Secure Shell (SSH) stands as a bastion of security in the vast landscape of computer networks, reminiscent of a fortified castle guarding its treasures behind high walls and vigilant watchtowers. This protocol provides encrypted communications over an unsecured network, making it a critical tool for system administrators, developers, and anyone who yearns to protect their data during transmission. However, the question persists: can this supposedly impenetrable fortress ever be compromised? How secure really is your shell?
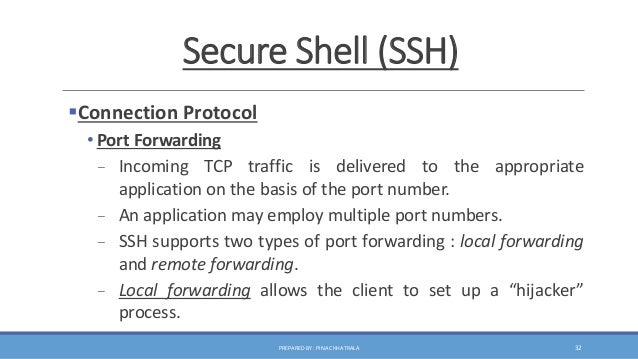
To understand the security landscape of SSH and its vulnerabilities, one must delve into both the architecture of SSH itself and the potential threats that could shine a spotlight on its weaknesses. SSH operates on a client-server model, where a client initiates a connection to a server, allowing for secure command execution and file transfers. This interaction is fortified through encryption, making eavesdropping on the data stream exceedingly difficult. At its core, SSH uses cryptographic algorithms to secure the communication channel, providing integrity, confidentiality, and authentication. Yet, the very nature of technology invites scrutiny and potential exploitation.
Firstly, an examination of the encryption methodologies employed in SSH reveals an intricate tapestry of cryptographic protocols that form the backbone of its security. SSH typically relies on a combination of symmetric and asymmetric encryption. Asymmetric encryption, often considered a mathematical marvel, facilitates a secure exchange of keys, allowing the client and server to establish a unique session key. Subsequent data transferred between these entities is encrypted using symmetric encryption, which is theoretically faster and more efficient for continuous data streams. However, albeit robust, no encryption scheme is wholly immune to the relentless efforts of cyber attackers.
One prevalent tactic that could jeopardize the sanctity of SSH is the man-in-the-middle (MitM) attack. This is akin to a cunning thief donning a disguise to infiltrate the castle; the attacker positions themselves between the client and server, intercepting the communication channel. While SSH is designed to mitigate the risk of MitM attacks through its authentication mechanisms, such as public key fingerprint verification, users must remain vigilant. If an adversary successfully masquerades as a trusted server, the result could be devastating. To counteract this, it’s imperative that users verify key fingerprints before initiating a session, much like a knight must scrutinize a herald’s credentials before entering the castle gates.
Moreover, key management is another crucial aspect that can greatly influence the security of SSH. If SSH keys, which facilitate authentication and access, are not managed correctly, they can become a proverbial chink in the armor. Storing these keys in unsecured locations or failing to implement robust passphrase protection leaves them susceptible to theft. In a world where digital identities are paramount, protecting these keys is akin to safeguarding the sword that leads a charge into battle. Employing best practices, such as using non-default port configurations and disabling root login, can significantly enhance the security posture of an SSH environment.
Furthermore, SSH is continually evolving to counteract emerging threats, leading to the adoption of various versions and extensions. The most recent iterations implement advanced features, like public key infrastructure (PKI) and multi-factor authentication, offering yet another layer of defense. Embracing these innovations is imperative for organizations intent on fortifying their digital stronghold against sophisticated attack methodologies. Just as the architects of ancient fortifications adapted to include moats and drawbridges, modern-day guardians of networks must adapt to the ever-changing threat landscape.
However, the bastion of SSH security is not solely reliant on the nuances of its protocol but also on the human element. The weakest link in any security framework often resides with its users. Recklessness in handling credentials, neglect in applying security updates, or ignorance of the latest phishing schemes can unravel even the most robust encryption. Training and awareness are fundamental—proactive education can equip users with the knowledge to recognize potential threats, much like instilling a sense of vigilance in the castle’s guards, trained to discern friend from foe.
In essence, while SSH offers a formidable defense in the realm of secure communications, it is not impenetrable. The question—can SSH be intercepted—evokes a nuanced understanding; it is not the protocol itself that is inherently flawed, but rather the myriad of possibilities for human error and systematic vulnerability. Acknowledging this reality empowers users, creating a culture of security that fosters not just dependence on technology but a dynamic interplay between technology and human vigilance.
Ultimately, as with a well-fortified castle, ongoing maintenance and vigilance are paramount. Regular audits, continuous education, and embracing best practices can elevate the security of SSH beyond its intrinsic design, fortifying its place as a trusted ally in the quest for safe digital communications. The interplay of encryption and human awareness can transform the SSH environment from a mere digital shell into a veritable fortress of security.






Leave a Comment