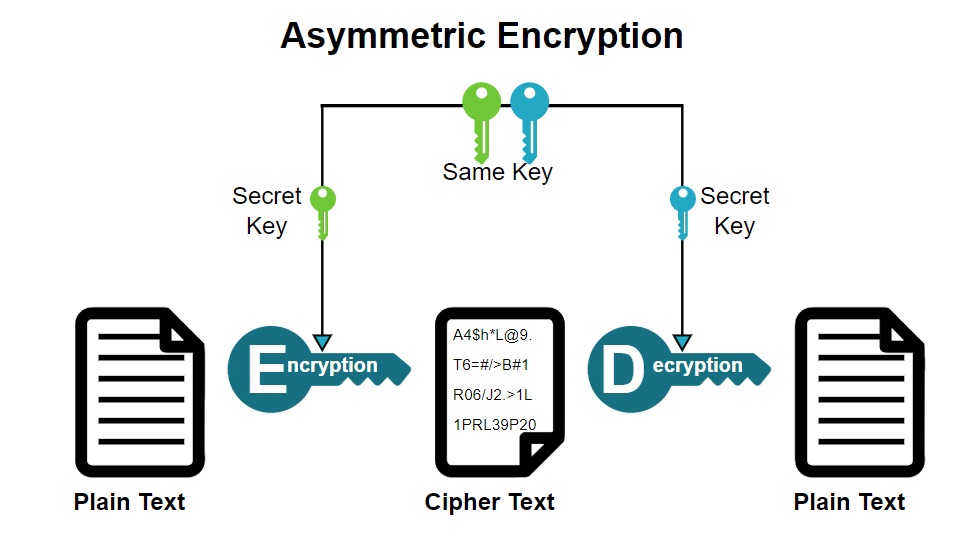
At the core of Clef’s methodology is a fusion of public-key cryptography and smartphone technology. Users authenticate their identity through a mobile application that utilizes asymmetric encryption. In this model, each user possesses a unique pair of cryptographic keys: a public key, which can be shared with any entity, and a private key, which remains confidential and is stored securely on the user’s device. This separation of keys ensures that even if a public key is compromised, the security of user data remains intact, provided the private key is safeguarded.
The convenience of Clef’s system stems from the fact that it does not require users to remember or input traditional passwords. Instead, authentication occurs swiftly through a simple gesture—such as tapping a button or scanning a QR code with their mobile application. This seamless experience enhances usability while simultaneously fortifying security. The elimination of passwords reduces the risk of phishing attacks, as users are less likely to fall victim to fake login prompts when there are no passwords to enter.
Moreover, Clef operates on the principle of a two-factor authentication model, which adds an additional layer of security to the authentication process. Following user verification through the Clef app, the service generates a time-limited access token. This token is a cryptographic signature that validates the user’s identity and grants access to online services. Since these tokens expire after a short duration, they mitigate the risks of unauthorized access, even if intercepted by malicious actors.
The underlying technology is an intriguing confluence of various cryptographic techniques. For instance, Clef employs the Diffie-Hellman key exchange algorithm to facilitate secure communication between users and service providers. This algorithm allows two parties to generate a shared secret over a potentially insecure channel. The beauty of this process lies in its mathematical complexity, which ensures that only the intended recipients can access the encrypted data.
As we explore the architecture of Clef’s system, it is essential to consider its implications beyond mere convenience. The shift away from traditional passwords prompts a philosophical discourse about the nature of security in the digital age. Are passwords a relic of an earlier era, or do they still hold value in contemporary security paradigms? In questioning the efficacy of passwords, one must contemplate the relationship between users and their digital identities. The democratization of cryptography, as exemplified by Clef, represents a significant step toward reimagining this relationship.
Additionally, as cyber threats evolve and become increasingly sophisticated, the need for robust security measures becomes paramount. The growing prevalence of mobile devices amplifies this necessity. Since users frequently access sensitive information via smartphones, employing a mobile-centric authentication strategy, such as Clef’s, is not only practical but essential for contemporary security frameworks.
Transitioning to a passwordless authentication system also poses both challenges and opportunities for organizations seeking to adopt Clef’s methodology. While the initial integration may require investment in infrastructure and training, the long-term benefits—enhanced security, improved user experience, lower support costs associated with password retrieval—are significant. As consumers demand more streamlined experiences, businesses cannot afford to ignore the advantages of adopting cutting-edge cryptographic solutions.
Yet, with every technological advancement comes the responsibility of educating users about potential vulnerabilities and threats. Even with the best systems in place, vigilance is essential. Users must remain aware of phishing attempts and other nefarious activities, recognizing that while innovations like Clef can bolster security, they are not foolproof.
In conclusion, Clef’s revolutionary approach to cryptography offers a compelling solution to the pervasive issue of password fatigue. By harnessing the power of asymmetric encryption and mobile technology, it provides a seamless and secure user experience. As we continue to navigate the complexities of the digital realm, understanding and embracing advanced cryptographic methods will be crucial in safeguarding our digital identities. The eagerness to explore passwordless alternatives reflects a growing recognition of the need for innovation in security practices. Ultimately, the future of digital authentication lies not in the strength of our passwords, but in the elegance of our cryptographic solutions.






Leave a Comment